Comprehensive Guide to Freewheel Parts Diagram
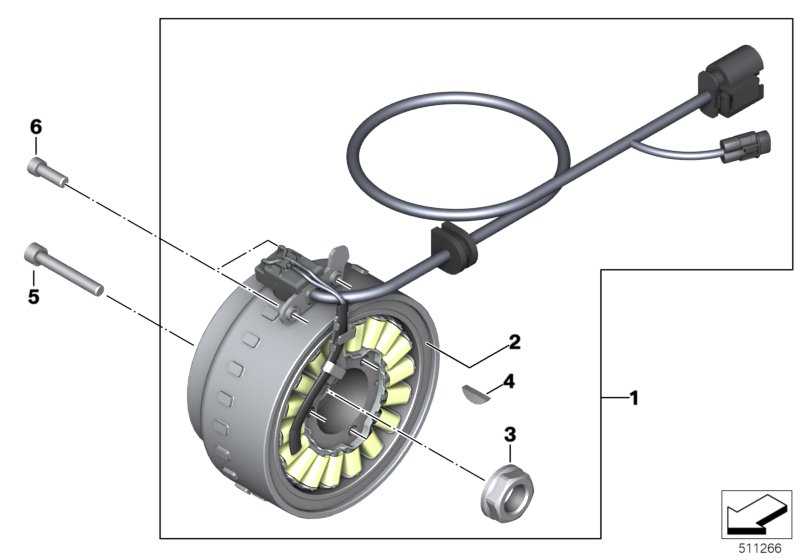
In the world of cycling, the efficiency of motion relies heavily on the intricate interplay of various elements within the drive system. These essential components work together to ensure a smooth and reliable transfer of power from the rider to the wheels. A deeper exploration into these mechanisms reveals their significance and complexity, highlighting how they contribute to the overall performance of a bicycle.
Each individual piece plays a crucial role, influencing factors such as speed, durability, and responsiveness. From the smallest cog to the larger assemblies, understanding the arrangement and function of these elements is vital for both maintenance and enhancement of cycling experiences. By delving into the specifics of these components, cyclists can gain valuable insights into optimizing their rides.
Furthermore, visual representations of these assemblies can serve as valuable tools for enthusiasts and professionals alike. They not only clarify the relationships between different components but also assist in troubleshooting and upgrading. Grasping the layout of these systems enables cyclists to make informed decisions when it comes to repairs or modifications, ultimately enhancing their riding experience.
Understanding Freewheel Components
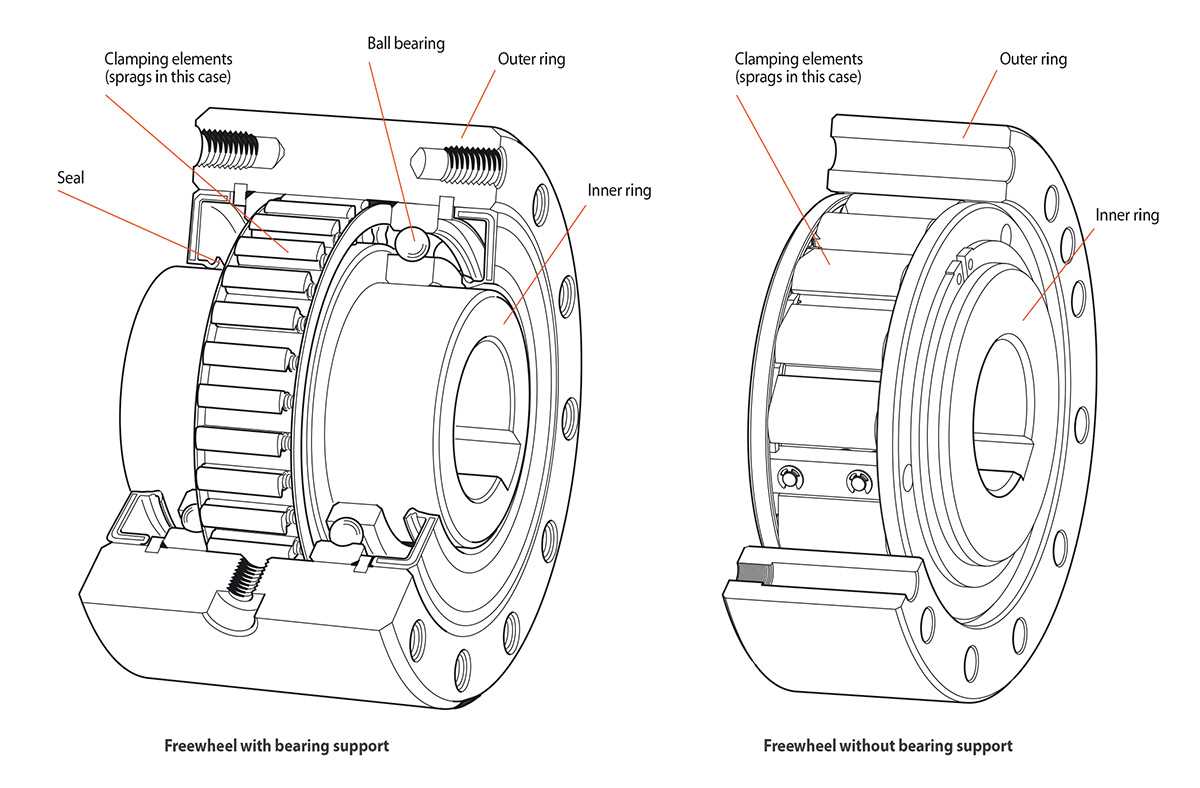
In the realm of cycling mechanics, a vital assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient performance. This system consists of various elements that work in harmony, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the ride. Recognizing these components is essential for any enthusiast looking to enhance their cycling experience.
The primary element is typically responsible for allowing rotation in one direction while preventing backward movement. This characteristic is essential for maintaining momentum during rides. Accompanying this, the ratchet mechanism facilitates the engagement and disengagement of the system, allowing seamless transitions between pedaling and coasting.
Additionally, the pawls serve as crucial components, engaging with the ratchet to secure the drive during forward motion. Their design impacts the efficiency and responsiveness of the entire assembly. Furthermore, the housing encases these elements, providing protection and structural integrity, while the lubrication within is vital for reducing friction and wear.
Understanding these components not only aids in maintenance and repair but also enhances appreciation for the intricate engineering behind cycling. With knowledge of each element’s function, riders can ensure their gear operates at its ultimate potential.
Function of Freewheel Mechanism
The mechanism in question plays a crucial role in allowing a rotational system to function smoothly by enabling a unidirectional movement. It facilitates the transfer of energy from one component to another while preventing backward motion, which can be detrimental to the overall operation of a device. This feature is essential in various applications, particularly in cycling and machinery, where efficiency and control are paramount.
Operational Principles
The core principle behind this mechanism involves a set of pawls and ratchets that engage and disengage based on the direction of rotation. When force is applied in one direction, the pawls lock into place, ensuring that energy is effectively transmitted. Conversely, when the force is reversed, the pawls release, allowing free rotation without resistance. This design not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of the components involved.
Applications and Benefits
Such mechanisms are widely utilized in various industries, from bicycles to industrial equipment. Their primary benefits include:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Minimizes energy loss during operation. |
| Control | Allows for precise management of motion direction. |
| Durability | Reduces wear on components by preventing unwanted backspin. |
| Versatility | Can be adapted for use in various applications. |
Types of Freewheel Systems
This section explores the various mechanisms that allow for smooth pedaling and disengagement of motion in cycling. Each type has its own unique features and advantages, catering to different riding styles and preferences.
- Coaster Mechanism: Activated by pedaling backward, this system is simple and requires minimal maintenance.
- Ratchet Design: Utilizes pawls to engage and disengage, providing reliable performance under varied conditions.
- Multi-Speed Gear: Combines multiple ratios, allowing cyclists to select optimal gear for terrain and speed.
- Clutch System: Offers enhanced control by preventing backward movement, making it ideal for off-road cycling.
Each of these mechanisms serves specific cycling needs, ultimately enhancing the overall riding experience.
Common Freewheel Part Names
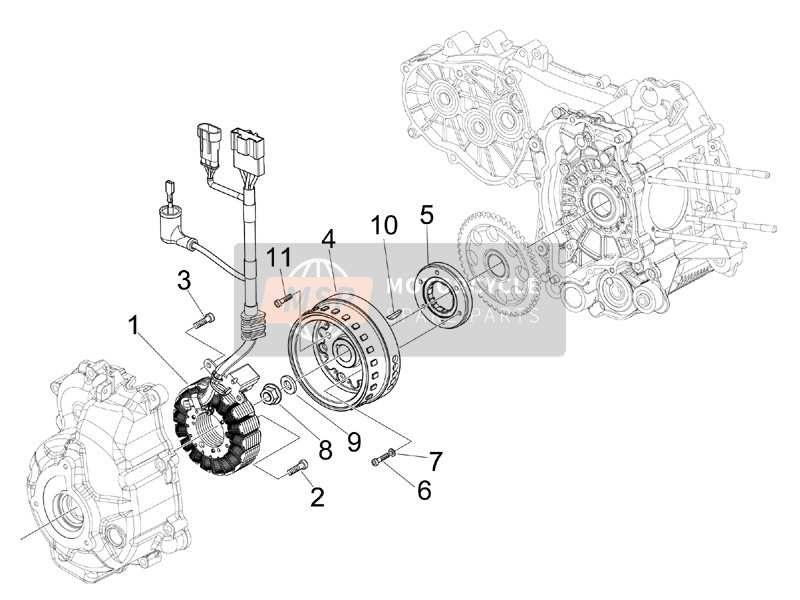
Understanding the components of a bicycle’s drive mechanism is essential for maintenance and upgrades. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth performance and reliability.
Key Components
Ratchet: This mechanism engages and disengages to allow for smooth pedaling and coasting. Its design is critical for effective gear shifting.
Spring: This component helps maintain tension, ensuring that the ratchet engages properly and supports the overall functionality of the system.
Additional Elements
Body: The outer shell that houses the internal mechanisms, providing protection and support for the inner workings.
Rings: These are essential for interfacing with the chain, facilitating the transfer of power from the pedals to the wheels.
How to Read Diagrams
Understanding visual representations can enhance your ability to interpret complex systems effectively. By familiarizing yourself with the symbols and layouts, you can quickly grasp essential information.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Familiarize with Symbols: Each icon or graphic often has a specific meaning. Knowing these can prevent confusion.
- Observe the Layout: The arrangement can indicate relationships and hierarchies within the components.
- Follow Labels: Pay attention to any annotations that clarify the roles of different elements.
To deepen your understanding:
- Start with a basic overview before diving into details.
- Practice interpreting various types of visuals.
- Seek additional resources to clarify any uncertainties.
With practice, you can navigate these visuals with confidence and unlock their ultimate potential in conveying information.
Identifying Wear and Tear
Recognizing the signs of deterioration in cycling components is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Over time, various elements can exhibit fatigue, affecting the overall functionality of the mechanism.
Visual Inspection: Regularly examine the surfaces for cracks, discoloration, or uneven wear. These indicators often signal that a component may need replacement.
Performance Evaluation: Pay attention to unusual sounds or decreased efficiency during operation. Any change in responsiveness could point to underlying issues that require immediate attention.
Measurement: Utilizing precise tools to gauge the thickness and alignment of key elements can help identify excessive wear. If measurements exceed recommended limits, it’s time to consider an upgrade.
Regular maintenance and keen observation can prolong the lifespan of crucial components, ensuring a smoother and safer ride.
Tools Needed for Repairs
Having the right equipment is essential for effective maintenance and fixing of components. This section outlines the key tools that will help streamline the repair process, ensuring efficiency and precision.
Essential Tools
- Wrenches – for loosening and tightening various fittings
- Screwdrivers – essential for handling different types of screws
- Pliers – useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting
- Chain whip – for holding the assembly in place
- Socket set – provides versatility for different sizes
Specialized Equipment
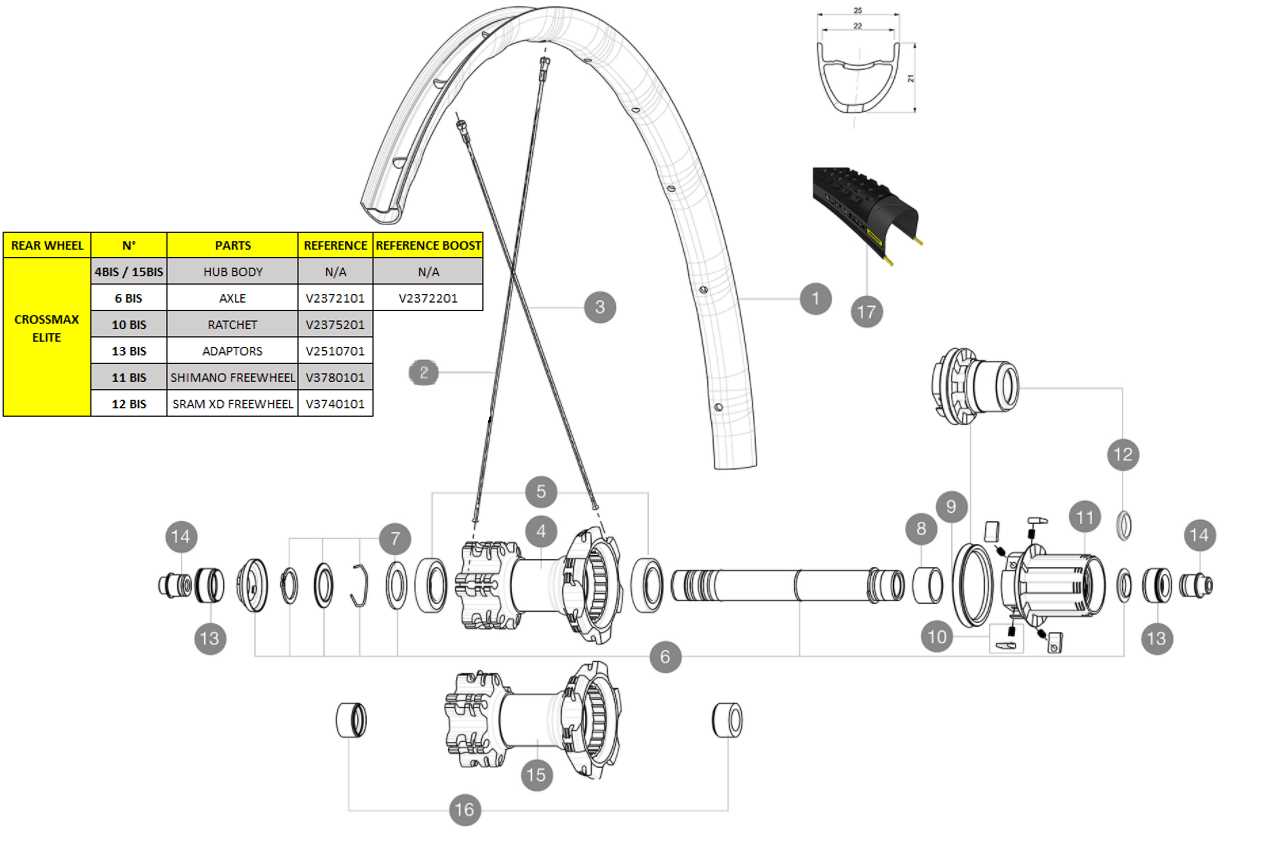
- Torque wrench – ensures proper tightening of bolts
- Brake cleaner – for maintaining cleanliness and function
- Lubricants – vital for reducing friction and wear
- Cleaning brushes – for thorough maintenance of components
Step-by-Step Assembly Guide
This section provides a clear and concise method for putting together the components of a bicycle’s rear mechanism. Following these steps will ensure that everything functions smoothly and efficiently. Each phase of the assembly process is crucial, and attention to detail is essential for optimal performance.
Step 1: Begin by gathering all necessary elements. Ensure that you have the required tools on hand to facilitate the assembly process. This preparation will save time and help avoid frustration later on.
Step 2: Start by attaching the first component to the designated location on the hub. Make sure it is secured properly to prevent any movement during operation. Check that the alignment is correct before proceeding.
Step 3: Next, carefully add the subsequent elements in the order specified. This systematic approach will prevent confusion and help maintain the integrity of the assembly. Use a torque wrench to tighten connections as necessary.
Step 4: After all components are in place, perform a thorough inspection. Look for any loose connections or misalignments that could affect performance. Adjust as needed to ensure everything is properly seated.
Step 5: Finally, conduct a test run to confirm that everything operates smoothly. Pay attention to any unusual sounds or behaviors during the initial use, as these could indicate areas that need further adjustment. Once satisfied, your assembly is complete and ready for use.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your cycling components requires regular attention and care. By following a few essential practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your gear and enhance overall performance. This section outlines key strategies to maintain your equipment in optimal condition.
Regular cleaning is fundamental. Accumulated dirt and grime can lead to premature wear, affecting functionality. After each ride, take a moment to wipe down your gear and remove any debris.
Lubrication plays a critical role in maintaining smooth operation. Applying the right type of lubricant to the moving parts minimizes friction and reduces the risk of damage. Always choose a lubricant suited to the conditions you ride in, whether wet or dry.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Clean Regularly | Remove dirt and debris after each ride to prevent wear. |
| Lubricate | Use appropriate lubricant to ensure smooth operation. |
| Inspect Components | Check for signs of wear or damage and replace as needed. |
| Store Properly | Keep equipment in a dry, cool place to avoid corrosion. |
Lastly, regular inspections are essential. Look for signs of wear and tear, and replace any damaged components promptly. This proactive approach will help maintain the functionality of your setup and ensure a safer ride.
Common Issues and Solutions
Understanding typical problems that arise with cycling components is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Identifying these challenges allows enthusiasts to ensure a smoother riding experience and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
1. Slipping Mechanism: One of the most frequent issues is a slipping mechanism, which often occurs due to wear or lack of lubrication. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and applying appropriate grease, can resolve this issue effectively.
2. Noisy Operation: Unusual noises during use can indicate misalignment or inadequate lubrication. Ensuring components are correctly aligned and lubricated can significantly reduce noise and improve functionality.
3. Sticking Components: Components that stick or fail to engage smoothly may require cleaning or replacement. Inspecting for debris and ensuring all parts are in good condition is crucial for seamless operation.
4. Excessive Wear: Over time, some parts may experience excessive wear, affecting overall performance. Regular inspections and timely replacements are necessary to avoid further complications.
5. Poor Engagement: Difficulty in engagement often stems from dirt accumulation or improper adjustments. Regular cleaning and precise tuning can enhance responsiveness and reliability.
When to Replace Freewheel Parts
Understanding the optimal timing for the replacement of critical components in your bike’s drivetrain can significantly enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of your equipment. Regular maintenance and observation are key to ensuring that everything functions smoothly.
Signs of wear include unusual noises during operation, difficulty in shifting gears, or a noticeable decrease in efficiency. If you experience any of these symptoms, it may be time to assess the condition of your system.
Frequent usage can accelerate wear and tear, making it essential to monitor your gear engagement and responsiveness. A general rule of thumb is to conduct a thorough inspection after a certain mileage or after extensive rides, especially in challenging conditions.
Additionally, if you notice any slippage or inconsistent engagement, it indicates that components may be reaching the end of their useful life. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more severe damage and ensure a smoother riding experience.
In summary, keeping an eye on performance indicators and scheduling regular check-ups will help you determine when to refresh the essential elements of your bike’s drivetrain.
Choosing the Right Freewheel Model
Selecting the appropriate mechanism for your bicycle is crucial for achieving optimal performance and comfort. The right choice can enhance your riding experience, ensuring smooth transitions and effective power transfer. Understanding the various models available can help you make an informed decision tailored to your cycling needs.
Factors to Consider
- Riding Style: Determine whether you are a casual rider, a commuter, or a competitive cyclist, as this influences the type of mechanism you should choose.
- Gear Ratios: Analyze the number of gears and their ratios. More options can provide better adaptability to various terrains.
- Compatibility: Ensure the selected mechanism is compatible with your bike’s drivetrain and frame.
- Weight: Consider the overall weight of the mechanism, as lighter options may improve performance but can sometimes sacrifice durability.
Types of Mechanisms
- Threaded Models: These are common and easy to replace, making them suitable for casual riders.
- Integral Designs: Often found in higher-end bikes, they offer better performance but can be more complex to install.
- Sealed Variants: These provide better protection against dirt and moisture, extending lifespan in harsh conditions.
Ultimately, understanding your specific requirements and the options available will guide you in selecting the best mechanism for your bike, enhancing both efficiency and enjoyment on your rides.
Resources for Further Learning
Expanding your knowledge in this area can greatly enhance your understanding and skills. Numerous materials and platforms offer valuable insights, tutorials, and technical documentation that can aid both beginners and experienced individuals alike. Engaging with these resources will facilitate a deeper comprehension of mechanisms and functionalities involved.
Books and Manuals
Printed materials provide in-depth exploration of concepts and practical applications. Here are some recommended titles:
| Title | Author | Year |
|---|---|---|
| The Bicycle Repair Manual | Tom S. Harris | 2021 |
| Understanding Mechanical Systems | Jane L. Smith | 2019 |
| Advanced Bicycle Mechanics | Mark T. Johnson | 2020 |
Online Courses and Tutorials
Digital platforms offer structured learning paths and hands-on experiences. Consider exploring these options:
| Course Name | Provider | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction to Bicycle Systems | Coursera | 4 weeks |
| Mechanics of Bicycle Components | Udemy | 6 weeks |
| Practical Skills for Repair and Maintenance | Skillshare | 3 weeks |