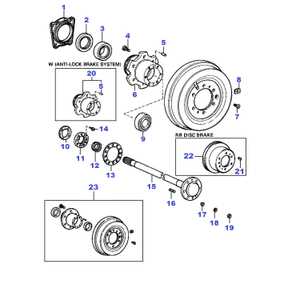
Understanding the Diagram of Wheel Bearing Parts
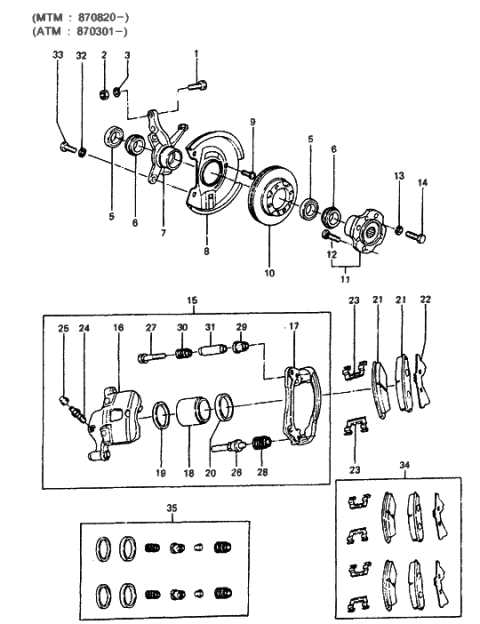
The functionality of a vehicle’s wheel assembly is crucial for ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience. This intricate system comprises several essential elements that work in unison to provide stability and performance. Understanding how these components interact can help in diagnosing issues and maintaining optimal vehicle condition.
In this section, we will explore the various elements that make up this vital assembly. Each component plays a specific role in supporting the overall operation, contributing to the safety and efficiency of the vehicle. By breaking down these individual parts, we can gain insights into their functions and importance.
Furthermore, recognizing how these components fit together will aid in comprehending the assembly’s overall design. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a curious car owner, this knowledge will enhance your understanding of vehicle maintenance and performance. Delving into the specifics of this assembly will empower you to address potential concerns more effectively.
Various designs are utilized in the automotive industry to facilitate smooth rotation of wheels. Each type serves a specific purpose and comes with unique characteristics, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of vehicles.
1. Ball Type

This design features spherical elements that minimize friction during rotation. They are widely used due to their versatility and efficiency.
- Low friction levels for improved performance
- Suitable for light to moderate loads
- Commonly found in passenger vehicles
2. Roller Type
This variant employs cylindrical elements, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity. It is particularly beneficial for heavy-duty applications.
- Higher load capacity compared to ball types
- More stability under heavy stress
- Ideal for trucks and larger vehicles
Key Parts of Wheel Bearing Assembly
The assembly responsible for smooth rotation in vehicles consists of several critical elements that work in harmony to ensure optimal performance. Each component plays a vital role in facilitating motion and maintaining stability, contributing to the overall safety and efficiency of the vehicle.
Core Components
At the heart of this assembly lies the inner and outer rings, which provide a durable framework for the other elements. These rings are typically made of high-strength steel, designed to withstand the immense forces encountered during operation. Alongside them, the rolling elements, often spherical or cylindrical, reduce friction and allow for smooth movement between the rings.
Additional Elements
Seals are another essential aspect, serving to protect the internal components from contaminants such as dirt and moisture. This helps preserve the integrity of the assembly and extends its lifespan. Furthermore, retaining clips play a crucial role in securing the various components in place, ensuring everything remains properly aligned during operation.
Wheel Bearing Installation Process
This section outlines the procedure for correctly installing crucial components that ensure smooth rotation and optimal performance of a vehicle’s suspension system. A systematic approach is necessary to achieve a proper fit and functionality, thereby enhancing the overall driving experience.
Preparation Steps
Before commencing the installation, gather all necessary tools and components. Ensure the work area is clean and organized to facilitate a smooth workflow. The following items are typically required:
| Tool/Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Jack | To lift the vehicle for access to the undercarriage. |
| Socket Set | For loosening and tightening fasteners. |
| Grease | To lubricate components during installation. |
| Torque Wrench | To ensure proper tension on fasteners. |
Installation Steps
Begin by safely lifting the vehicle and removing the wheel assembly. Next, detach the components that secure the assembly to access the installation site. Clean any debris or old lubricant to ensure a smooth surface. Apply a thin layer of grease to the new unit to facilitate movement.
Align the new component carefully and secure it using the appropriate fasteners, ensuring they are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications using a torque wrench. Finally, reassemble the wheel assembly and lower the vehicle back to the ground. Test the functionality by rotating the wheel manually to ensure there are no obstructions or irregularities.
Signs of Worn Wheel Bearings
Understanding the indicators of deterioration in vital components is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and safety. Recognizing the symptoms early can prevent further damage and ensure a smoother driving experience. Here are some common signs that may suggest issues with these critical elements.
One of the primary signs is an unusual noise emanating from the wheels, which can often be described as grinding or humming sounds. This noise typically intensifies with increased speed or when turning. Additionally, vibrations felt through the steering wheel or the floor can indicate that the components are no longer functioning optimally.
Another noticeable symptom is uneven tire wear, which may lead to reduced traction and handling. If you observe irregular patterns on your tires, it might be worth investigating the condition of the associated components. Furthermore, a loose feeling in the steering or excessive play can signify that these elements need attention, potentially affecting overall vehicle stability.
Lastly, any signs of fluid leakage around the wheel area should not be ignored, as this can indicate damage to the seals protecting the internal mechanisms. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial for maintaining a safe and reliable driving experience.
Tools Required for Wheel Bearing Replacement
Replacing crucial components in your vehicle’s assembly requires specific tools to ensure a smooth and efficient process. Having the right equipment on hand not only saves time but also prevents damage to the surrounding structures. Below is a list of essential instruments needed for this task.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive set of sockets is vital for loosening and tightening various nuts and bolts.
- Torque Wrench: This tool is essential for applying the correct amount of force to the fasteners, ensuring they are securely tightened.
- Hammer: A hammer may be necessary for tapping components into place or dislodging stubborn parts.
- Pry Bar: A pry bar can help in separating components that are tightly fitted together.
- Slide Hammer: Useful for extracting components that are difficult to remove.
- Impact Wrench: This tool can expedite the removal of fasteners, especially those that are rusted or overtightened.
- Grease Gun: A grease gun is important for applying lubricant to moving parts after installation.
By ensuring you have these tools ready before starting, you can facilitate a more organized and effective replacement process.
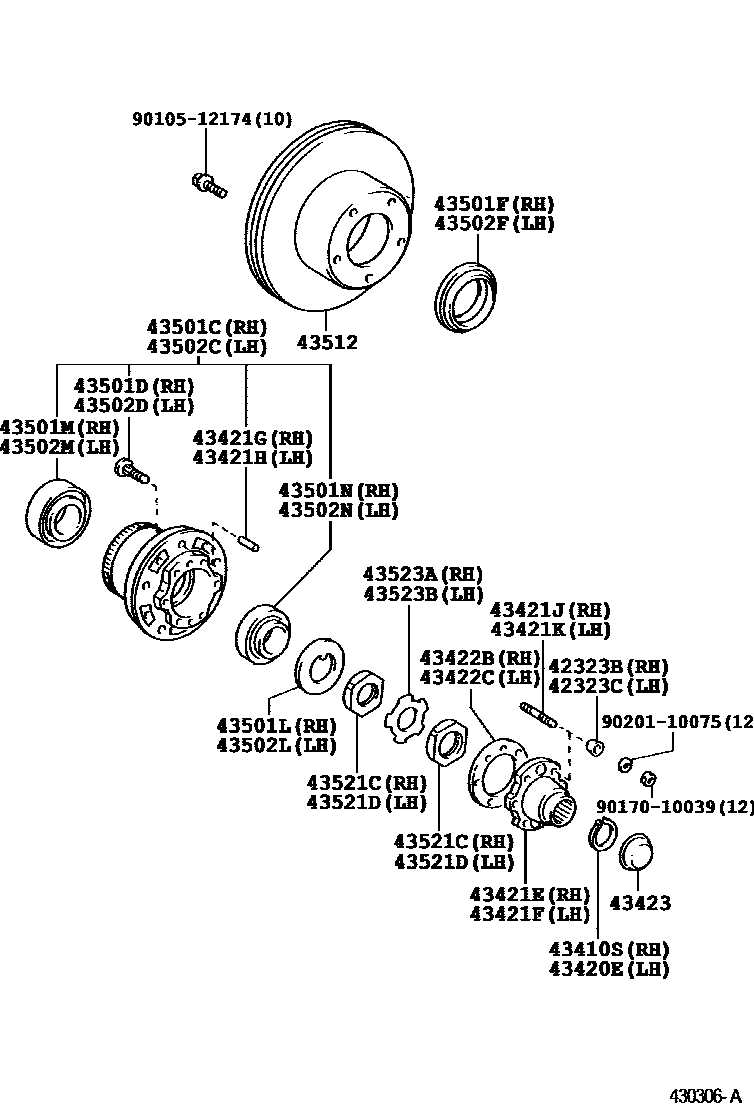
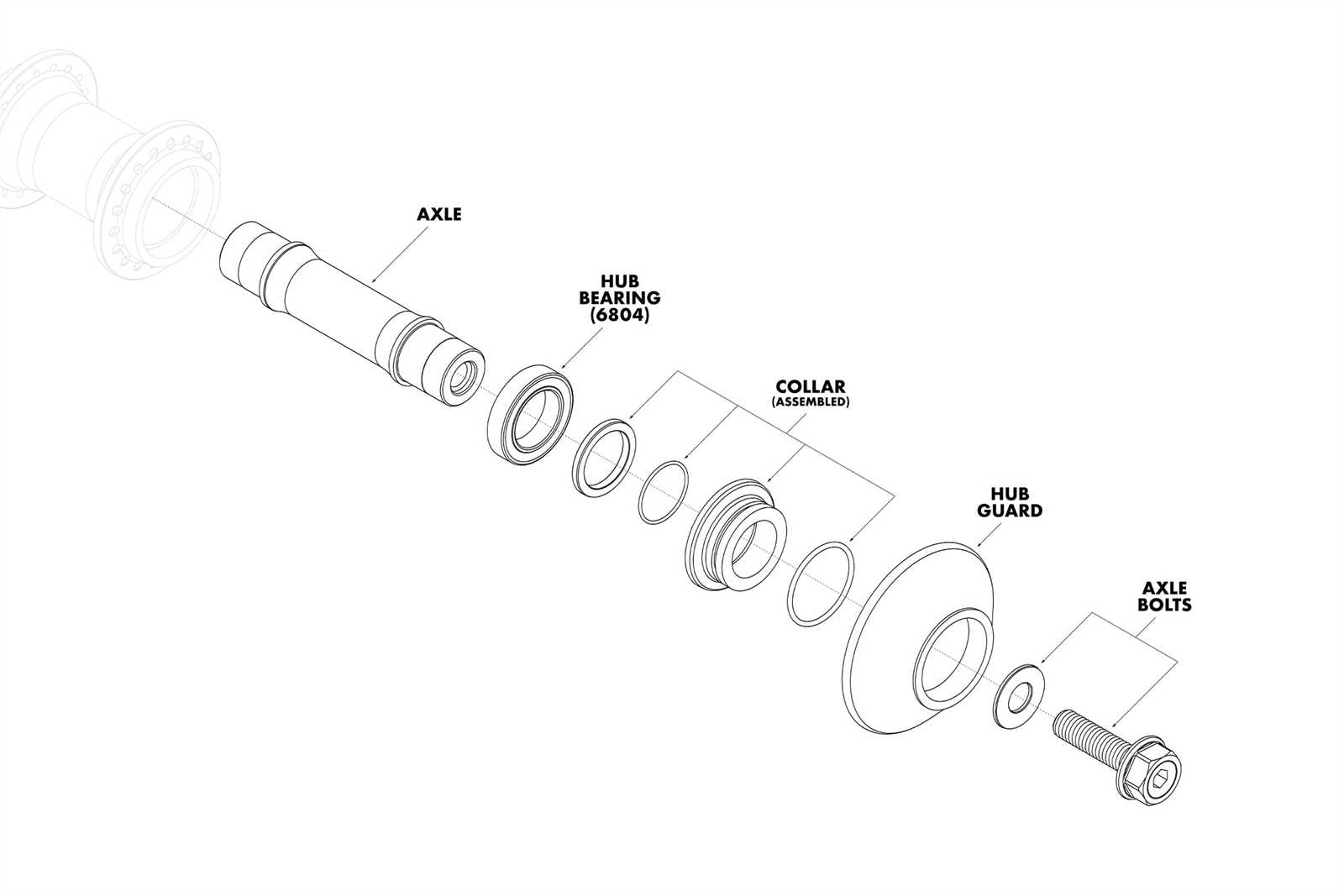
Step-by-Step Bearing Diagram Explanation
This section provides a detailed examination of the essential components involved in the rotational support mechanism. Understanding these elements is crucial for recognizing their roles and interactions within the assembly. Each section will break down the individual elements, illustrating their functions and relationships.
Understanding the Components
The first step in grasping the mechanics involves identifying each element’s position and purpose. The outer casing serves as a protective layer, ensuring durability while containing the inner mechanisms. The inner structure, responsible for facilitating smooth movement, works in conjunction with various seals and spacers to maintain efficiency and prevent contamination.
Assembly and Functionality
Next, we will explore how these components come together to create a cohesive unit. The assembly process involves precise alignment and securing of each piece, ensuring optimal performance under various conditions. The interplay between the different elements is vital, as it allows for smooth operation and longevity of the entire system.
Maintenance Tips for Wheel Bearings
Regular upkeep of your vehicle’s rotating components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. These elements play a significant role in ensuring smooth motion, stability, and safety while driving. Adopting proper maintenance practices can help prevent premature wear and costly repairs.
Routine Inspections
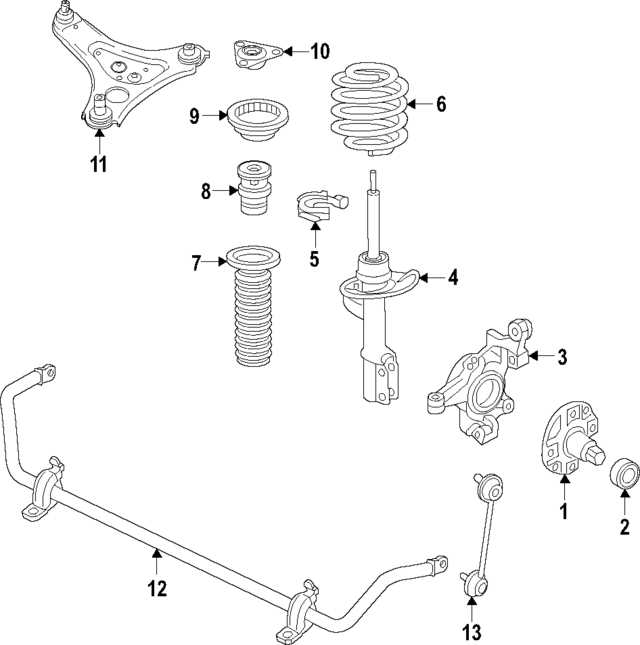
Conducting periodic checks is essential to detect any signs of wear or damage. Look for unusual noises, vibrations, or irregularities during operation. Inspect for any visible signs of leakage or corrosion that could indicate potential issues. Early detection can save time and resources in the long run.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Maintaining proper lubrication is vital for the smooth operation of rotating components. Ensure that the lubrication used is appropriate for the specific application. Regularly clean the area to remove debris and contaminants that may interfere with functionality. Proper lubrication and cleanliness will enhance performance and extend the lifespan of these crucial elements.
Impact of Bearing Quality on Performance
The quality of essential components significantly influences overall functionality and reliability in mechanical systems. Superior materials and precise manufacturing processes lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced friction, and prolonged lifespan. In contrast, substandard components can result in increased wear and premature failure, impacting the entire system’s performance.
When high-quality elements are utilized, they provide optimal support for rotational movements, ensuring smooth operation. This smoothness translates into better energy efficiency and lower operational costs. Furthermore, high-performance components are designed to withstand extreme conditions, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and maintenance needs.
Ultimately, investing in quality elements not only boosts performance but also enhances safety and reliability. Choosing reliable suppliers and conducting regular inspections can ensure that the system operates at its best, reflecting the importance of component quality in mechanical efficiency.
Comparing Sealed vs. Open Bearings
When it comes to choosing between different types of rolling elements, understanding the distinctions between enclosed and exposed designs is essential. Each variation has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications, impacting performance, maintenance, and durability.
Advantages of Sealed Designs
Enclosed configurations provide a significant advantage by keeping contaminants such as dirt, dust, and moisture out of the interior. This protection often leads to a longer lifespan, as the internal components are less susceptible to wear. Additionally, these assemblies require less frequent maintenance, making them a practical choice for environments where accessibility is limited.
Benefits of Open Designs
Exposed configurations, on the other hand, offer ease of access for lubrication and inspection. This can be particularly beneficial in applications where regular maintenance is feasible and desired. Furthermore, these designs tend to have lower friction, which can enhance efficiency in certain settings, making them a viable option for specialized uses.
Frequently Asked Questions on Bearings
This section addresses common inquiries regarding rolling components used in various applications. Understanding these elements can enhance their performance and longevity, leading to smoother operation in machinery and vehicles.
Common Inquiries
- What are the signs of wear in these components?
- How often should they be replaced?
- What maintenance practices can extend their lifespan?
- Are there specific types for different applications?
Understanding Maintenance
- Regular inspection is crucial to detect any potential issues early.
- Proper lubrication can significantly reduce friction and heat buildup.
- Ensure correct alignment during installation to prevent premature failure.