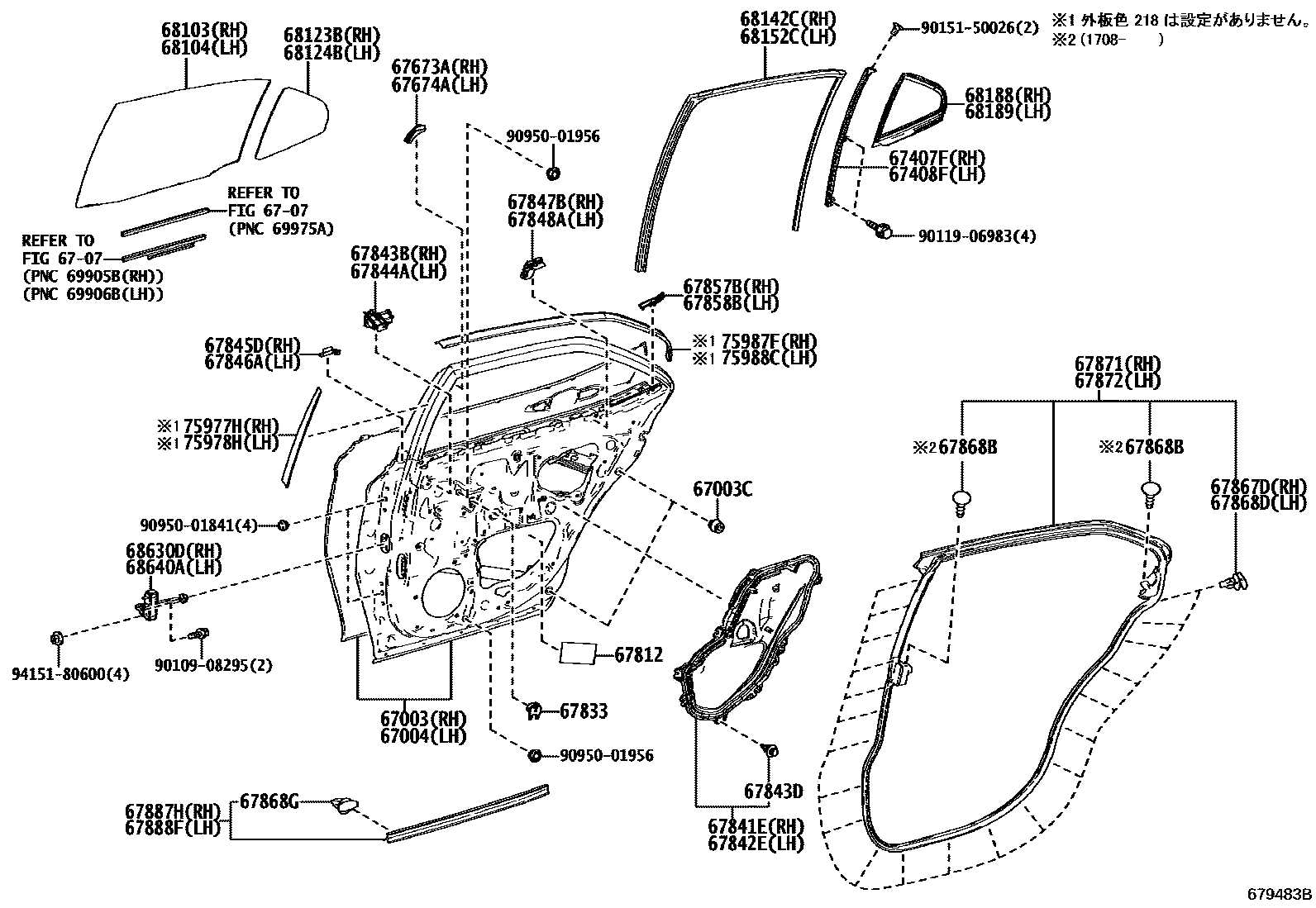
Understanding the Parts Diagram for the 2017 Toyota Camry
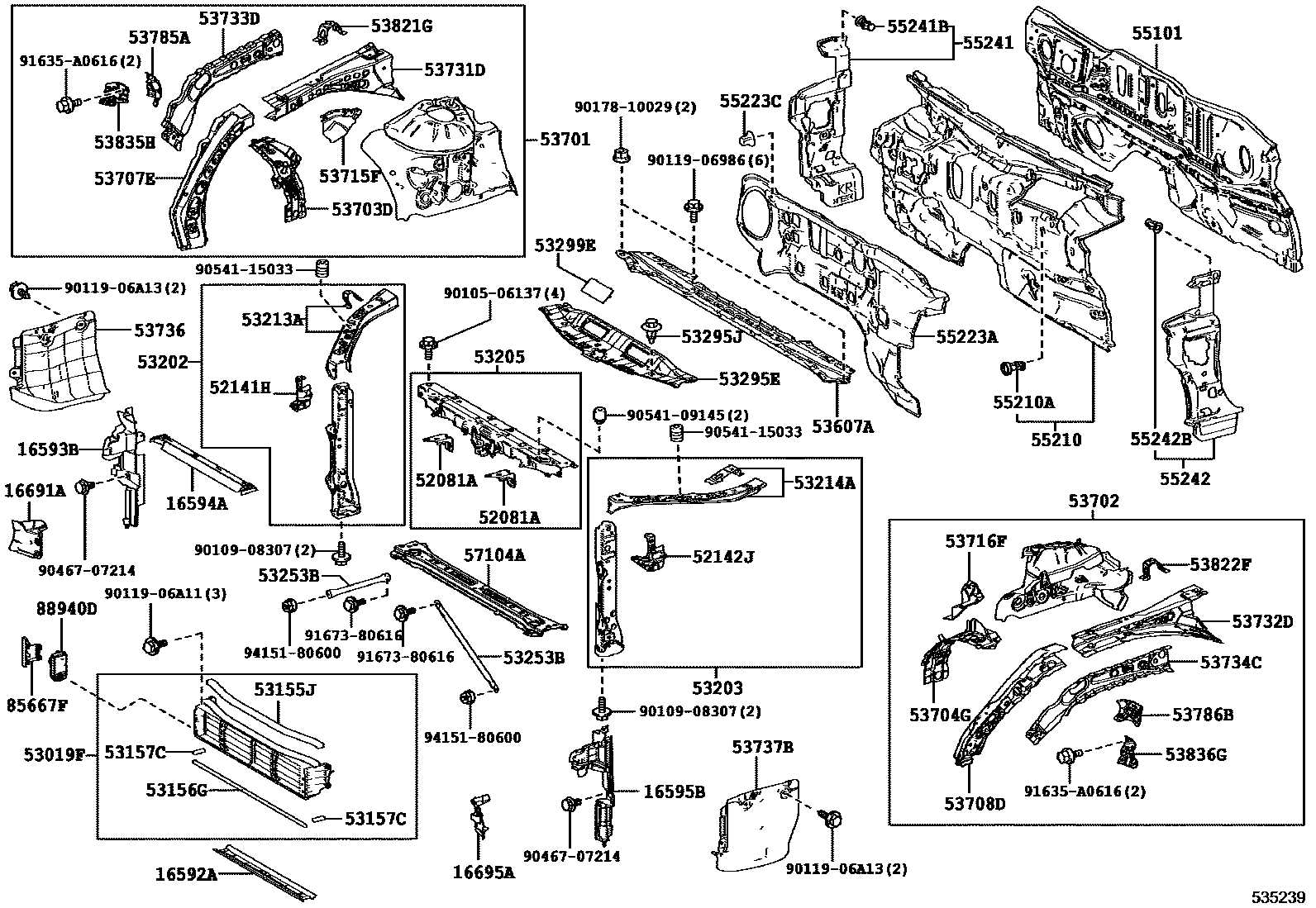
In the realm of automotive engineering, a comprehensive visual representation of a vehicle’s structure is crucial for both enthusiasts and professionals. This guide aims to delve into the intricate arrangement of various elements within a specific sedan, highlighting their functionality and interconnectivity. By exploring this layout, readers can gain valuable insights into how different components collaborate to ensure optimal performance.
Each vehicle consists of a multitude of essential mechanisms, from the powertrain to the electrical systems, all meticulously designed to work in harmony. This section will outline the significant features, showcasing how they contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of the automobile. Understanding these relationships is fundamental for maintenance, upgrades, or troubleshooting.
Furthermore, an in-depth exploration of the structural organization aids in recognizing potential areas for improvement and innovation. By familiarizing oneself with the layout, one can appreciate the engineering marvels that enhance both safety and comfort in modern vehicles. This knowledge serves as a solid foundation for any automotive-related endeavors.
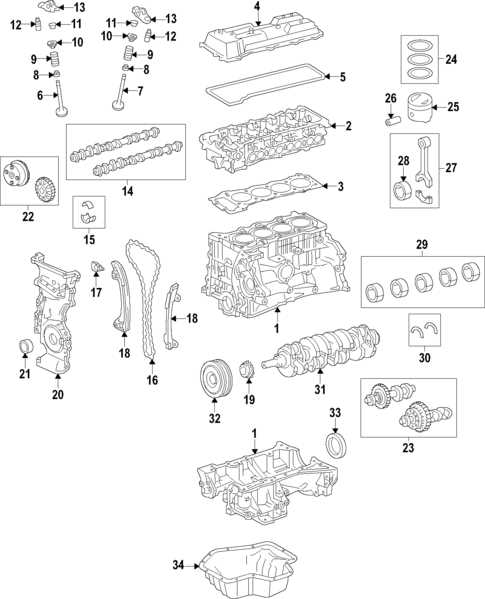
This section explores the intricate components that comprise an automotive power unit, focusing on the configuration and interrelationships of various elements. A comprehensive understanding of the assembly not only enhances maintenance skills but also aids in troubleshooting performance issues effectively.
Key Components of the Engine Assembly
- Block: The main structure housing the cylinders and other integral parts.
- Cylinders: The chambers where fuel combustion occurs, converting energy into mechanical motion.
- Pistons: Components that move up and down within the cylinders, transferring force to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: A rotating shaft that converts linear motion from the pistons into rotational energy.
- Valvetrain: A system that controls the intake and exhaust valves, ensuring efficient air-fuel mixture and exhaust expulsion.
Assembly Process Overview
- Begin with the installation of the block, ensuring it is securely mounted.
- Insert pistons into the cylinders, applying proper lubrication to minimize friction.
- Attach the crankshaft, ensuring alignment with the connecting rods.
- Install the valvetrain components, adjusting timing to synchronize with the crankshaft rotation.
- Conduct a final inspection to verify that all components are properly assembled and secured.
Transmission System and Functionality
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of a vehicle, serving as the vital link between the engine and the wheels. This system is responsible for converting the power generated by the engine into a form that can effectively drive the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move efficiently. Understanding its components and functionality can enhance the appreciation of how vehicles operate.
Key Components

- Transmission: The main component that manages gear shifting and power distribution.
- Torque Converter: A device that allows the engine to continue running while the vehicle is stationary and helps in transferring power smoothly.
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission to allow for gear changes.
- Gears: Different gear ratios provide the necessary torque and speed for various driving conditions.
Functionality Overview
- Power Transfer: The system transfers power from the engine to the wheels through a series of mechanical components.
- Gear Shifting: Automatic or manual mechanisms allow the driver to select appropriate gears based on speed and load conditions.
- Efficiency Optimization: The transmission adjusts gear ratios to ensure optimal fuel efficiency and performance.
- Adaptive Response: Advanced systems can adapt to driving conditions, enhancing responsiveness and control.
Electrical System Layout Explained

The electrical framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in its overall functionality, providing the necessary energy to various components. Understanding this layout is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. The intricate arrangement of wiring, connectors, and control units ensures seamless communication between electrical devices, enhancing the performance and reliability of the automotive system.
At the core of the electrical system are various circuits responsible for powering everything from lighting to infotainment. These circuits are designed to distribute energy efficiently, reducing the risk of overload and enhancing safety. A comprehensive grasp of the wiring layout aids in pinpointing issues, making repairs more manageable.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy and provides power to start the engine and run electrical systems. |
| Alternator | Generates electrical energy to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine is running. |
| Fuses | Protect electrical circuits by breaking the connection in case of an overload, preventing damage. |
| Wiring Harness | A network of wires that connects various electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution. |
| Control Modules | Electronic units that manage and regulate different systems within the vehicle, such as engine performance and climate control. |
A clear understanding of the electrical configuration helps in diagnosing faults, enhancing the longevity of the vehicle’s systems. Proper attention to this layout can significantly improve overall vehicle performance and driver satisfaction.
Suspension Parts and Their Roles
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle stability, comfort, and handling. It consists of various components that work together to absorb shocks from the road and maintain proper tire contact, contributing to an overall smooth driving experience.
Key Components of the Suspension System
- Shock Absorbers: These devices help to dampen the oscillations caused by bumps and dips in the road, ensuring a stable ride.
- Springs: Springs support the weight of the vehicle and allow for vertical movement, absorbing energy from impacts and returning the vehicle to its normal height.
- Control Arms: These link the vehicle’s frame to the wheels, allowing for controlled movement and alignment during turns and while driving over uneven surfaces.
- Stabilizer Bar: This component reduces body roll during cornering, enhancing stability and control.
Functions of the Suspension Elements
- Comfort: By absorbing road imperfections, the suspension system enhances passenger comfort.
- Handling: A well-designed suspension contributes to improved steering response and cornering capabilities.
- Tire Longevity: Proper suspension alignment helps ensure even tire wear, extending the lifespan of the tires.
- Safety: A functional suspension system maintains tire contact with the road, which is vital for safe braking and handling.
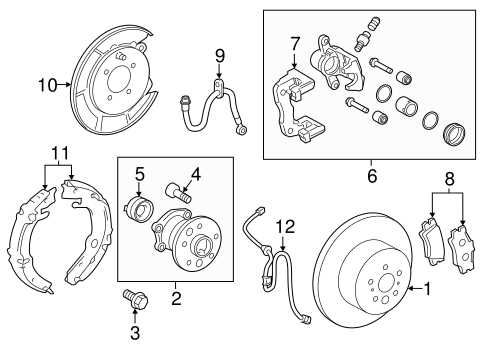
Brake System Components Breakdown
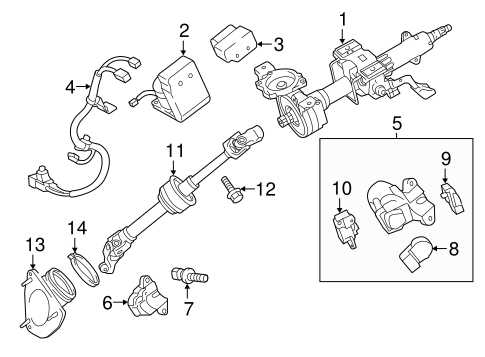
The braking mechanism of a vehicle consists of various essential elements that work in harmony to ensure safety and performance. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and responding effectively to any issues that may arise.
Master Cylinder: This component acts as the heart of the braking system, converting the force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. It plays a vital role in initiating the braking process.
Brake Lines: These tubes transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brakes at each wheel. Their integrity is critical, as any leaks can lead to a loss of braking power.
Brake Pads: Situated within the brake caliper, these friction materials are responsible for clamping down on the brake rotor, creating the necessary friction to slow or stop the vehicle.
Brake Rotors: These circular discs are mounted to the wheel hub and work in conjunction with the brake pads. When pressure is applied, the pads grip the rotors, which ultimately brings the vehicle to a halt.
Calipers: These components house the brake pads and apply pressure to them against the rotors when the brakes are engaged. They are crucial for the effective functioning of the braking system.
Brake Booster: This device enhances the force applied to the brake pedal, allowing for easier and more effective braking. It utilizes vacuum pressure to amplify the driver’s input.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, vehicle owners can better appreciate the complexity of their braking system and the importance of regular maintenance and inspections.
Fuel System Overview and Diagrams
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of any vehicle. It is responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance and emissions control. Understanding the components and layout of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
This section will provide an overview of the fuel delivery mechanism, including the key elements involved in the process. Below are the primary components that make up this system:
- Fuel Tank
- Fuel Pump
- Fuel Filter
- Fuel Injectors
- Fuel Lines
- Pressure Regulator
Each of these components serves a specific purpose:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel until it is needed by the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine, maintaining proper pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel before it reaches the injectors, preventing contamination.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel, ensuring an even mixture with air for combustion.
- Fuel Lines: Transport fuel between components under pressure.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains optimal fuel pressure for efficient engine operation.
Understanding these components and their interactions can help in diagnosing issues and performing necessary repairs. Below, we will explore the configuration of these elements in more detail, providing helpful illustrations to assist in visualizing the setup.
Interior Parts and Configurations
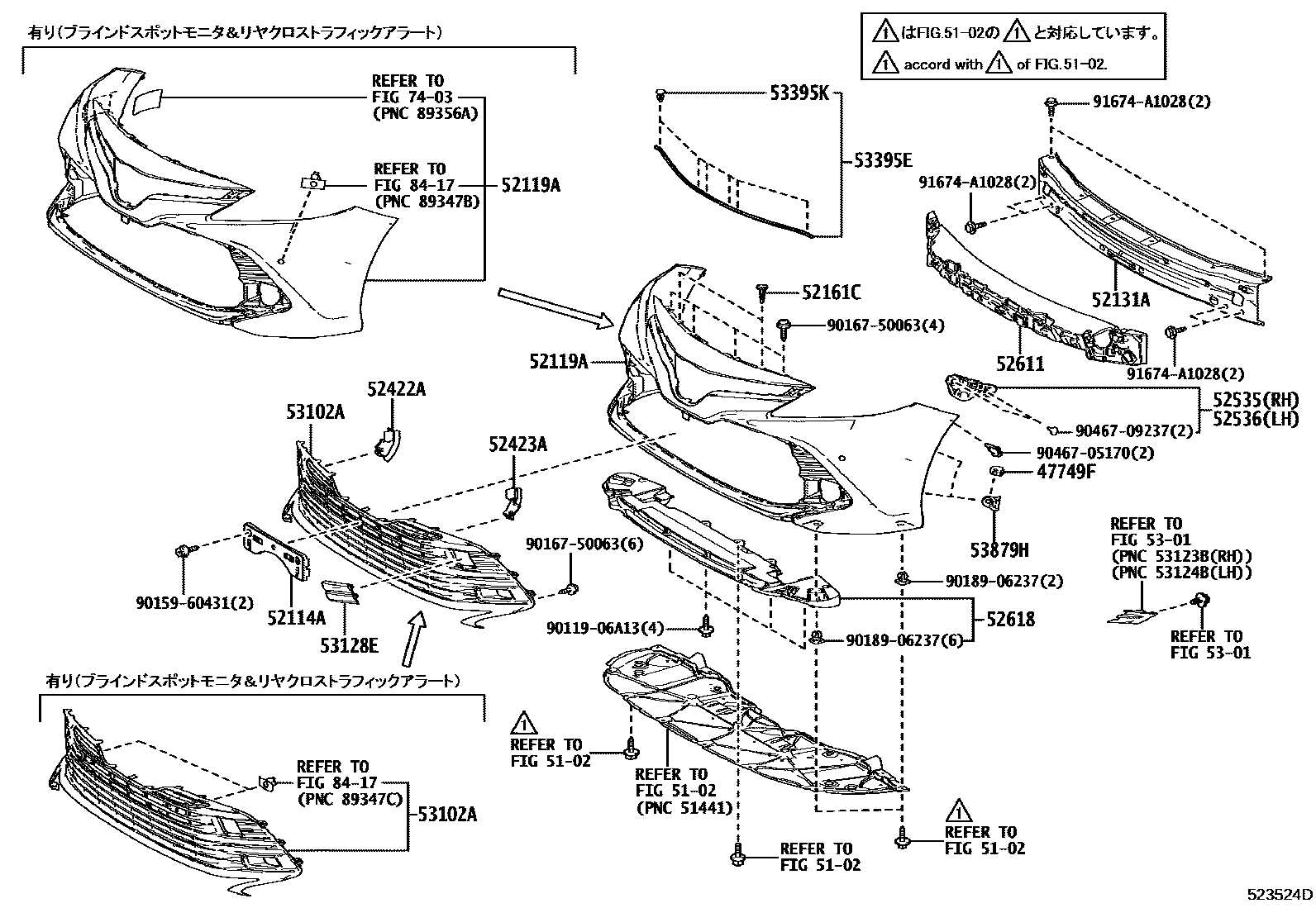
The layout and components within a vehicle’s cabin play a crucial role in both functionality and aesthetics. Understanding these elements is essential for maintaining comfort, accessibility, and overall driving experience. This section delves into the various features and arrangements that contribute to an inviting and practical interior space.
Main Features

- Seating: Arrangements and material options that enhance comfort and support.
- Dashboard: Key controls and display elements that provide essential information.
- Storage Compartments: Strategic placements for convenience and organization.
- Climate Control: Systems designed for optimal temperature management.
Configuration Options
- Seating Configurations:
- Front seating adjustments for driver and passenger comfort.
- Rear seating flexibility to accommodate passengers and cargo.
- Control Layout:
- Centralized infotainment system for easy access to entertainment and navigation.
- Instrument cluster design for quick reference to vital information.
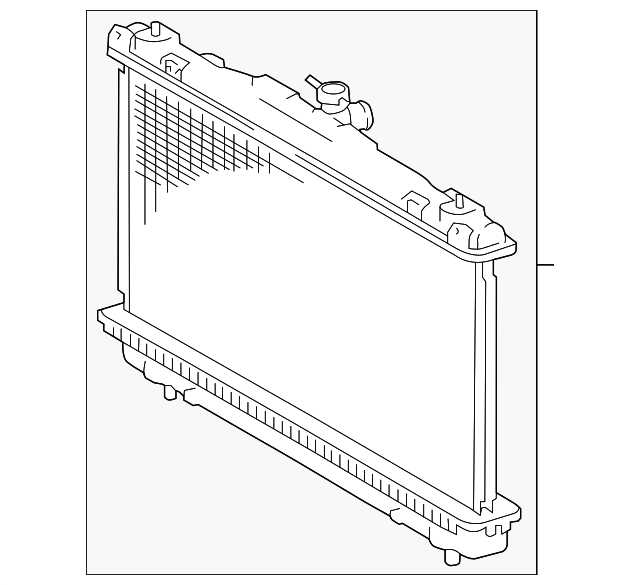
Cooling System Functionality Explained
The cooling mechanism in an automobile plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the engine and other vital components. This system ensures that heat generated during combustion is efficiently dissipated, preventing overheating and enhancing performance. Understanding how this intricate setup works can provide insights into vehicle maintenance and longevity.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism
The primary elements involved in this system include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant. Each part contributes to the overall efficiency by circulating the cooling fluid and regulating temperature. The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, while the water pump facilitates the movement of the fluid throughout the engine and back to the radiator. The thermostat acts as a control valve, ensuring that the engine warms up to an optimal temperature before allowing the coolant to flow into the radiator.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
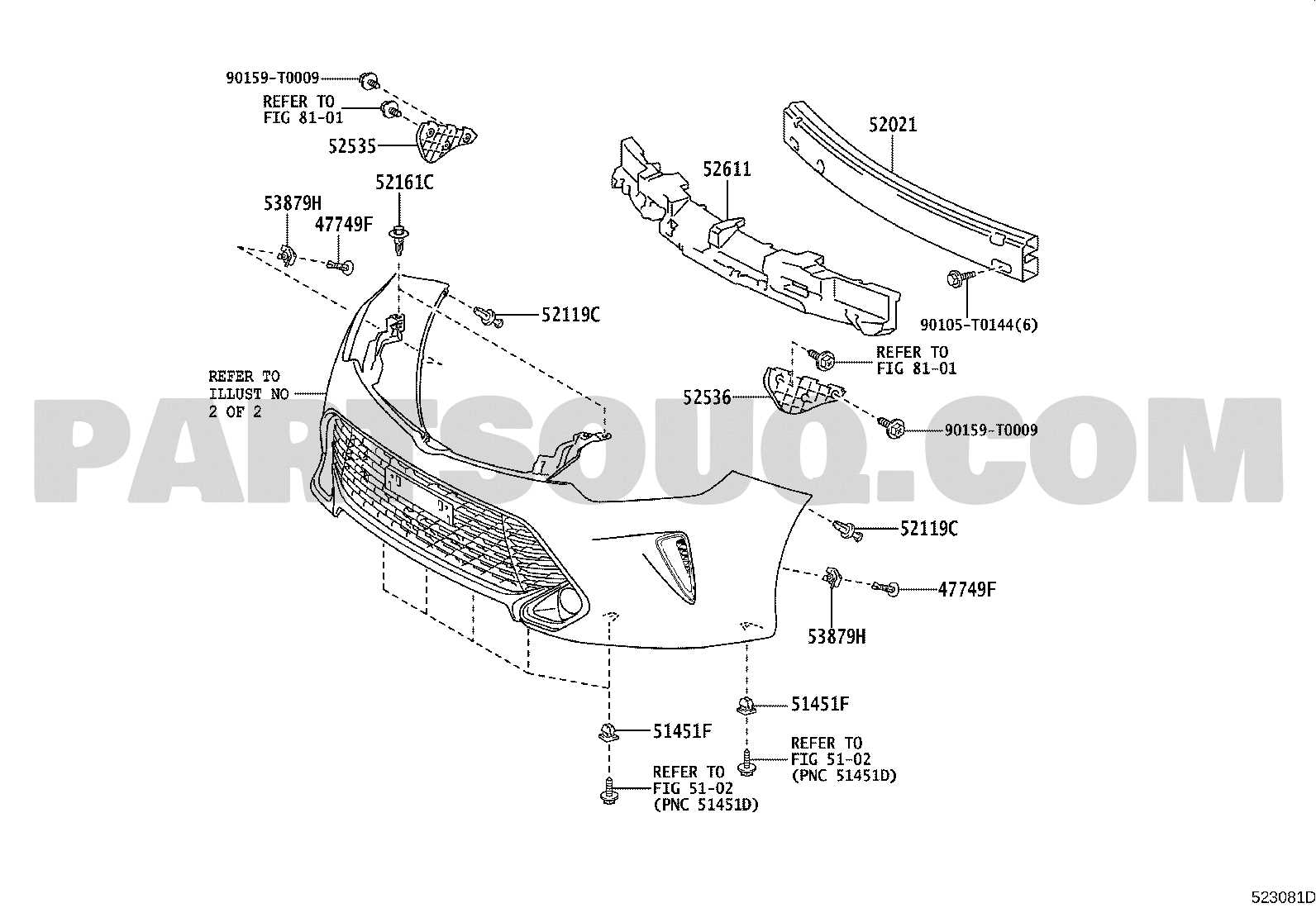
To ensure the effective operation of the cooling mechanism, regular maintenance is essential. This includes checking the coolant levels, inspecting for leaks, and flushing the system periodically. Neglecting these tasks can lead to overheating, which may result in severe engine damage. Maintaining this system not only prolongs the lifespan of the vehicle but also improves fuel efficiency and performance.
Common Maintenance Parts and Their Functions
Regular upkeep of a vehicle is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the essential components that require periodic attention can greatly enhance driving safety and comfort. This section outlines key elements commonly involved in vehicle maintenance, highlighting their roles and significance.
Engine Components
- Oil Filter: This part removes contaminants from engine oil, ensuring smooth operation and reducing wear on moving parts.
- Air Filter: It prevents dirt and debris from entering the engine, promoting better fuel efficiency and engine performance.
- Fuel Filter: This component filters impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine, ensuring optimal combustion and efficiency.
Brake System Elements
- Brake Pads: These create friction against the brake rotors, slowing down or stopping the vehicle when needed.
- Brake Rotors: They provide a surface for the brake pads to clamp down on, essential for effective braking.
- Brake Fluid: This hydraulic fluid transfers force from the brake pedal to the braking mechanism, enabling smooth operation.
By familiarizing oneself with these fundamental components and their functions, vehicle owners can ensure timely replacements and maintenance, leading to improved safety and performance.