Understanding the Components of Window Diagrams
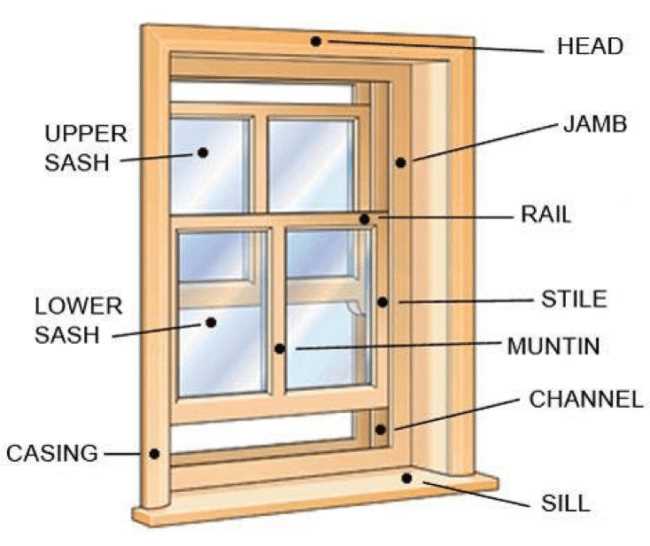
The construction of an opening serves as a critical element in architecture, providing both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Each segment plays a specific role in the overall efficiency and design, contributing to the integrity and performance of the structure.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various elements that make up an opening. From the frame that supports it to the moving sections that allow for ventilation and light, every component works in harmony to achieve the ultimate balance of style and practicality.
By examining these individual components, one gains insight into their interrelationships and the significance of their roles. This knowledge enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship involved and guides informed choices in both design and maintenance.
Understanding Window Components
Exploring the various elements that make up an opening in a building is essential for grasping how they function together. Each component plays a vital role in aesthetics, efficiency, and durability, contributing to the overall performance and appeal of the structure.
Main Elements
The primary components include frames, sashes, and glazing. The frame serves as the foundational structure, while the sash holds the glazing in place, ensuring stability and insulation. Together, these elements form a cohesive unit that supports both functionality and style.
Understanding the mechanisms behind features such as locks, weather stripping, and operating hardware is crucial. These elements enhance security, provide ease of use, and improve thermal efficiency, making the entire assembly more effective in protecting against external elements.
Types of Window Frames
When selecting a framework for openings in structures, it’s essential to understand the various options available. Each type offers unique advantages and caters to different aesthetic preferences, functionality, and energy efficiency. This choice significantly impacts not only the appearance of the architecture but also its performance and longevity.
Material Options
Frames can be crafted from a variety of materials, each contributing distinct characteristics. Wood is prized for its natural beauty and excellent insulation properties, though it requires regular maintenance to prevent deterioration. Vinyl is a popular choice due to its durability and low maintenance needs, offering good thermal performance and resistance to moisture. Aluminum frames, while less insulating, are favored for their strength and sleek appearance, making them ideal for modern designs.
Styles and Designs
The design of the frame can also vary, impacting both aesthetics and functionality. Single-hung and double-hung variants are common, with the latter allowing for greater ventilation. Casement styles, which open outward, provide unobstructed views and excellent airflow. Additionally, sliding frames are space-efficient, making them suitable for compact areas. Understanding these variations helps in making an informed choice that complements the overall structure.
Glass Options for Windows
Choosing the right transparent material can significantly influence energy efficiency, aesthetics, and durability in a building. Various types provide distinct advantages and can cater to specific needs.
Types of Transparent Materials
- Single Glazing
- Double Glazing
- Triple Glazing
Key Features to Consider
- Energy Efficiency
- Sound Insulation
- UV Protection
Each option offers unique benefits, allowing individuals to delve deeper into features that align with their ultimate goals.
Seals and Weatherstripping Explained
In any structure, maintaining a comfortable environment is crucial, and achieving this often hinges on the effectiveness of various components designed to prevent unwanted elements from entering. These elements play a vital role in enhancing energy efficiency and ensuring a pleasant indoor atmosphere.
Seals are integral in minimizing air leakage and protecting interiors from moisture and dust. They provide a barrier that helps to maintain consistent temperatures and reduce energy costs. Meanwhile, weatherstripping serves a similar purpose but is often applied to movable components, allowing for flexibility while still ensuring a snug fit when closed.
Both of these features come in various materials, such as rubber, foam, or felt, each offering distinct advantages based on the specific needs of a given structure. Proper installation and maintenance of these elements can significantly extend their lifespan and improve overall performance, making them essential for any homeowner or builder seeking to enhance comfort and efficiency.
Window Hardware and Mechanisms
This section explores the essential components that enable the functionality and efficiency of openings in structures. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and upgrades, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frames | Support structures that hold the glazing in place, contributing to stability and insulation. |
| Handles | Devices used for operation, allowing users to open, close, or lock the structure easily. |
| Hinges | Mechanisms that facilitate swinging actions, providing access and ventilation. |
| Locks | Security features that ensure the safety of the premises when closed. |
| Weatherstripping | Seals that prevent drafts and water infiltration, enhancing energy efficiency. |
Importance of Energy Efficiency
In today’s world, the emphasis on sustainable living has never been more critical. Maximizing the efficiency of our structures not only benefits the environment but also enhances comfort and reduces costs. Implementing measures that minimize energy consumption is essential for creating a healthier and more sustainable future.
Economic Benefits
Adopting energy-saving strategies can lead to significant financial savings. Lower utility bills result from improved insulation and advanced technologies, allowing homeowners and businesses to allocate funds elsewhere. Additionally, energy-efficient designs often increase property values, making them a wise investment for the long term.
Environmental Impact
Reducing energy use plays a vital role in decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. Efficient structures require less energy for heating and cooling, thereby reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. This shift not only helps combat climate change but also promotes a cleaner environment, fostering a more sustainable ecosystem for future generations.
Common Window Styles and Designs
This section explores various styles and designs that enhance both functionality and aesthetics in residential and commercial settings. Each option offers unique characteristics, appealing to different architectural tastes and practical needs.
Popular Styles
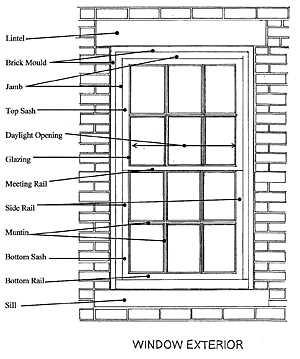
Among the most favored designs are traditional and modern styles, each presenting distinct features. Traditional designs often showcase intricate detailing and classic shapes, while modern aesthetics lean towards minimalism and clean lines.
Functional Variations
Different styles also serve specific purposes, such as maximizing natural light or improving ventilation. Understanding these variations can guide choices based on environmental needs and personal preferences.
| Style | Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Casement | Side-hinged, opens outward | Excellent ventilation |
| Sash | Sliding panels, vertical movement | Space-saving design |
| Bay | Projecting structure, multiple panels | Increased natural light |
| Fixed | Non-operable, stationary | Unobstructed views |
Maintenance Tips for Windows
Regular upkeep of your openings is essential for ensuring their longevity and functionality. By implementing a few simple practices, you can enhance the performance and appearance of your installations while preventing costly repairs in the future.
Clean Regularly: Dust and dirt can accumulate, obstructing light and diminishing the aesthetic appeal. Use a gentle cleaner and a soft cloth to wipe down surfaces frequently. Pay attention to corners and seals, where grime often gathers.
Inspect Seals: Over time, the protective barriers may wear down. Check for any gaps or cracks that could allow air or moisture to seep through. Promptly address any issues to maintain energy efficiency and prevent damage.
Lubricate Moving Components: Hinges and sliding mechanisms benefit from occasional lubrication. A silicone spray or a similar product can ensure smooth operation, reducing wear and tear on the mechanisms.
Check for Condensation: Moisture build-up between layers can indicate a failing seal. If you notice fogging or condensation, consider consulting a professional to evaluate the integrity of the installation.
Perform Seasonal Maintenance: Different weather conditions can affect functionality. Before winter, ensure that your openings are sealed properly to prevent drafts. In spring, check for any damage caused by snow or ice.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your fixtures and enjoy their benefits for years to come.
Installation Process of Windows
Properly setting up new fixtures is essential for ensuring energy efficiency and durability. The procedure involves several critical steps that contribute to a secure and effective installation, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality in living spaces.
Preparation and Measurements
Before beginning the installation, it’s vital to take accurate measurements of the opening. This includes checking for level and square dimensions. Preparation also entails selecting appropriate tools and materials, ensuring everything needed for the task is readily available.
Fitting and Sealing
Once the site is prepared, the next phase involves fitting the new structure into place. Careful attention to alignment and level is necessary during this stage. After securing it, sealing gaps with insulation is crucial to prevent drafts and improve thermal performance.
Window Safety Features Overview

Ensuring the security and protection of any structure involves various essential elements designed to enhance safety. Among these, specific mechanisms play a crucial role in preventing accidents and improving overall safety for occupants. Understanding these components can significantly impact the safety measures adopted in residential and commercial buildings.
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Secure Locks | High-quality locking systems that prevent unauthorized access. | Enhanced security and peace of mind. |
| Safety Glass | Tempered or laminated glass that minimizes the risk of breakage. | Reduces injury from shards and increases durability. |
| Child Safety Locks | Mechanisms designed to prevent accidental opening by young children. | Protects children from falls and potential accidents. |
| Shatter-Resistant Film | Thin film applied to glazing to hold shattered pieces in place. | Improves safety during impacts and adds privacy. |
| Emergency Release | Features that allow quick exit in case of emergencies. | Facilitates safe evacuation during critical situations. |
Implementing these features is vital for creating a secure environment, ensuring that both safety and comfort are prioritized. By considering these aspects, individuals can make informed decisions regarding protection measures in their spaces.
Trends in Modern Window Design
The contemporary landscape of openings and their frames showcases a shift towards functionality and aesthetics, harmonizing with evolving architectural styles. Designers are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency, versatility, and innovative materials, reflecting a broader commitment to sustainability and user experience.
Key Features
Recent developments emphasize large, expansive views while maintaining durability and insulation. The integration of smart technology is also becoming commonplace, enhancing convenience and security in residential and commercial spaces.
Material Innovations
Modern craftsmanship often explores diverse materials such as fiberglass, aluminum, and advanced composites, allowing for greater customization and longevity. This evolution enables a seamless blend of indoor and outdoor environments, promoting natural light and airflow.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Sustainability | Focus on energy-efficient designs and eco-friendly materials. |
| Smart Technology | Integration of automated features for enhanced usability. |
| Minimalism | Streamlined aesthetics that prioritize simplicity and function. |
| Versatile Designs | Customizable shapes and sizes to fit diverse architectural needs. |