Microscope Components Overview
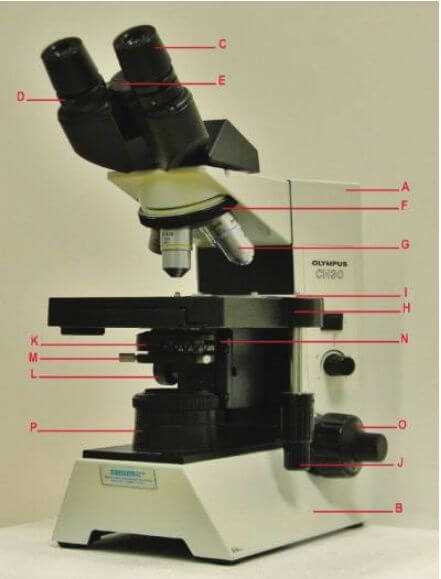
Optical devices, known for their precision and functionality, rely on various elements to function effectively. These elements play a crucial role in magnifying tiny objects, allowing for detailed observation. By understanding the main components, one can gain a clearer picture of how these instruments operate.
The design of these devices is built upon essential sections that work together to achieve the desired level of magnification. Each section serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall efficiency of the device. This cooperation between the parts ensures clarity and precision during observation.
Learning how each section functions not only improves the understanding of the instrument but also enhances the ability to use it more effectively. With a solid grasp of these components, users can maximize the capabilities of their optical tools for various applications.
Understanding the Basic Structure
The structure of this optical tool consists of multiple elements that work together to create an enhanced view of tiny objects. Each component has a specific role, contributing to the overall function of the device. By using light and glass elements strategically arranged, the tool is capable of significantly enlarging the details of the subject being studied.
Primary elements include lenses that focus the light, enhancing the view and making fine details visible. These components work in harmony with other adjustment mechanisms that allow for precise control over the focus and positioning of the sample.
Understanding how these elements interact is crucial for proper use, allowing the observer to achieve clear, sharp images.
This section gives an overview of the basic structure
Magnifying Components Overview

The visual enhancement system relies on several key elements that work together to provide a clear and detailed view of tiny objects. These components are specifically designed to enlarge and sharpen the image, allowing for detailed observation of even the smallest structures. By optimizing light and focus, these elements make it possible to explore intricate details that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye.
Primary Optical Lens
The main component responsible for magnification is the primary optical lens. This element ensures initial enlargement by bending light in a way that makes the observed object appear much larger than it actually is. It serves as the foundation for clarity in the visualization process.
Secondary Enhancing Lens
Another vital piece is the secondary enhancing lens, which provides additional magnification and fine-tunes the sharpness of the image. This helps in achieving a precise and detailed view, especially in high-precision observations.
Function of the Eyepiece
Significance of the Objective Lens
The objective lens plays a crucial role in visualizing detailed structures. Its ability to gather light efficiently and bring it into focus determines the clarity of the image produced. By precisely aligning with light, it enhances the sharpness of the image, enabling the observation of fine details that might otherwise go unnoticed. The design and quality of this lens directly influence the overall quality
Exploring the Focus Mechanism

The focus adjustment plays a crucial role in enhancing clarity by fine-tuning how
Purpose of the Stage Platform
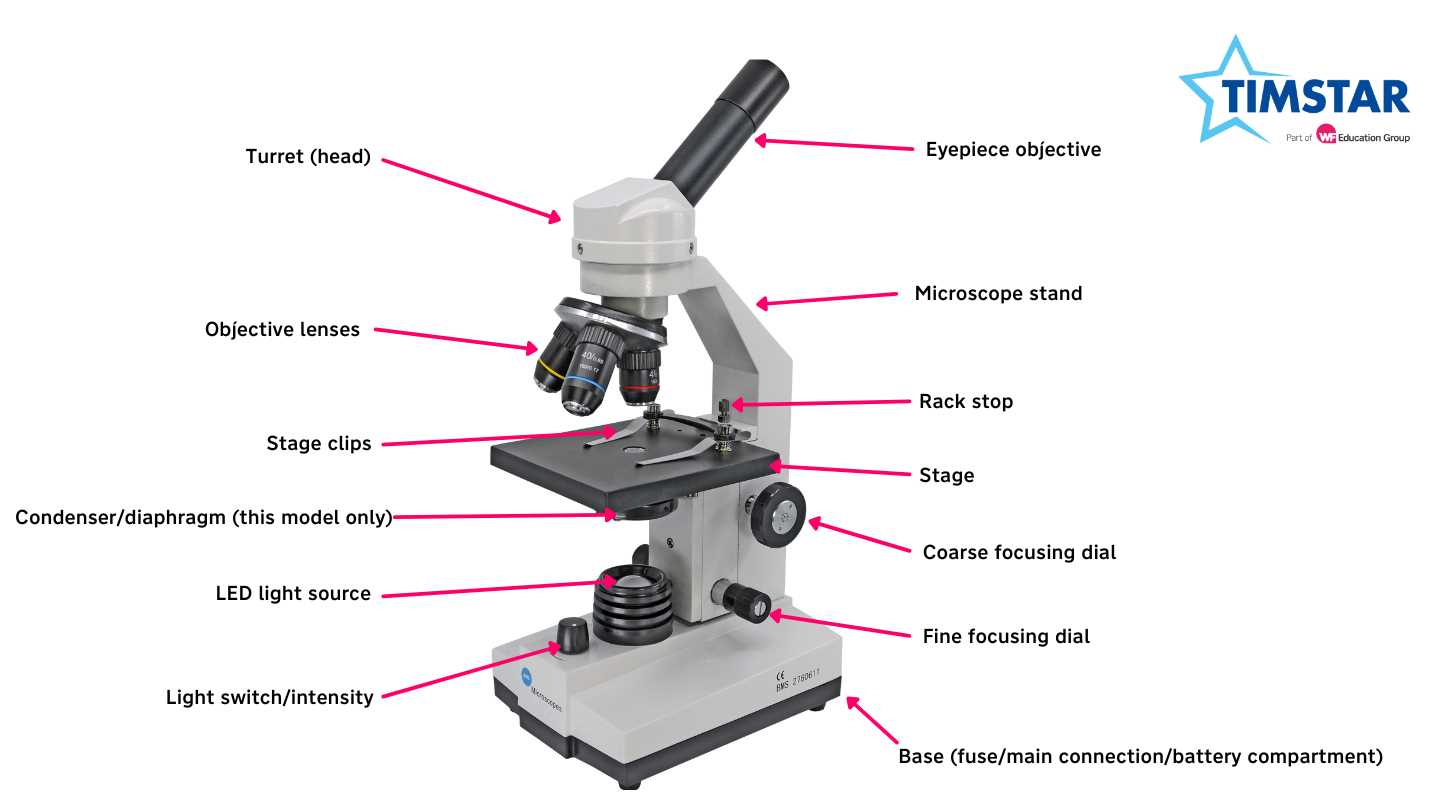

The stage platform serves as a fundamental component in the examination of specimens. It provides a stable and supportive area where samples can be positioned for observation under a lens. This crucial element enhances the overall viewing experience by allowing precise alignment and manipulation of the material being studied.
Primarily, the stage enables the user to easily access and adjust the location of the specimen, ensuring optimal focus and clarity. By utilizing mechanisms such as clips or holders, it secures the sample in place, preventing any unwanted movement during analysis. This stability is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable results.
In addition, the stage platform often includes features that facilitate light passage, contributing to better illumination of the specimen. The design of this area is vital for various techniques, allowing for both transparent and opaque samples to be effectively examined. Overall, the stage is integral to the functionality and efficiency of the entire observational process.
Role of the Illuminator
The illuminator serves a crucial function in enhancing visibility during observation. It provides the necessary light to illuminate the specimen, facilitating detailed examination and analysis. Without proper lighting, it would be challenging to discern intricate details, making this component vital for effective study.
Importance of Adequate Lighting
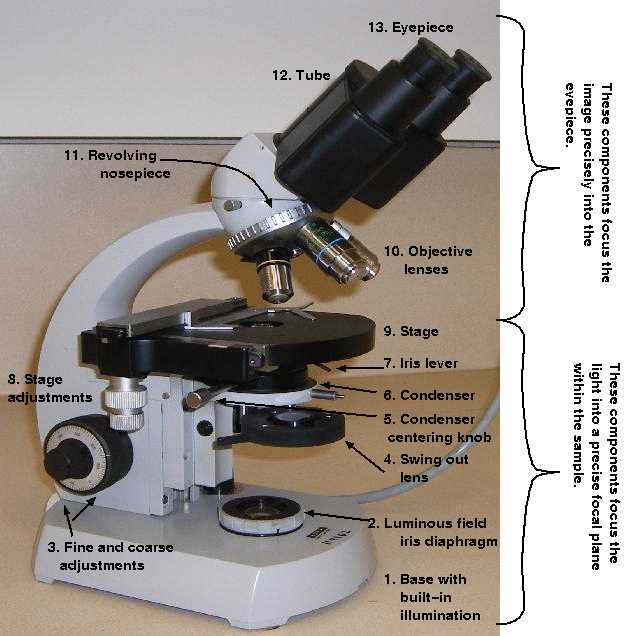
Optimal illumination levels are essential for achieving clarity and contrast in the viewed sample. Different lighting techniques can be employed to reveal various aspects of the specimen, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of its characteristics.
Types of Light Sources
Illuminators can utilize various light sources, including LEDs and halogen bulbs. Each type offers distinct advantages, influencing the quality of illumination and the overall viewing experience. Choosing the right source enhances the accuracy of observations and contributes to successful outcomes in research and educational settings.
Adjusting with the Diaphragm
The diaphragm plays a crucial role in controlling the amount of light that reaches the specimen. Proper adjustment is essential for enhancing visibility and contrast, which aids in clearer observation of details.
To effectively manage illumination, consider the following steps:
- Identify the appropriate setting based on the type of specimen being examined.
- Gradually adjust the diaphragm to find the optimal light level.
- Observe the changes in brightness and clarity as you modify the opening.
Additionally, different preparations may require specific adjustments:
- Transparent specimens: Use minimal light for better definition.
- Opaque samples: Increase the light intensity to reveal structure.
Regular practice with the diaphragm adjustment will lead to improved skills in specimen analysis and overall proficiency in the observational process.
Importance of the Coarse Adjustment
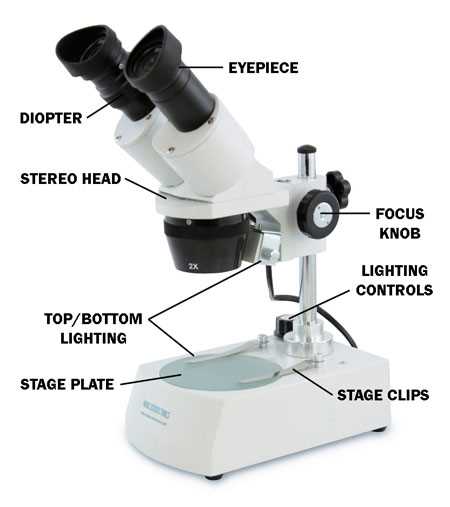

The coarse adjustment mechanism plays a crucial role in the functioning of optical instruments, allowing users to quickly focus on specimens. This essential feature enhances the efficiency of viewing and examining minute details by facilitating rapid changes in the distance between the optical components and the sample.
Enhancing Focus
This component is primarily responsible for bringing objects into general focus. By providing a broader range of movement, it enables the user to make significant adjustments, ensuring that the specimen is adequately positioned for detailed observation. This is particularly beneficial when switching between different magnification levels.
Facilitating Observation
Furthermore, the coarse adjustment allows for a smoother transition when initially locating an object. It aids in quickly finding the area of interest, making the overall examination process more efficient. This functionality is vital for both educational and research purposes, where precise viewing is necessary.
Detailed Look at Fine Adjustment
The fine adjustment mechanism plays a crucial role in achieving precise focus in optical instruments. This feature allows users to make subtle changes to the focus, enhancing the clarity and detail of the observed specimen. Understanding its function and operation is essential for optimal performance.
Importance of Precision
Precision in focus is vital for obtaining clear images of specimens. The fine adjustment tool enables users to fine-tune their observations, ensuring that even the most intricate details are visible. This is particularly important in fields such as biology and materials science, where accurate imaging is paramount.
How It Works
This mechanism typically consists of a knob that, when turned, moves the optical system very slightly. By allowing for minute adjustments, it complements the coarse adjustment, which makes larger changes. The smooth movement of the fine adjustment ensures that focus can be fine-tuned without overshooting the desired point.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Enables precise focusing of the optical system. |
| Mechanism | Operated by a knob for fine-tuning adjustments. |
| Applications | Essential for detailed observation in scientific research. |
Stability Provided by the Base
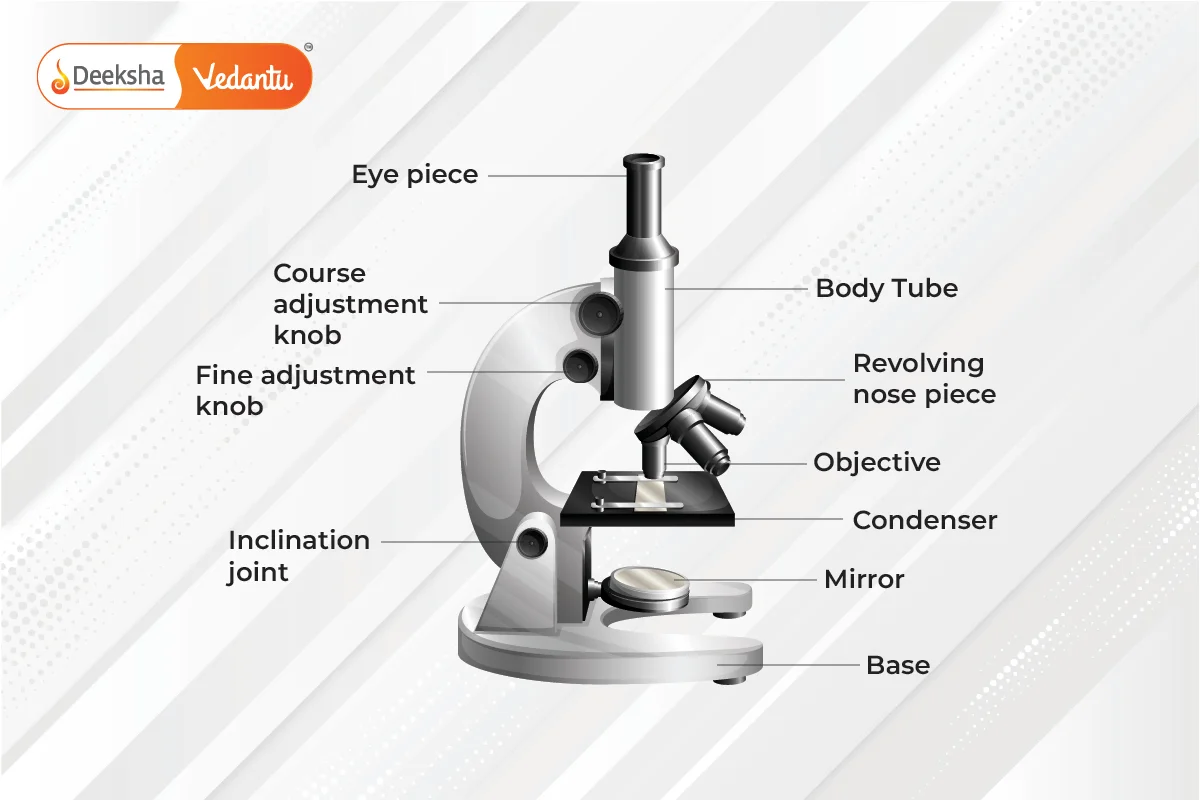
The foundation of any optical device plays a crucial role in ensuring proper functionality and reliable performance. A sturdy base is essential for maintaining balance and preventing unnecessary movements during observations. This stability allows users to focus on their studies without distractions, enabling clearer views and more accurate results.
Importance of a Firm Foundation
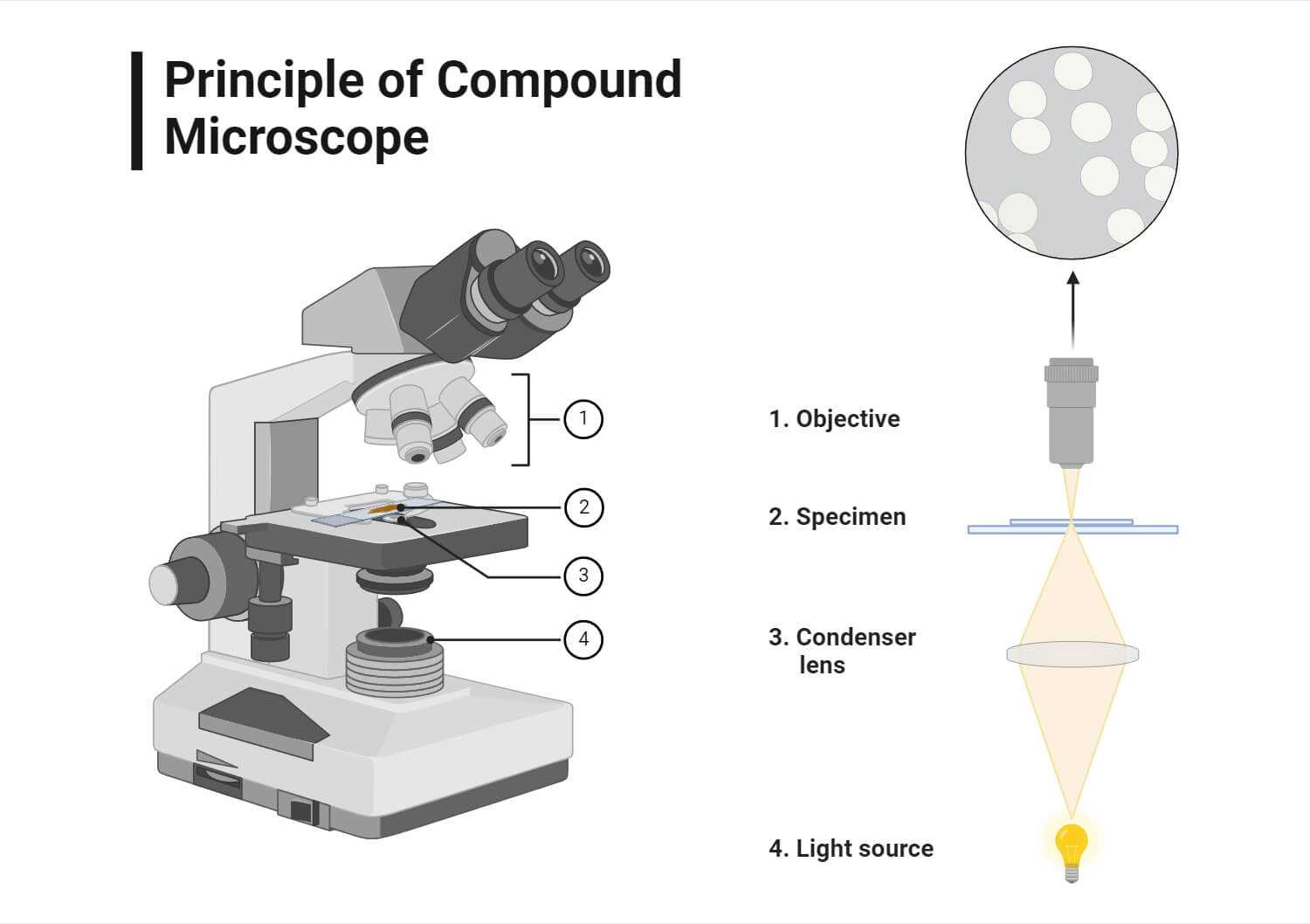
A well-constructed base enhances the overall usability of the instrument. It absorbs vibrations and minimizes the risk of tipping over, which is especially important in environments where precision is key. Moreover, a solid foundation supports the upper components, ensuring that they remain securely in place, even when adjustments are made.
Design Considerations for Stability
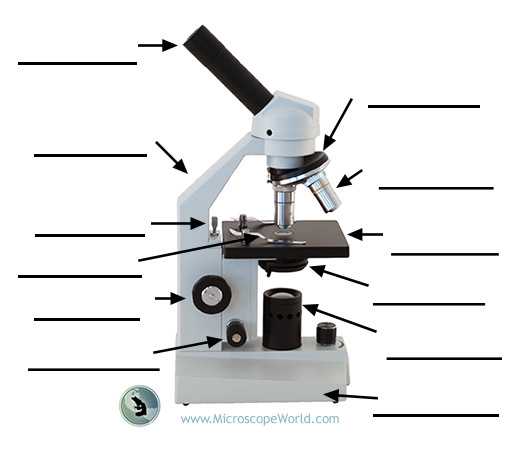
When designing the base, several factors must be taken into account. The weight distribution and materials used significantly impact stability. Heavy-duty materials can provide the necessary support, while a wider design can help lower the center of gravity, further enhancing stability. Additionally, non-slip surfaces can contribute to maintaining the device’s position, ensuring a safe and effective user experience.
Functions of the Arm Support
The arm support plays a crucial role in maintaining stability and facilitating movement in optical instruments. This component is essential for ensuring that the equipment remains securely positioned during use, allowing for precise adjustments and a clear view of the specimen being examined.
Stability and Support

One of the primary functions of the arm support is to provide a stable base for the device. This stability is vital for several reasons:
- Prevents unwanted movement while focusing on the specimen.
- Ensures consistent alignment with the optical path.
- Minimizes vibrations that could affect the clarity of the image.
Facilitating Adjustments
The arm support also allows for easier manipulation of the instrument. It enables users to:
- Adjust the height and angle for optimal viewing.
- Transition smoothly between different magnifications.
- Reposition the equipment without losing focus.