Detailed Water Boiler Parts Breakdown
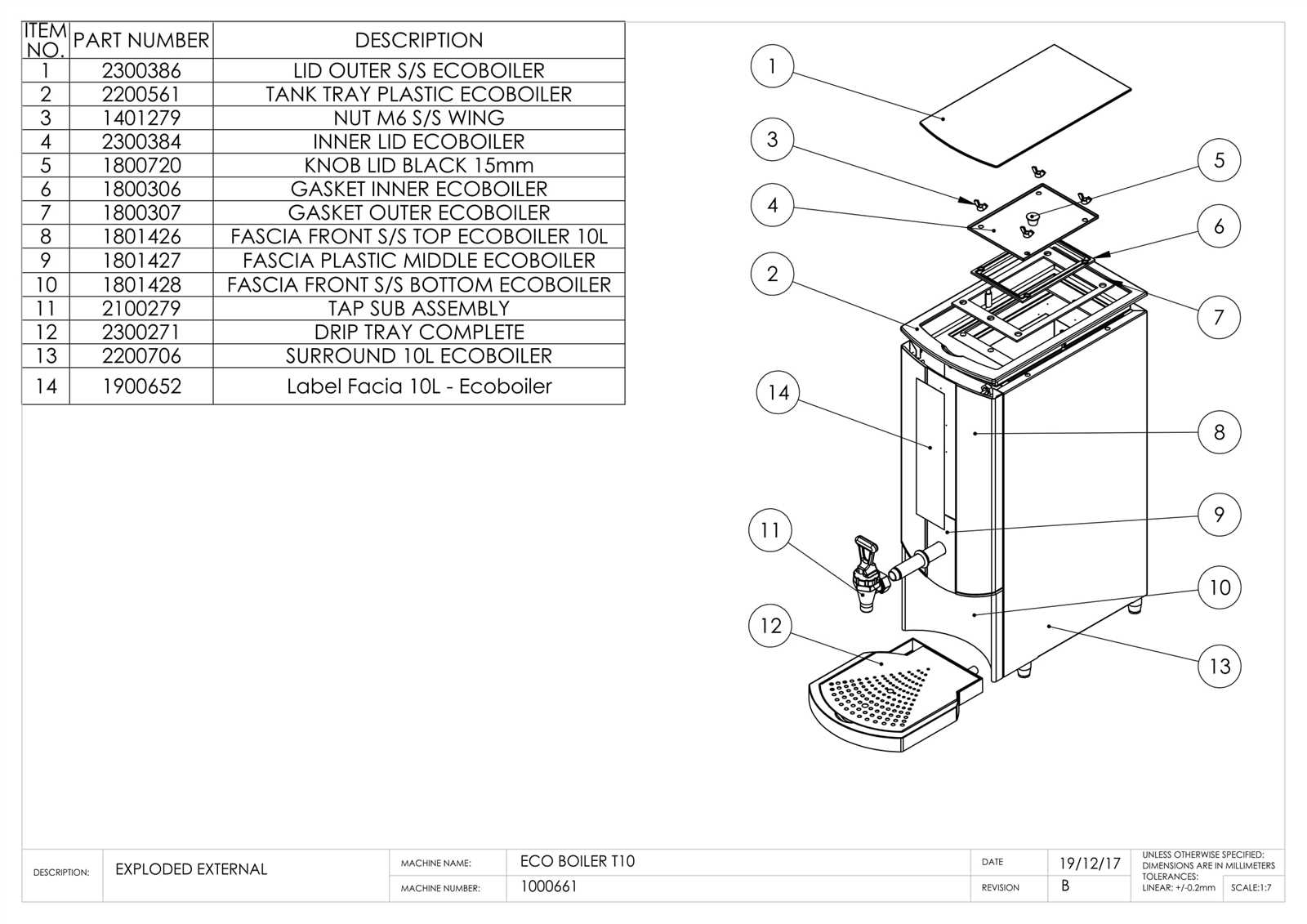
When discussing the functionality of a heating system, it is essential to recognize the various elements that come together to ensure efficient operation. These systems consist of numerous interconnected parts, each playing a vital role in maintaining consistent temperature control and safety. By understanding how these elements work in unison, one can better maintain and troubleshoot the equipment.
The main unit comprises several essential features, each designed for specific tasks such as heat generation, regulation, and distribution. Learning about these individual features can significantly help with both routine maintenance and identifying issues that may arise over time. Ensuring the proper function of these components is key to achieving an optimal indoor climate.
Exploring the detailed structure of this heating apparatus provides valuable insights into how heat transfer mechanisms work, as well as the importance of safety measures built into the design. Understanding this will enable more effective upkeep and possibly extend the lifespan of the entire system.
Water Boiler Parts Diagram
Understanding the components and structure of heating equipment is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. Various elements work together to ensure optimal functionality, and knowing how these parts are interconnected can help diagnose issues or improve overall efficiency.
Main Heating Element
The central heating unit serves as the core of the system, providing the necessary warmth. It is typically located in the heart of the mechanism and is responsible for transforming electrical energy into heat.
Control Systems
Various control mechanisms regulate temperature and pressure, ensuring safety and performance. These include thermostats, sensors, and pressure relief systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining a stable and efficient operation.
Key Components of a Water Boiler
Efficient heating systems rely on several crucial elements working together to maintain and distribute warmth effectively. These essential pieces ensure the unit operates safely, regulates temperature, and transfers heat where needed. Understanding these components can help in identifying issues or improving performance.
Heating Element
The heating element is the core part responsible for generating the warmth needed to function. It converts electrical energy into heat, ensuring the liquid reaches the desired temperature quickly and efficiently.
Control System
The control system regulates the overall performance by managing temperature levels, preventing overheating, and maintaining safety. It includes sensors, thermostats, and switches that work together to ensure smooth operation.
- Thermostat: Monitors and controls the temperature, keeping it within the set range.
- Pressure Relief Valve: Releases excess pressure, preventing potential damage.
- Insulation: Helps retain warmth by reducing heat loss, improving efficiency.
Understanding the Boiler Heating Mechanism
Heating systems work by converting energy sources into heat, which is then distributed throughout a designated space. The process involves various components that collaborate to ensure efficient heat generation and transfer. Understanding how these elements interact provides insight into the system’s overall functionality and efficiency.
Heat Generation Process: At the core of the system, a combustion or electrical unit ignites the energy source, initiating the transformation of energy into heat. This heat is then transferred to a medium, often a liquid or air, that circulates within the system.
Heat Exchange Mechanism: The heated medium flows through a series of tubes or pipes, where the heat is exchanged with the surrounding environment. The system design ensures that heat is evenly distributed to all required areas, maintaining a consistent temperature throughout.
Thermal Regulation: A thermostat or control unit monitors the temperature and adjusts the energy input accordingly. This regulation ensures that the system operates efficiently, minimizing energy waste while maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
Role of Thermostats in Temperature Control
Thermostats play a crucial function in regulating and maintaining consistent heat levels in various systems. They serve as an essential component, ensuring that the desired temperature is achieved and sustained without significant fluctuations. By responding to environmental changes, thermostats activate heating or cooling mechanisms to maintain equilibrium within the system.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulation | Ensures consistent temperature by switching between heating or cooling as needed. |
| Monitoring | Continuously tracks the current temperature, ensuring it stays within preset limits. |
| Activation | Automatically engages other components when temperature deviates from set ranges. |
Safety Valves and Their Importance
In any heating system, the presence of certain components is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Among these, one particular element plays a vital role in preventing potential hazards that can arise from excessive pressure. Understanding this component’s function and significance is essential for maintaining overall system integrity and user safety.
Functionality of Safety Valves
Safety valves serve as a protective mechanism designed to release pressure when it exceeds predetermined limits. By doing so, they help to mitigate the risks associated with over-pressurization, which can lead to catastrophic failures or accidents. These devices automatically activate, ensuring that the pressure within the system remains within safe boundaries, thus protecting both the equipment and the surrounding environment.
Types of Safety Valves
There are several types of safety valves, each suited for different applications and environments. Understanding their characteristics can aid in selecting the appropriate type for a specific system.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Spring-loaded | Utilizes a spring mechanism to hold the valve closed until a specific pressure is reached. |
| Pneumatic | Operated by air pressure, offering high precision in maintaining system pressure. |
| Hydraulic | Uses fluid pressure to control valve operation, suitable for larger systems. |
In conclusion, the incorporation of safety valves is indispensable for any heating apparatus. Their ability to manage pressure effectively ensures not only the longevity of the equipment but also the safety of users and their environment.
Water Circulation Process in Boilers
The flow of fluid through heating systems is essential for efficient thermal transfer. Understanding how this movement occurs is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring safety in various applications. The cycle involves multiple components working in harmony to deliver heat where it is needed most.
Initiation of Fluid Movement
At the core of the circulation mechanism, a source generates heat, prompting the fluid to absorb energy. This causes the temperature to rise, leading to changes in density that initiate upward movement. As the heated fluid ascends, it creates a natural flow, drawing in cooler liquid from adjacent areas.
Return and Recirculation
After reaching designated areas, the fluid cools and becomes denser, allowing it to descend back to the heating source. This process of return and recirculation ensures a continuous cycle, maintaining optimal temperatures and maximizing efficiency. Regular maintenance and monitoring are vital to uphold this cycle’s integrity and prevent any disruptions.
Heat Exchanger Function in Boilers
The role of a heat exchanger is crucial in optimizing energy transfer within heating systems. This component facilitates the efficient transfer of thermal energy, allowing one fluid to heat another without direct contact. Its effectiveness directly impacts the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
- Enhances thermal efficiency by maximizing heat transfer.
- Reduces energy consumption, leading to cost savings.
- Maintains optimal operating temperatures for better performance.
In various heating applications, the design and materials used in heat exchangers can significantly influence functionality. Common types include:
- Shell and tube exchangers
- Plate exchangers
- Air-cooled exchangers
Each type offers unique advantages suited to specific needs, ultimately contributing to a more efficient heating process.
Expansion Tank and Pressure Regulation
The management of pressure within a heating system is crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety. One essential component in this process is the expansion vessel, which helps absorb excess pressure fluctuations. This section delves into the significance of this device and its role in regulating pressure effectively.
Function of the Expansion Vessel
The expansion vessel serves multiple purposes:
- Absorbs excess pressure generated by temperature changes.
- Prevents water hammer and system damage.
- Ensures consistent pressure levels for optimal operation.
Pressure Regulation Importance
Effective pressure regulation is vital for:
- Extending the lifespan of the entire system.
- Enhancing safety by minimizing risks of leaks or bursts.
- Improving overall efficiency and energy consumption.
Understanding the functionality of the expansion vessel and the importance of pressure regulation ensures a well-maintained and reliable heating system.
Electrical System Overview in Boilers
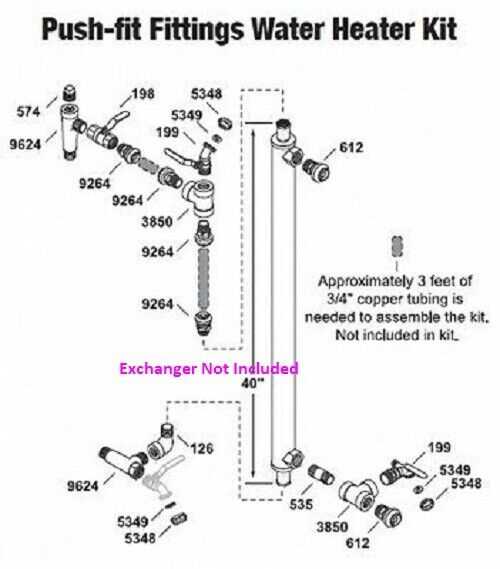
The electrical framework within heating units plays a crucial role in their efficient operation and control. It encompasses various components that facilitate the conversion of electrical energy into useful heating effects, ensuring optimal performance under varying conditions.
Key Components
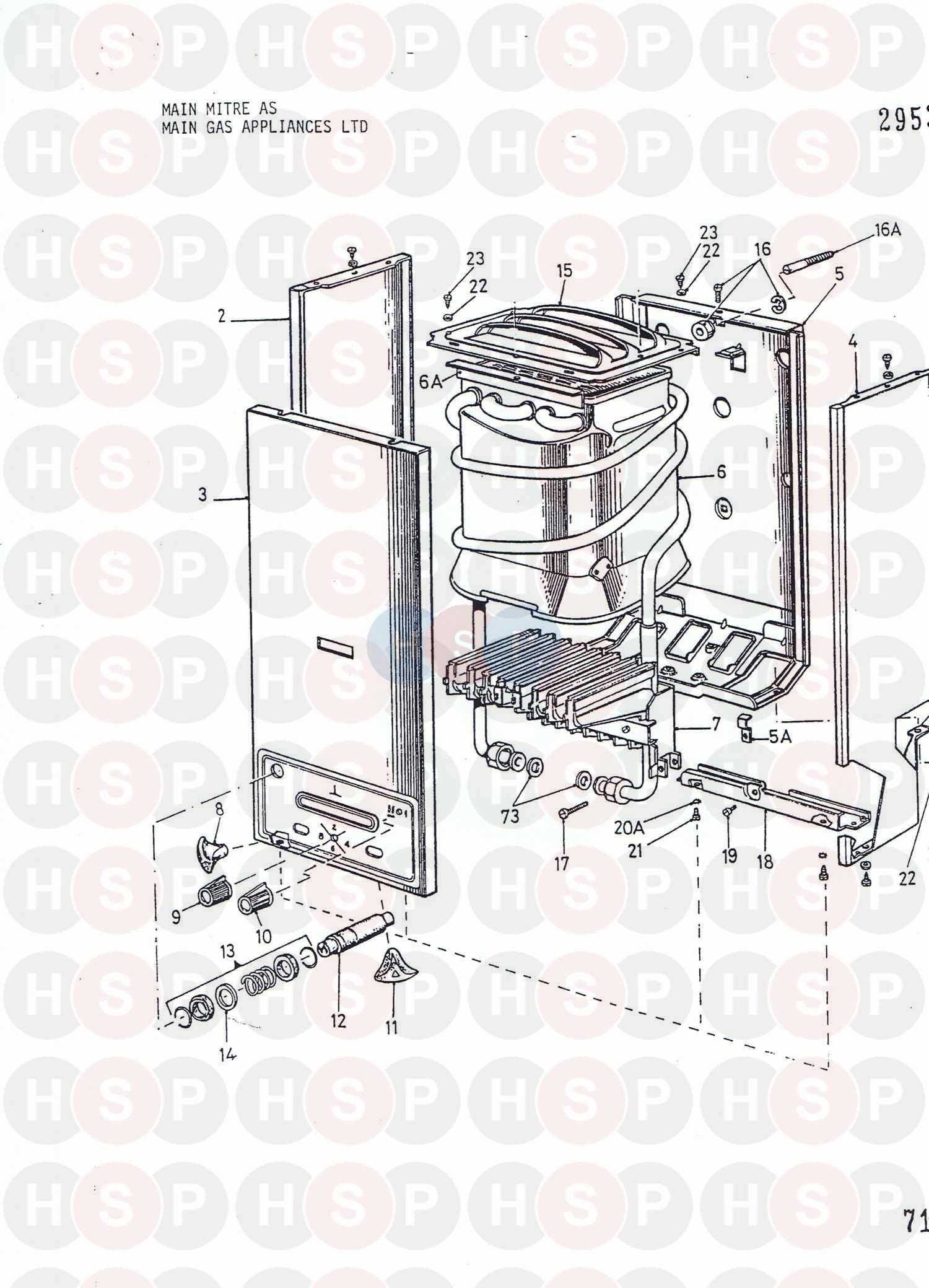
At the heart of the system are the control panels, which manage operations and safety protocols. Additionally, sensors and actuators are integral, providing real-time feedback and adjustments to maintain desired temperatures and pressures.
Operational Efficiency
The interplay between these elements not only enhances performance but also contributes to energy conservation. Proper maintenance and understanding of the electrical layout can significantly impact the longevity and effectiveness of heating systems.
Water Inlet and Outlet Valves Explained
This section delves into essential components that regulate the flow of liquid within heating systems. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for maintaining efficiency and ensuring proper operation.
Valves play a significant role in controlling the entry and exit of fluids, contributing to the overall functionality. Here’s a closer look at their characteristics:
- Inlet Valve: Responsible for allowing liquid to enter the system. It often features a mechanism that prevents backflow, ensuring that the flow is unidirectional.
- Outlet Valve: Facilitates the expulsion of fluid from the system. This valve can be manually or automatically operated to adjust the pressure and temperature levels.
Each valve is equipped with various features that enhance performance and safety:
- Control Mechanism: Most valves incorporate levers or electronic controls to manage flow rates effectively.
- Sealing Technology: Advanced sealing techniques prevent leaks and maintain system integrity.
- Material Selection: Valves are made from durable materials to withstand high temperatures and corrosive conditions.
In summary, understanding the functions and features of inlet and outlet valves is vital for ensuring the reliability and longevity of any heating system.
Maintenance Tips for Water Boiler Components
Regular upkeep of your heating system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. By focusing on various elements, you can prevent breakdowns and ensure efficiency, ultimately leading to lower energy costs and a more reliable system.
| Component | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|
| Heating Element | Inspect for mineral buildup and clean as necessary. |
| Thermostat | Test regularly for accuracy and adjust settings accordingly. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Check periodically to ensure it opens and closes properly. |
| Insulation | Inspect for wear and tear to maintain efficiency. |
| Pipes | Look for leaks and corrosion, and seal or replace as needed. |