Volvo XC90 Parts Layout and Components Guide
Understanding the inner workings of a modern vehicle is key to ensuring its proper upkeep and maintenance. A detailed illustration of the various elements within the system helps enthusiasts and professionals alike to pinpoint specific mechanisms and connections. These visual guides can be incredibly useful for repairs, upgrades, or simple curiosity about how each unit functions within the larger assembly.
In-depth schematics offer a bird’s-eye view of the intricate network of moving and stationary components. They highlight connections between critical systems, helping to simplify the often overwhelming complexity found in advanced engineering. These layouts ensure that each element can be understood in the context of its neighboring units, providing clarity to both experts and those just beginning their journey into vehicle mechanics.
Whether you’re addressing a minor issue or conducting major upgrades, having access to a clear representation of the internal structure is invaluable. These guides allow for precise identification, making it easier to diagnose problems and find suitable replacements or adjustments for optimal performance.
Vehicle Component Overview
Understanding the essential elements that make up a modern vehicle is crucial for both maintenance and repair. This section explores key mechanical and electronic systems, offering insights into their functionality and how they contribute to overall performance. Each component plays a role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and comfort on the road.
Mechanical Systems
The mechanical side of the vehicle includes a variety of crucial elements such as the engine, transmission, and suspension. These parts work together to provide movement, stability, and smooth handling during various driving conditions.
- Engine: The heart of the vehicle, responsible for generating power and converting fuel into motion.
- Transmission: Ensures smooth transitions between gears, optimizing speed and fuel efficiency.
- Suspension: Absorbs shocks from uneven roads, enhancing comfort and vehicle control.
Electronic and Safety Features
The electronic systems include advanced technologies designed to improve the driving experience and protect passengers. These include systems for navigation, climate control, and safety monitoring.
- Navigation system: Offers real-time route guidance and traffic updates.
Engine Components Layout 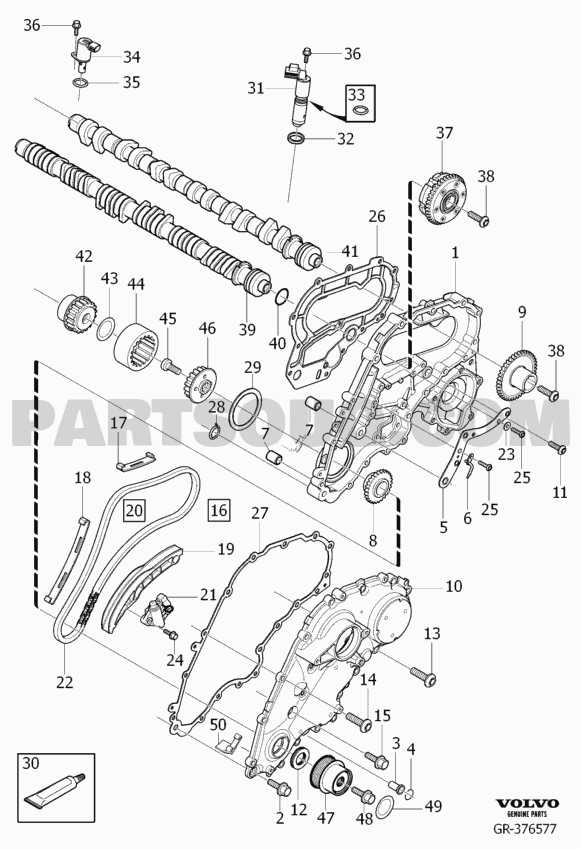
The arrangement of key elements under the hood plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle’s motor. Understanding the location and interaction of these essential components helps in maintaining, troubleshooting, and enhancing the efficiency of the engine.
Component Description Cylinder Block Forms the foundation of the engine, housing cylinders and other vital structures. Cylinder Head Sits atop the cylinder block and contains the combustion chamber and valve mechanisms. Crankshaft Converts the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion, driving the wheels. Camshaft Controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves. Timing Belt Synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft to ensure proper valve timing. Oil Pump Circulate Transmission System Diagram
The transmission system is a critical component in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth acceleration and optimal vehicle performance. It consists of various interconnected elements, each playing a key role in managing torque and controlling speed ratios. Understanding its structure is essential for maintaining its efficiency and longevity.
Main Components Overview
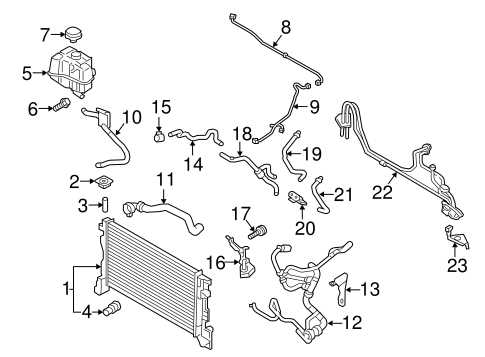
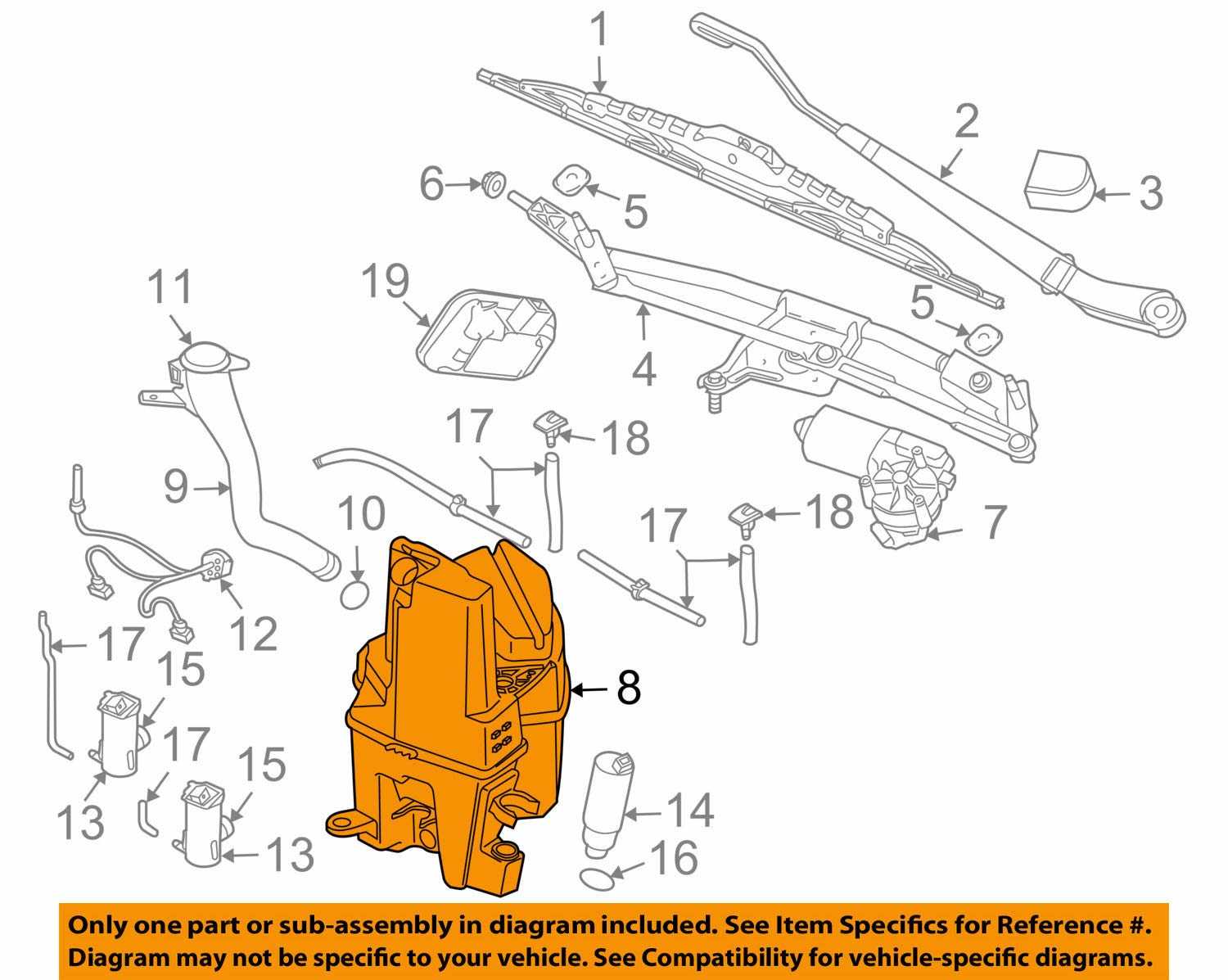
The transmission setup includes several primary parts that work together to regulate gear shifts and distribute engine output effectively. Below is a list of the fundamental elements:
- Clutch Assembly: Engages and disengages power transmission from the engine.
- Gearbox: Houses the gears that determine the vehicle’s speed and torque.
- Driveshaft: Transfers rotational force from the transmission to the differential.
- Differential: Distributes power to the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds.
Transmission Functionality and Interaction
Each part within the system works in harmony to handle different driving conditions, ensuring efficient power transfer while minimizing energy loss. Gear ratios are automatically or manually adjusted depending on the design, optimizing performance based on road speed and
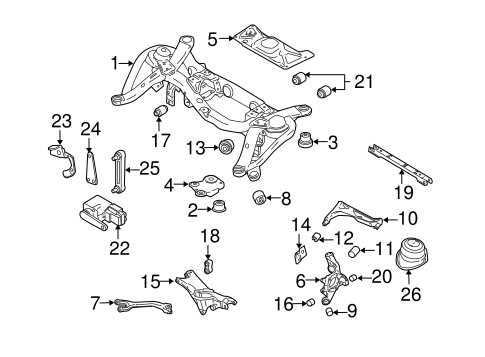
Suspension and Steering Structure
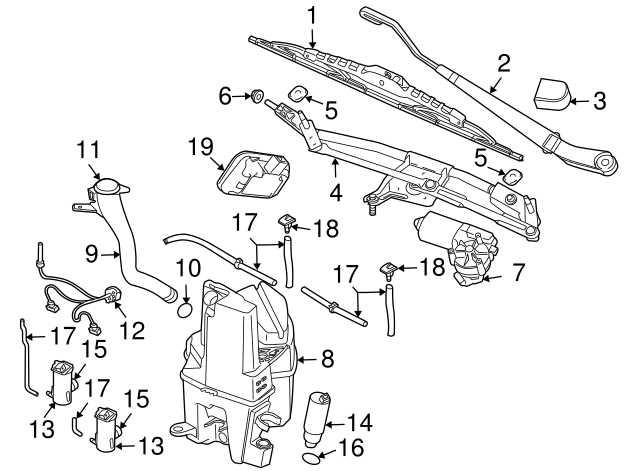
The suspension and steering systems are critical components in ensuring a smooth and controlled driving experience. These systems work in tandem to absorb shocks from uneven surfaces while maintaining precise control of the vehicle’s direction. The design and arrangement of these elements vary, but their core functions remain focused on enhancing comfort and safety during driving.
The suspension system primarily deals with managing the interaction between the wheels and the road, while the steering system focuses on providing the driver with accurate control of the vehicle’s trajectory.
- Shock absorbers: These components are essential for dampening vibrations and absorbing impacts from the road.
- Control arms: Responsible for connecting the suspension to the vehicle’s frame, these parts allow for controlled movement of the wheels.
- Steering rack and pinion: This is the central mechanism that translates the driver’s input into precise wheel movements.
- Fuel Pump: This component is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. Its reliability is crucial for maintaining engine performance.
- Fuel Filter: This filter cleans the fuel before it reaches the engine, removing impurities that could cause damage or affect performance.
- Injectors: These devices spray fuel directly into the combustion chamber, ensuring precise fuel delivery for efficient combustion.
- Throttle Body: This component regulates the amount of air entering the engine, which is essential for maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture.
- Exhaust Manifold: This collects exhaust gases from multiple cylinders and directs them into a single pipe.
- Catalytic Converter: This unit reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: This component reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases while also helping to manage exhaust flow.
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases, providing feedback to the engine control unit for optimal fuel efficiency.
- Fenders: Protect the wheels and enhance the vehicle’s styling.
- Hood: Covers the engine compartment, contributing to both safety and design.
- Doors: Provide access to the interior while ensuring passenger safety.
- Bumpers: Absorb impacts and protect the vehicle’s frame and body.
- Grille: Facilitates airflow to the engine while adding to the front-end design.
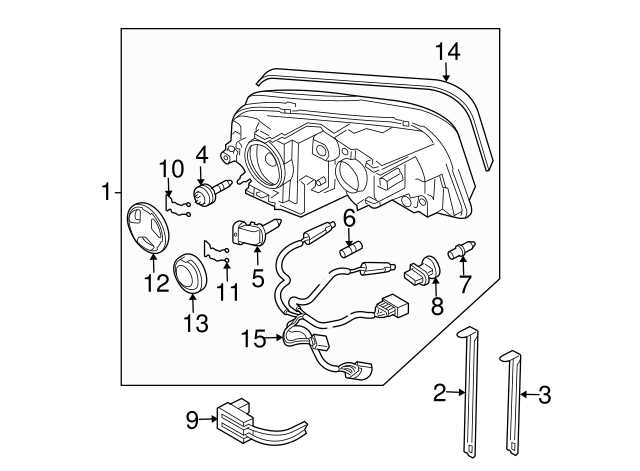
- Mirrors: Essential for visibility and safety, enhancing the vehicle’s profile.
- Lights: Including headlights and taillights, crucial for visibility and signaling.
- Trim: Adds aesthetic appeal and can also serve functional purposes.
- Windows: Allow light and visibility while contributing to the vehicle’s insulation.
Brake System Parts Breakdown
The brake system is a crucial component responsible for ensuring the safety of any vehicle. It involves various elements that work together to provide efficient stopping power. Understanding the structure of this system is essential for identifying potential issues or performing maintenance tasks.
Main Components Overview
The braking mechanism includes several key elements that function in harmony to bring a vehicle to a halt. These elements convert kinetic energy into heat, allowing for safe deceleration. Below is a breakdown of the primary components involved in the process:
Component Function Brake Pads Apply pressure to the rotors, creating friction that slows down the vehicle. Brake Rotors Discs that work with the pads to dissipate heat and convert kinetic energy. Calipers Hold the brake pads and squeeze them against the rotors when the brakes are applied. Electrical System and Wiring Guide
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical network and wiring arrangements within the vehicle. Understanding these components is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Key Electrical Components
The electrical setup encompasses various essential parts, including the battery, alternator, and fuses. Each component plays a crucial role in powering the vehicle’s systems, from lighting and infotainment to safety features. Regular checks and maintenance of these elements can prevent potential failures.
Wiring Schematics and Troubleshooting
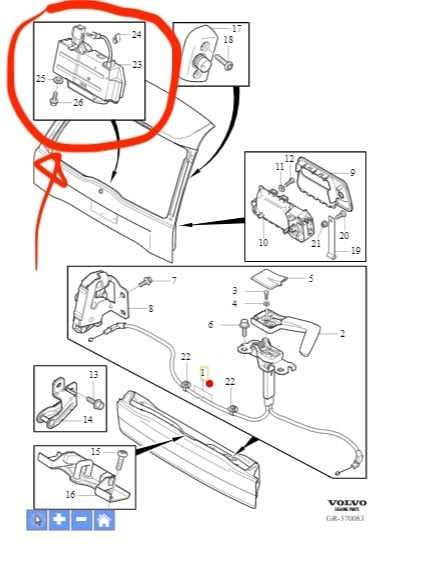
Wiring schematics are invaluable for diagnosing issues within the electrical system. By following these diagrams, technicians can identify faulty connections or damaged wires. A systematic approach to troubleshooting can enhance the longevity and reliability of the vehicle’s electrical systems.
Fuel Delivery and Exhaust Components
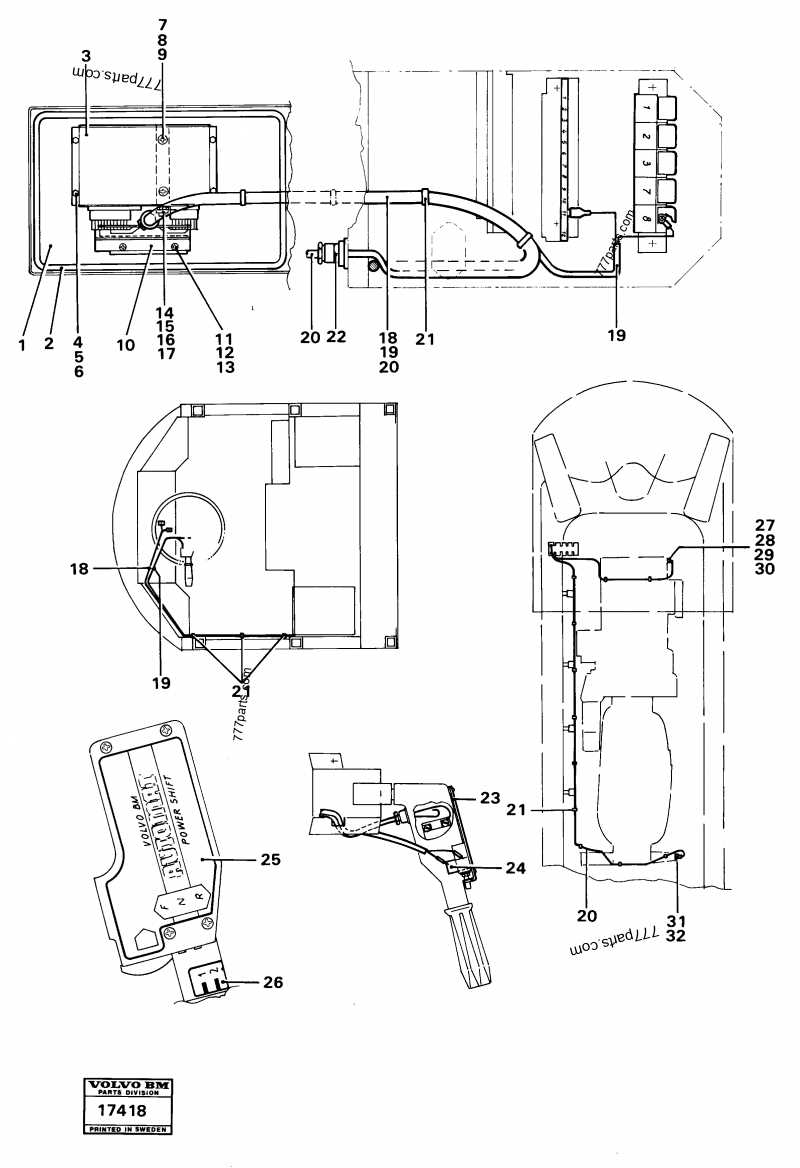
The efficiency of an internal combustion engine heavily relies on the effective operation of its fuel delivery and exhaust systems. These systems work together to ensure optimal performance by facilitating proper fuel intake and exhaust emission management.
On the exhaust side, effective management of emissions is equally important. Key components include:
Understanding the role of these components can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring that the vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
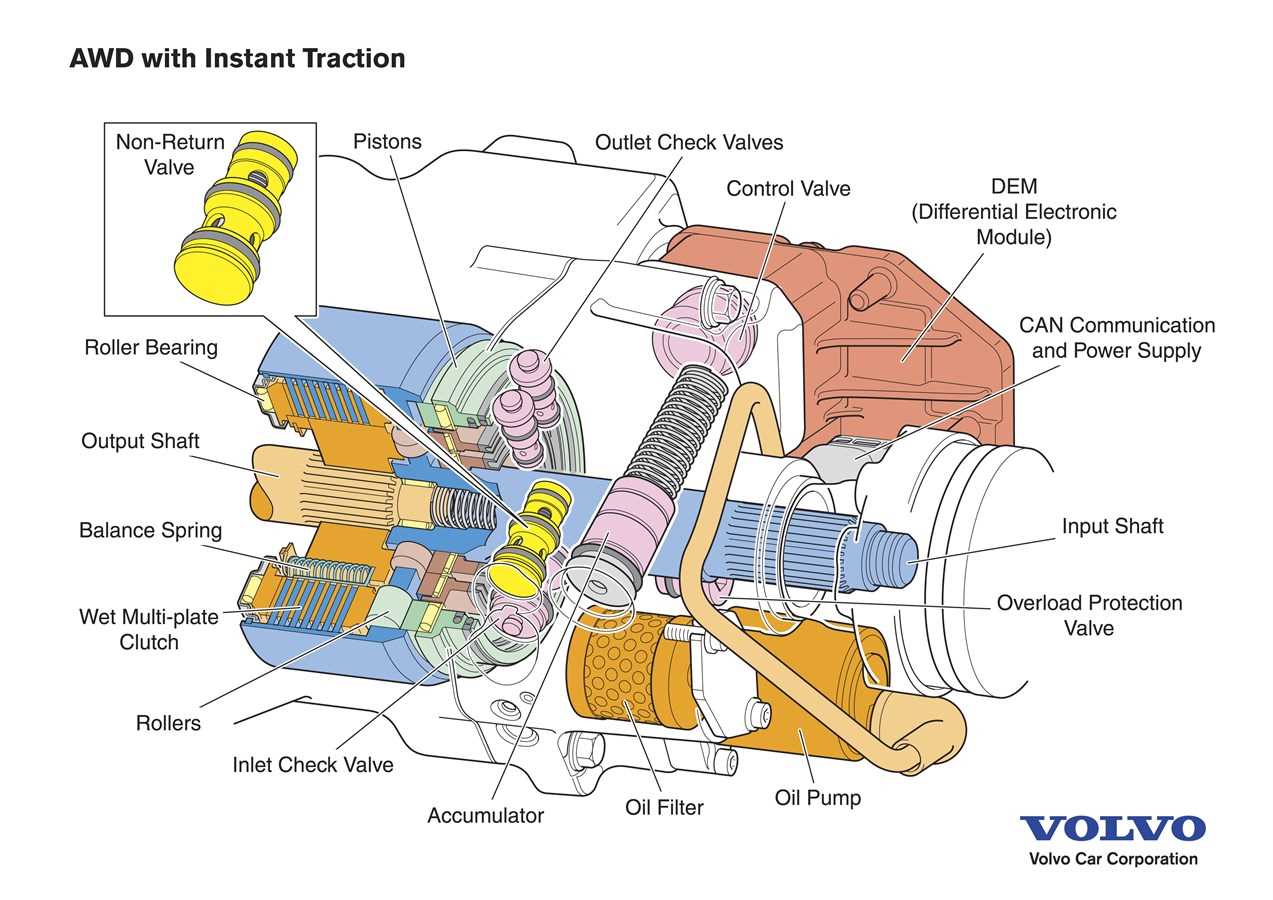
Cooling System Components Map
The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures within a vehicle, ensuring that the engine performs efficiently and avoids overheating. This section provides an overview of the various elements that make up this essential system, highlighting their functions and interconnections.
Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant as it circulates, allowing for temperature regulation. Its efficiency is vital for preventing engine overheating.
Water Pump: This pump facilitates the movement of coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring consistent circulation to maintain a stable temperature.
Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, opening and closing as needed to maintain optimal operating conditions.
Coolant Reservoir: This container holds excess coolant and provides a source for the system, ensuring that there is always enough fluid available for circulation.
Cooling Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between various components, allowing for efficient heat exchange and fluid movement within the system.
Fan: The cooling fan assists in drawing air through the radiator, enhancing the cooling process, especially during low-speed driving or idling conditions.
Understanding the layout and function of these components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting of the cooling system, ultimately ensuring the longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
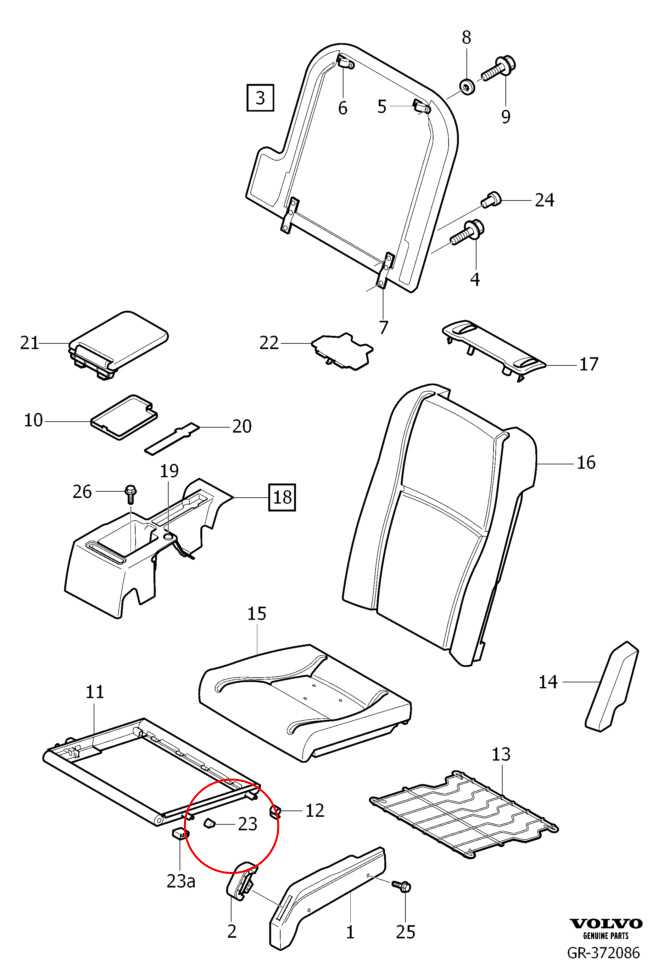
Interior and Comfort Features Diagram
The layout of interior elements and comfort-enhancing attributes plays a vital role in creating a pleasant driving experience. This section outlines key components that contribute to the overall functionality and aesthetics of the cabin space.
Seating Arrangements and Materials
The choice of seating materials and configurations significantly impacts passenger comfort. High-quality upholstery and ergonomic designs ensure a cozy environment, while adjustable seating options accommodate various body types.
Entertainment and Connectivity
Modern vehicles incorporate advanced entertainment systems and connectivity options, allowing occupants to enjoy their journeys. Features such as touchscreen interfaces, smartphone integration, and premium audio systems enhance the overall driving experience.
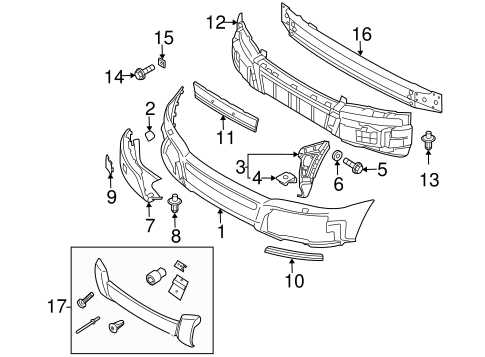
Body and Exterior Parts Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at the components that form the outer structure and aesthetic features of the vehicle. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance, repair, and enhancing the overall appearance.
Key Components
Exterior Finishing Touches
Climate Control System Layout
The climate control system in modern vehicles is a sophisticated assembly designed to maintain a comfortable environment inside the cabin. This system comprises several key components that work together seamlessly to regulate temperature and airflow. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the System
At the heart of the climate management system lies the HVAC unit, which controls heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions. Attached to this unit are various sensors that monitor internal and external temperatures, ensuring optimal climate settings. Additionally, the blower motor plays a crucial role by distributing air throughout the cabin.
Air Distribution and Control
Airflow is directed through a network of ducts and vents strategically placed within the vehicle. Each vent can be adjusted to direct air precisely where needed, providing a personalized experience for occupants. The integration of electronic controls allows for precise adjustments, enhancing comfort levels in various driving conditions.