Bottom Bracket Components Diagram Overview
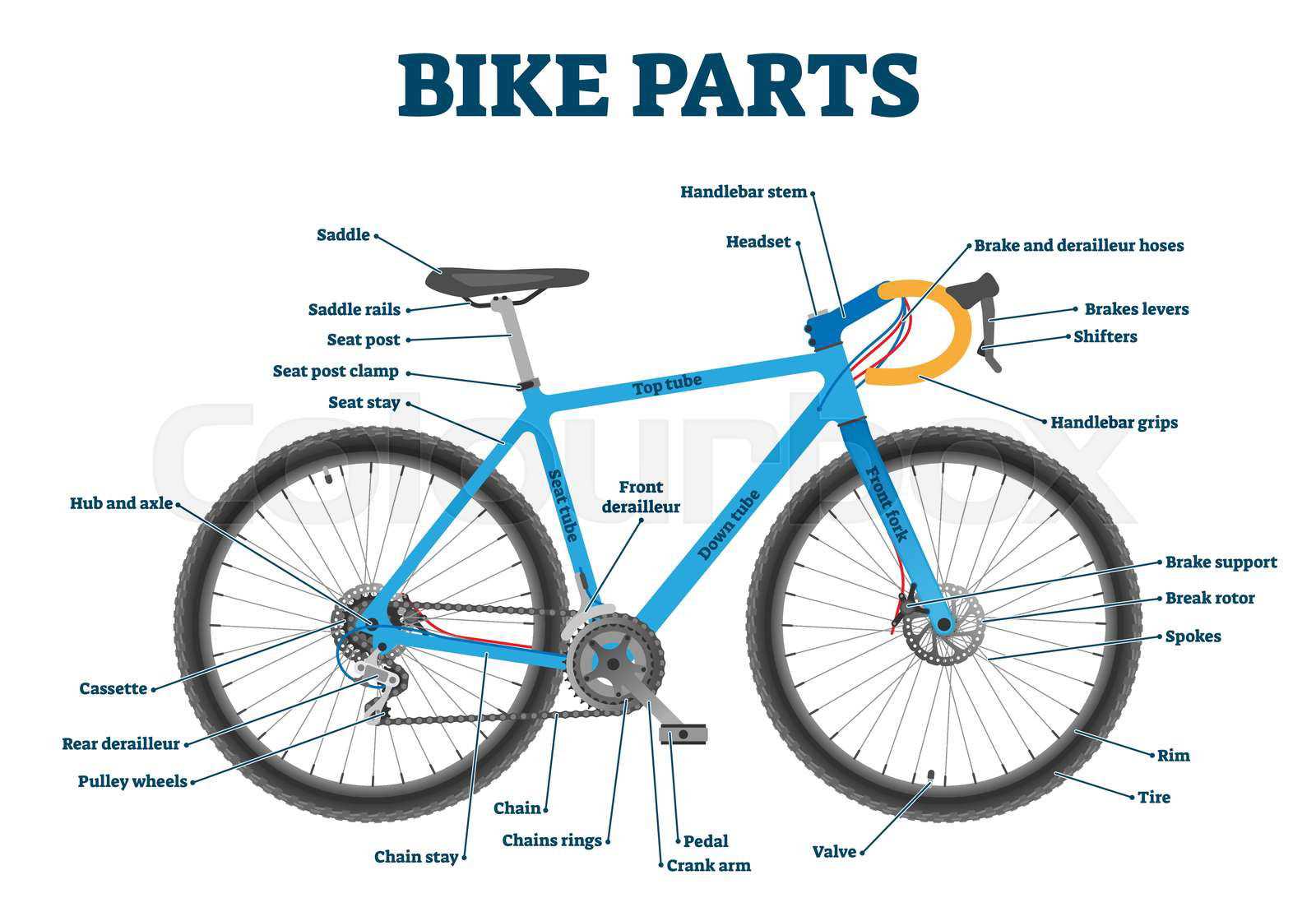
Understanding the core elements that connect various sections of a bicycle is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and durability. These components serve as the foundation for efficient pedaling and overall bike performance, making them a vital area to explore for both enthusiasts and professionals.
The internal mechanisms within this structure play a significant role in maintaining balance and functionality. Each element works in unison to transfer energy effectively, allowing for seamless riding experiences. Proper maintenance and knowledge of these elements can greatly extend the lifespan of your cycling equipment.
In this section, we will delve into the essential components that contribute to this system, highlighting their purpose and importance. Knowing how each piece interacts within the larger framework is key to keeping your bike in top condition.
Bottom Bracket Overview and Function
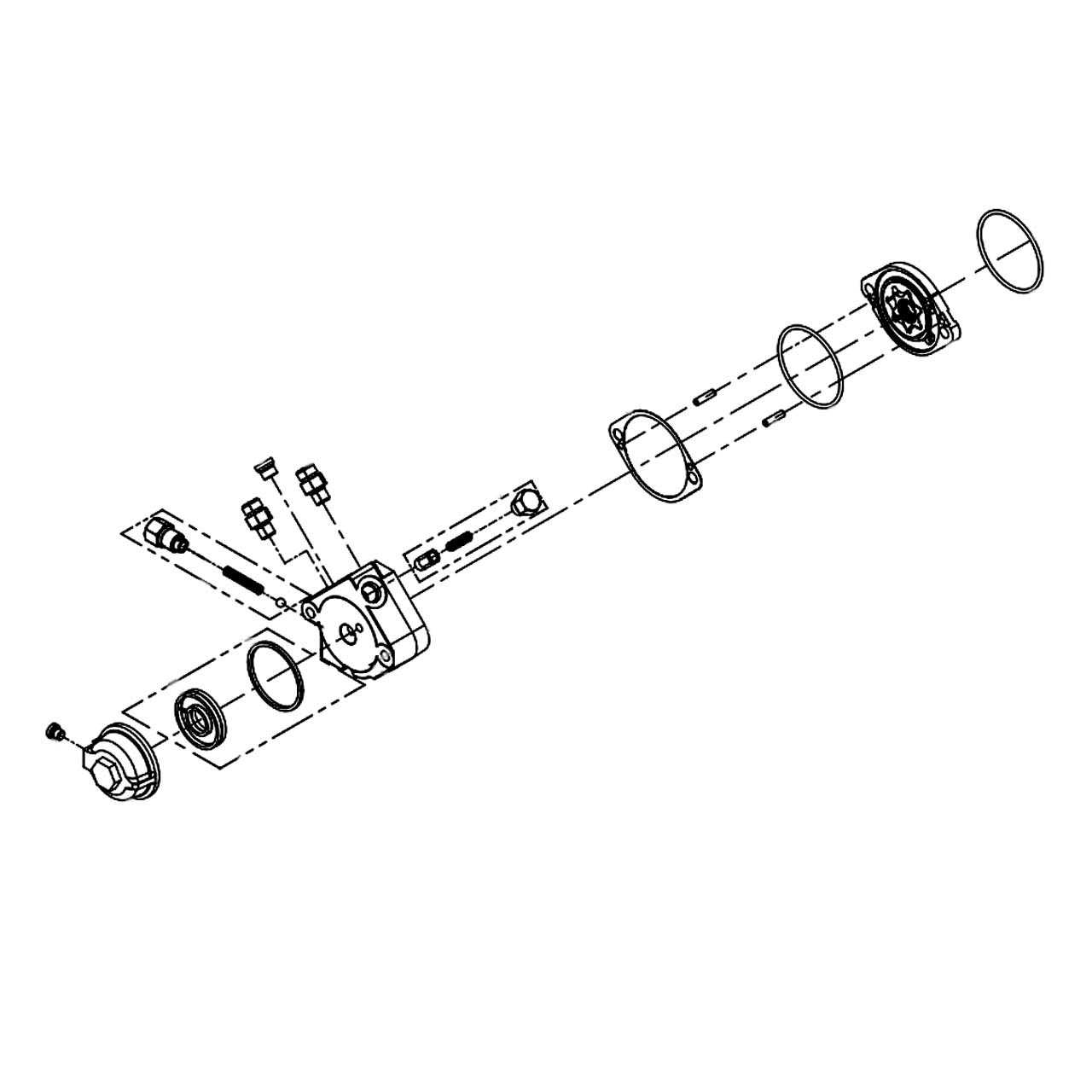
One of the crucial components in a bicycle’s drivetrain ensures smooth pedaling and efficient power transfer. Located at the junction where the frame meets the crankset, this mechanism plays a pivotal role in maintaining stability and providing support during rides.
Below is a brief look at how this component functions:
- Power transfer: It helps transfer energy from the rider’s legs to the chain, ensuring seamless movement.
- Support:
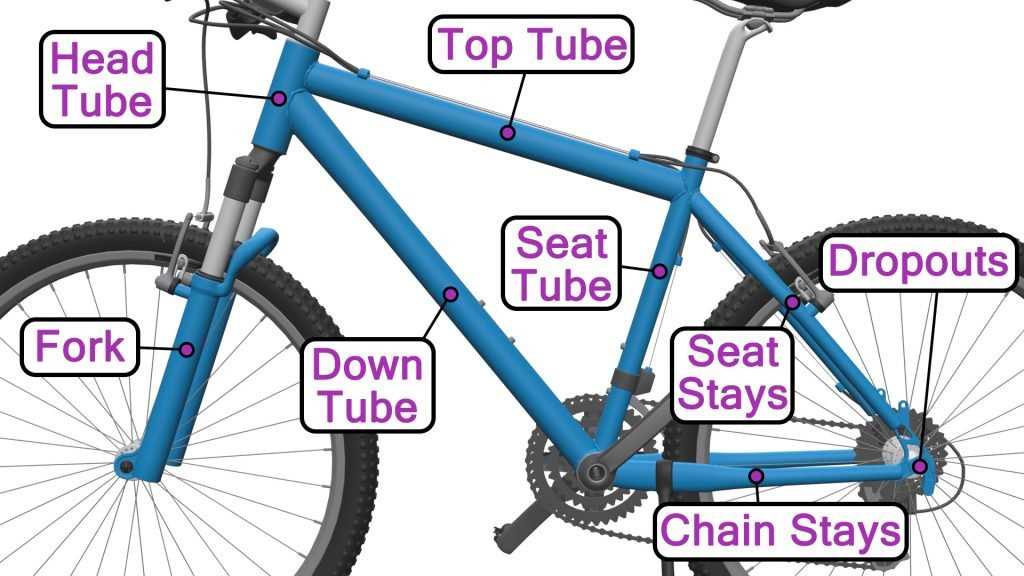
Key Components of a Bottom Bracket
The central unit that connects the frame with the drivetrain is essential for smooth pedaling and stability. It is composed of various elements that allow for efficient transfer of power, while ensuring the longevity and durability of the whole structure. Understanding these elements helps in maintaining the efficiency of the entire system.
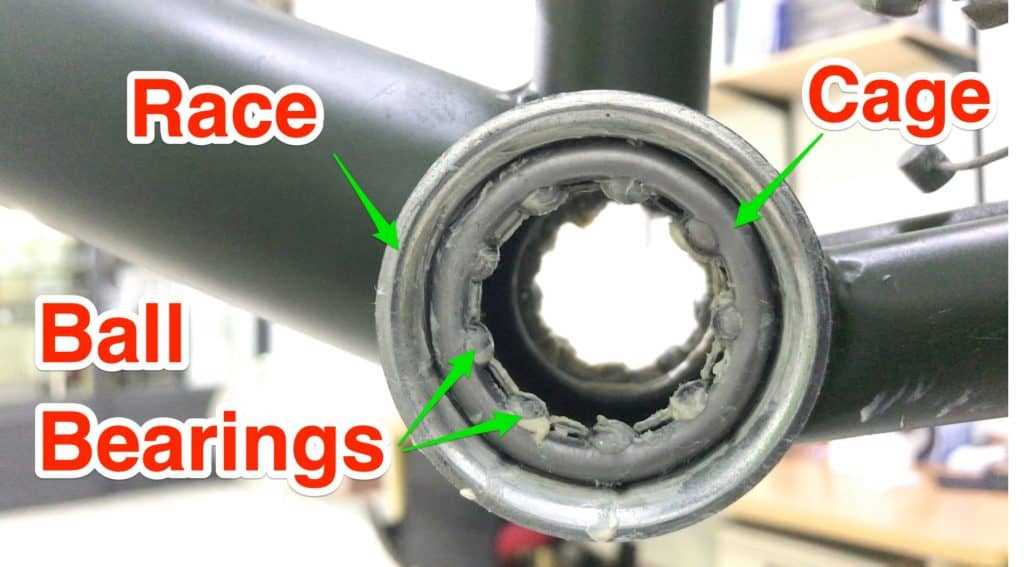
Component Types of Bearings in Bottom Brackets
Bearings play a critical role in ensuring smooth rotation and durability in cycling components. Different types of these mechanisms are used to provide optimal support, depending on the design and performance requirements of the bicycle. The choice of bearing type can impact both efficiency and longevity, offering various levels of resistance and protection.
One of the most common types is the cartridge bearing, known for its compact and sealed structure, which protects against dirt and moisture. Another widely used option is the cup-and-cone bearing, a more adjustable system that requires regular maintenance but allows for fine-tuning to suit rider preferences. Both types offer unique advantages, making them suitable for different cycling needs.
Axle and Crankset Connection Explained
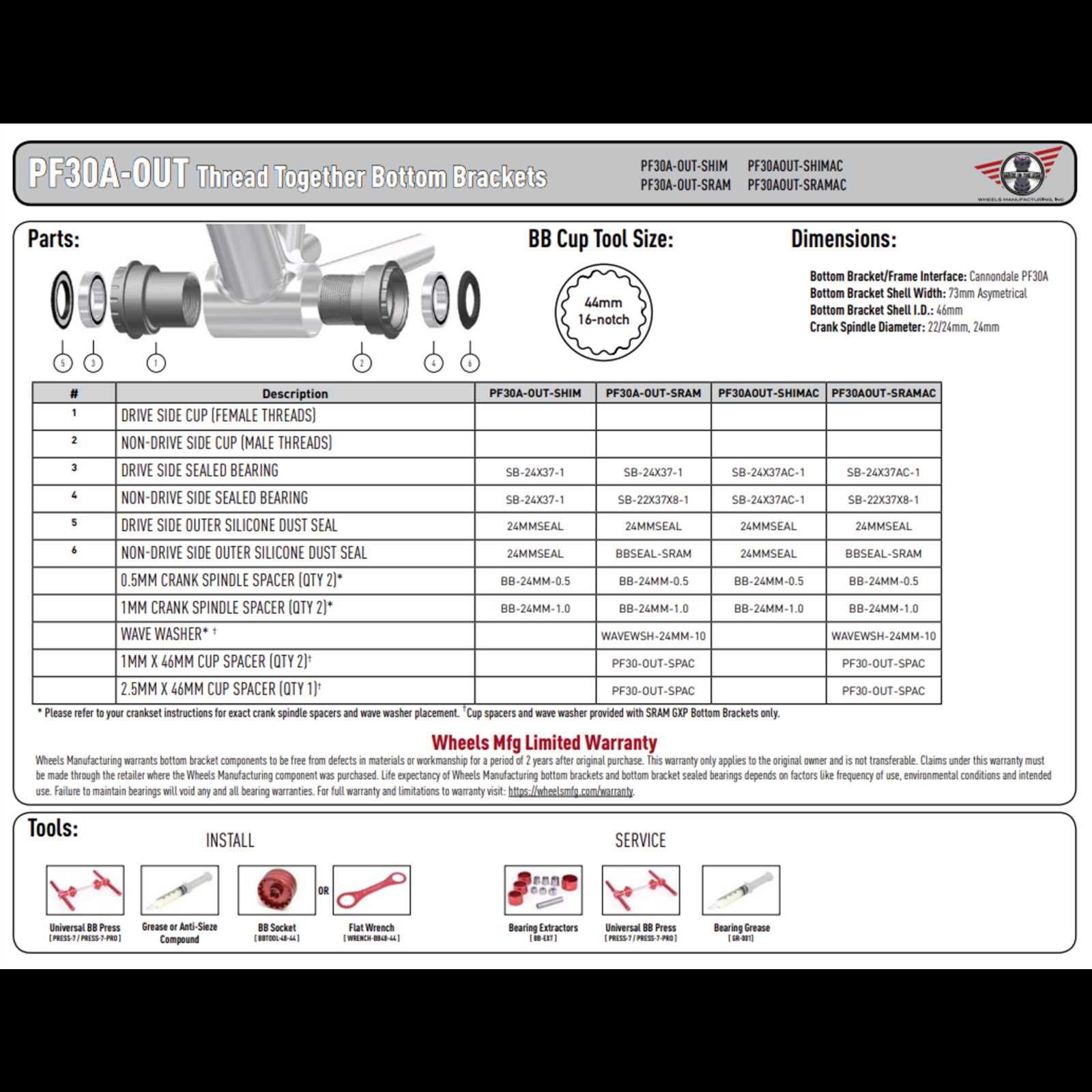
The connection between the axle and crankset plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth pedaling and power transfer on any bicycle. This interaction impacts the overall performance of the bike, allowing for efficient motion and stability during a ride. Understanding how these components work together helps improve the setup and maintenance of the drivetrain.
How the Axle Supports the Crankset
Seals and Their Role in Durability
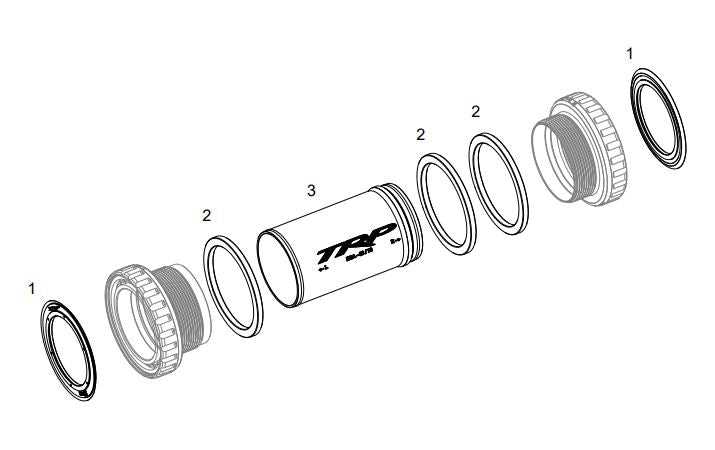
Seals play a crucial role in enhancing the longevity and performance of mechanical systems. By preventing the entry of contaminants and maintaining the integrity of lubricants, they help in minimizing friction and wear, ensuring smoother operation over time. The effectiveness of these components is vital in protecting other internal elements from premature damage, which can lead to system failure.
Types of Seals

There
Bottom Bracket Shell Compatibility Guide
This section provides essential information regarding the compatibility of shell components within various bicycle frameworks. Understanding these aspects ensures that cyclists can choose the right components for their bicycles, optimizing performance and enhancing the riding experience.
Types of Shell Configurations
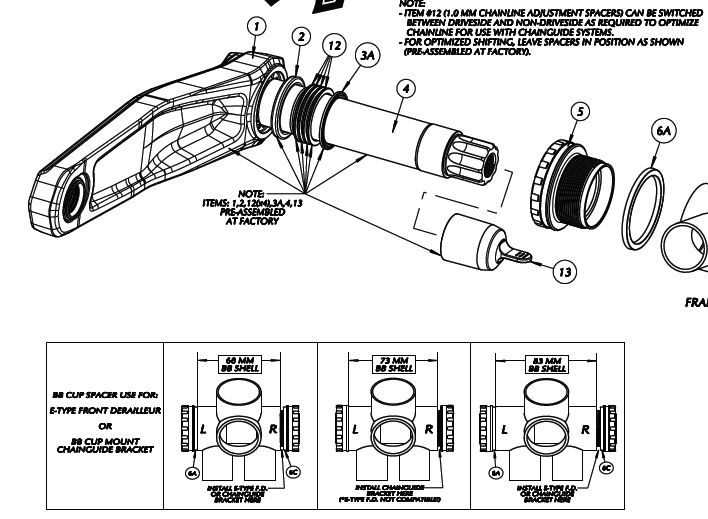
There are several configurations available in the market, each designed to fit specific frames and components. Below are the most common types:
- Threaded: Features screw-in fittings for secure attachment.
- Press-Fit: Uses a tight fit to secure components within the frame.
- BB30: A specific design allowing wider spacing for cranks.
- PF30: Similar to BB30 but offers different shell dimensions.
Factors Affecting Compatibility
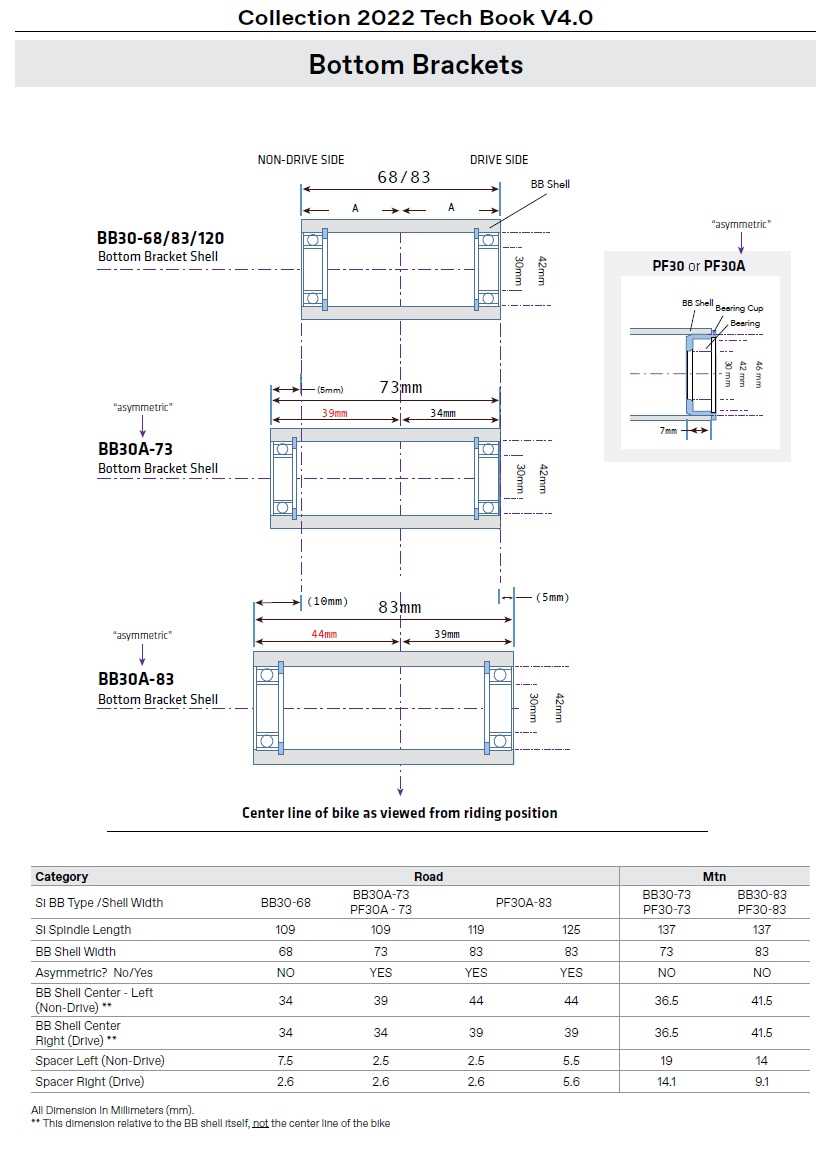
When selecting a shell, several factors must be considered to ensure proper fit and functionality:
- Frame Material: Different materials may require specific designs.
- Crankset Type: Ensure compatibility between the crankset and the shell.
- Shell Width: Measured to ensure that components fit correctly.
- Internal Diameter: Affects the choice of bearings and installation method.
Understanding these components can significantly enhance the selection process, leading to improved performance and durability of the bicycle system.
Threaded vs. Press-Fit Bottom Brackets
In the realm of cycling, the method of attaching the pedal assembly to the frame is crucial for performance and durability. Two prominent approaches have emerged: the traditional threaded style and the more contemporary press-fit design. Each method has its distinct advantages and drawbacks, impacting how cyclists experience ride quality and maintenance.
Threaded System

The threaded configuration has been a staple in the cycling community for many years. This classic design offers several benefits:
- Ease of Installation: The threaded option typically allows for straightforward installation using standard tools, making it accessible for home mechanics.
- Compatibility: This system often ensures compatibility with a wide range of frames and components.
- Durability: The secure fit of the threads can provide longevity and stability, reducing the chances of movement during rides.
Press-Fit System

On the other hand, the press-fit variant has gained traction in modern designs. This innovative approach presents its own set of characteristics:
- Weight Reduction: The absence of threads can lead to lighter overall construction, appealing to competitive cyclists.
- Increased Stiffness: The design may enhance power transfer, resulting in improved efficiency during pedaling.
- Variety of Options: Manufacturers often produce different sizes and standards, catering to diverse cycling needs and preferences.
Choosing between these two systems ultimately depends on individual preferences, riding style, and maintenance capabilities. Understanding the unique features of each can assist cyclists in making informed decisions for their specific needs.
Understanding Bottom Bracket Size Standards
When it comes to the assembly of cycling components, one of the critical elements is the standardized sizing of certain fixtures. These dimensions ensure compatibility and optimal performance of various components within the drivetrain system. The correct sizing is essential for achieving smooth operation and enhancing the overall riding experience.
Importance of Sizing
Correct sizing is crucial in ensuring that the interface between different components operates seamlessly. Variations in dimensions can lead to misalignment, which may result in premature wear and inefficient power transfer. By adhering to established size standards, manufacturers create products that fit together harmoniously, providing a reliable and enjoyable riding experience.
Common Size Standards
Several prevalent sizing standards exist, each serving specific types of cycling applications. Understanding these standards helps cyclists make informed decisions about component selection and compatibility. Below is a table highlighting some common size standards:
Standard Width (mm) Thread Type English 68/73 BSA (1.37” x 24 TPI) Italian 70 ITA (36mm x 24 TPI) French 65 French (35mm x 1.0) Press-Fit 86.5/92 Press-Fit Installation Tools and Techniques
To ensure a successful setup of the component system, utilizing the appropriate instruments and methods is crucial. Each tool plays a specific role in facilitating the installation process, allowing for efficiency and precision. Understanding the various techniques will empower users to achieve a seamless assembly experience.
Common tools required for this undertaking include a torque wrench, various sizes of wrenches, and specific aligners designed for the task. The torque wrench is essential for applying the correct amount of force, preventing damage while ensuring that everything is securely fitted. Meanwhile, adjustable and socket wrenches can accommodate different sizes of fittings, making them versatile choices for this job.
Employing proper techniques is equally important. It is advisable to clean the surfaces thoroughly before beginning the installation to ensure optimal contact and fit. Additionally, following a systematic approach, such as starting from one end and working towards the other, can help maintain organization and prevent misalignment. Regularly checking for any signs of wear or improper fitting during the installation will further enhance the longevity and performance of the assembled components.
Common Bottom Bracket Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep of crucial bicycle components ensures optimal performance and longevity. Implementing effective maintenance practices can prevent issues, enhance functionality, and contribute to a smoother riding experience. Here are some essential tips for maintaining these integral elements of your bicycle.
1. Keep It Clean: Regularly clean the exterior to prevent dirt accumulation, which can lead to wear over time. Use a damp cloth and gentle soap to remove grime without damaging the surface.
2. Inspect for Wear: Periodically check for signs of damage or excessive wear. Look for any cracks or unusual noises during operation, which may indicate the need for replacement or repair.
3. Lubricate Components: Proper lubrication is key to ensuring smooth operation. Apply a suitable lubricant to reduce friction and prevent corrosion, especially in areas subject to movement.
4. Adjust Tightness: Ensure that all components are correctly tightened according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose fittings can lead to misalignment and reduced performance.
5. Seek Professional Help: If you notice persistent issues or lack the tools for maintenance, consult a professional technician. Expert service can address complex problems and ensure everything functions correctly.