Exploring the Anatomy of Honey Bee Mouth Parts

In the intricate world of insects, the mechanisms utilized for nourishment reveal fascinating adaptations. The structure and function of these specialized organs play a crucial role in how these creatures interact with their environment and acquire sustenance. By examining the anatomical features involved in feeding, one gains insight into the diverse strategies that different species employ to thrive.
Exploring the anatomy behind these feeding mechanisms unveils a complex arrangement of tools designed for specific purposes. Each element serves a unique function, whether for extracting liquids, grasping solid materials, or facilitating digestion. The diversity in these structures is a testament to the evolutionary pressures faced by various insect groups.
Furthermore, the efficiency of these adaptations can significantly influence ecological interactions. Understanding how these organisms gather nutrients not only sheds light on their survival but also highlights their role in the broader ecosystem. Through detailed examination, one can appreciate the intricate relationship between structure and function in the natural world.
Understanding Honey Bee Anatomy
Exploring the structure of these fascinating insects reveals a complex system that supports their various functions and behaviors. Each component plays a crucial role in their survival, communication, and foraging activities. Gaining insight into their morphology enhances our appreciation of their ecological significance.
Key Features of Insect Anatomy
Insects possess several distinctive features that differentiate them from other organisms. The primary elements include:
- Head: Houses sensory organs and mouth structures for feeding.
- Thorax: Supports wings and legs, enabling movement.
- Abdomen: Contains vital organs for digestion and reproduction.
Feeding Mechanisms
The feeding mechanism is a sophisticated system designed for efficiency. The main functions are:
- Collecting nectar and pollen.
- Utilizing specialized structures for manipulation of food sources.
- Transporting food back to the colony for nourishment.
Understanding these elements is essential for studying their behavior and the role they play in the ecosystem.
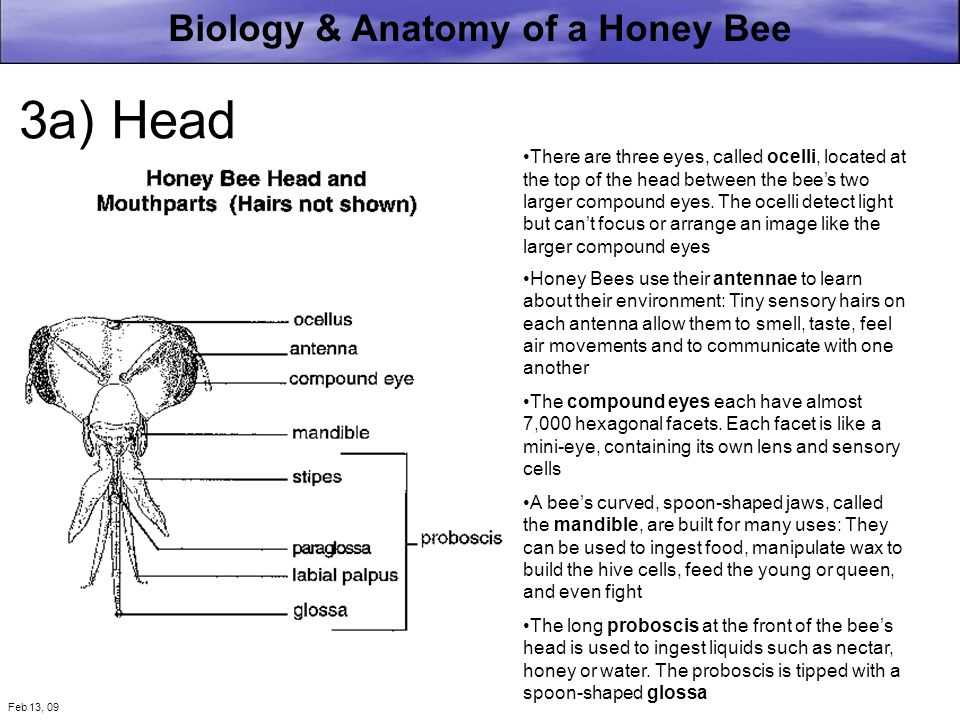
Importance of Mouth Parts in Bees
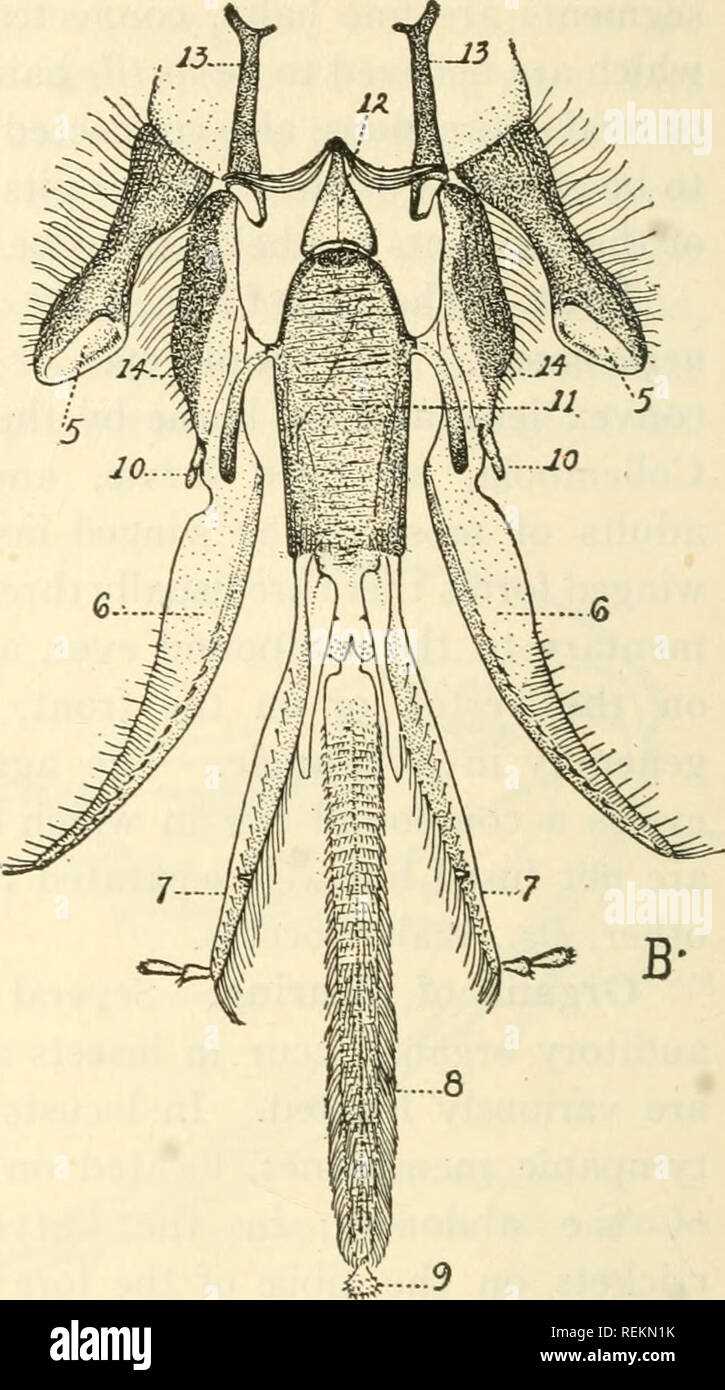
The specialized feeding mechanisms of these insects play a crucial role in their survival and ecological function. These adaptations enable them to efficiently access a variety of food sources, facilitating not only their nourishment but also contributing to pollination and ecosystem health.
Feeding Adaptations
The anatomy of these structures is uniquely suited for extracting nectar and pollen from flowers. The elongated and flexible components allow for precision and ease when accessing food, which enhances their foraging efficiency. This specialization is essential for their energy requirements, particularly during the active foraging season.
Pollination Role
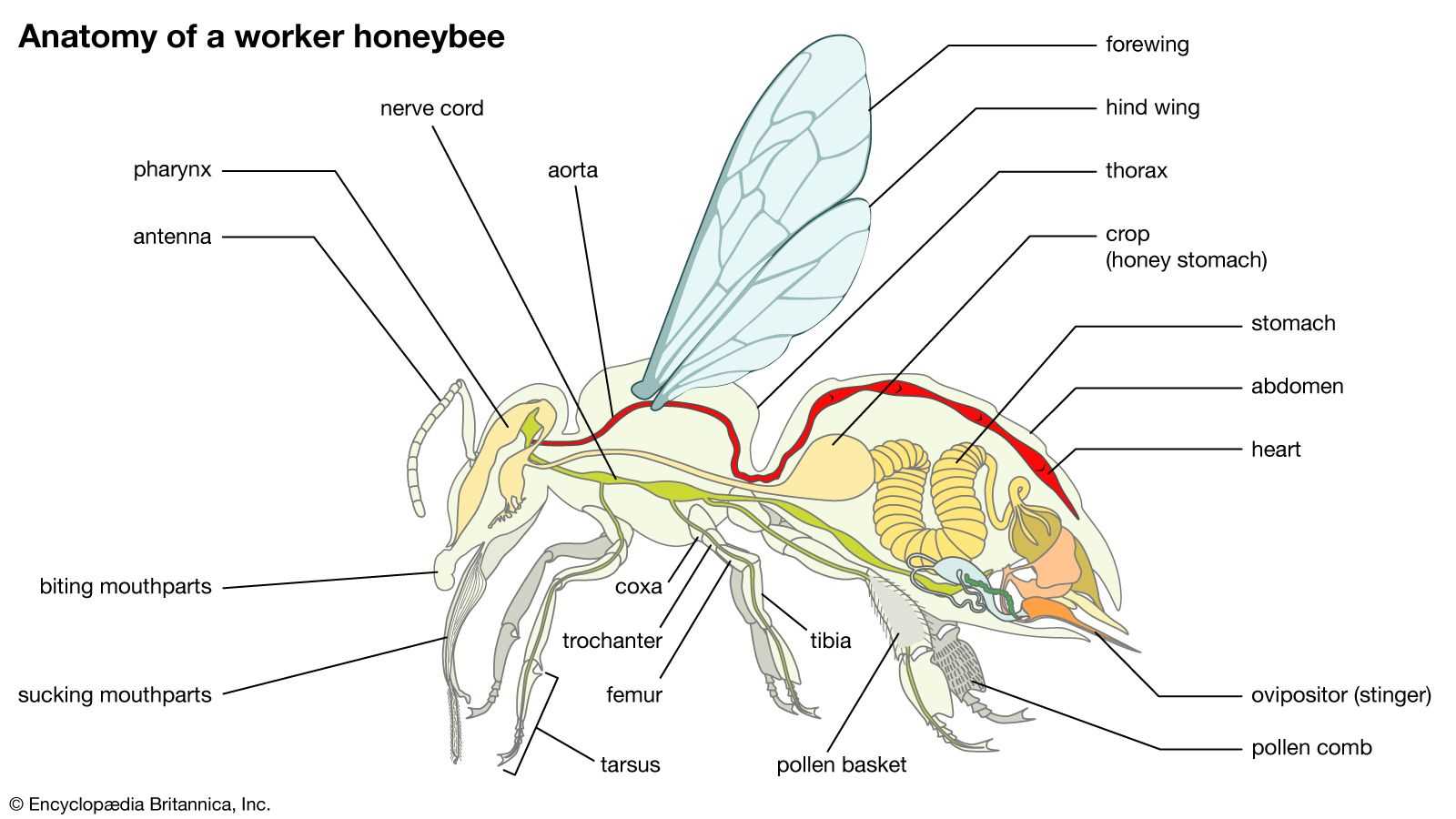
Beyond personal sustenance, these mechanisms significantly impact the pollination process. As these insects move from flower to flower, they inadvertently transfer pollen, promoting plant reproduction. This interaction is vital for the growth of many crops and wild plants, making their role in the environment indispensable.
In summary, the intricate design of these feeding mechanisms not only supports individual nutrition but also underlines the broader ecological significance of these insects as pollinators.
Types of Mouth Parts in Honey Bees
The various structures found in the feeding apparatus of these insects are specifically adapted to meet their diverse dietary needs. Each type serves distinct functions that facilitate the collection and processing of food, highlighting the remarkable evolution of these creatures.
Mandibles
These robust, jaw-like structures are essential for cutting and manipulating solid substances. They enable the collection of pollen and the construction of wax cells, demonstrating versatility in feeding and building tasks.
Proboscis
This elongated, tube-like organ is crucial for sipping liquids. It allows for efficient nectar extraction from flowers, showcasing the specialization of these insects in liquid feeding behaviors.
Functions of Bee Mandibles Explained
The mandibles of these industrious insects play a crucial role in their daily activities, enabling them to interact with their environment effectively. These specialized structures are not merely for feeding; they are versatile tools essential for a variety of tasks, from construction to grooming.
Feeding and Processing
One of the primary functions of the mandibles is to aid in the manipulation of solid food. They are adept at cutting and grinding materials, allowing the creatures to access nutrients from pollen and other sources. This processing capability is vital for their sustenance and overall health.
Construction and Maintenance
In addition to feeding, the mandibles serve a significant purpose in the construction of nests. These insects utilize their robust jaws to gather and shape materials such as wax and plant fibers, crafting intricate structures for habitation. Furthermore, they maintain their environment by cleaning and repairing their living spaces, showcasing the multifunctional nature of these remarkable appendages.
How Bees Collect Nectar Efficiently
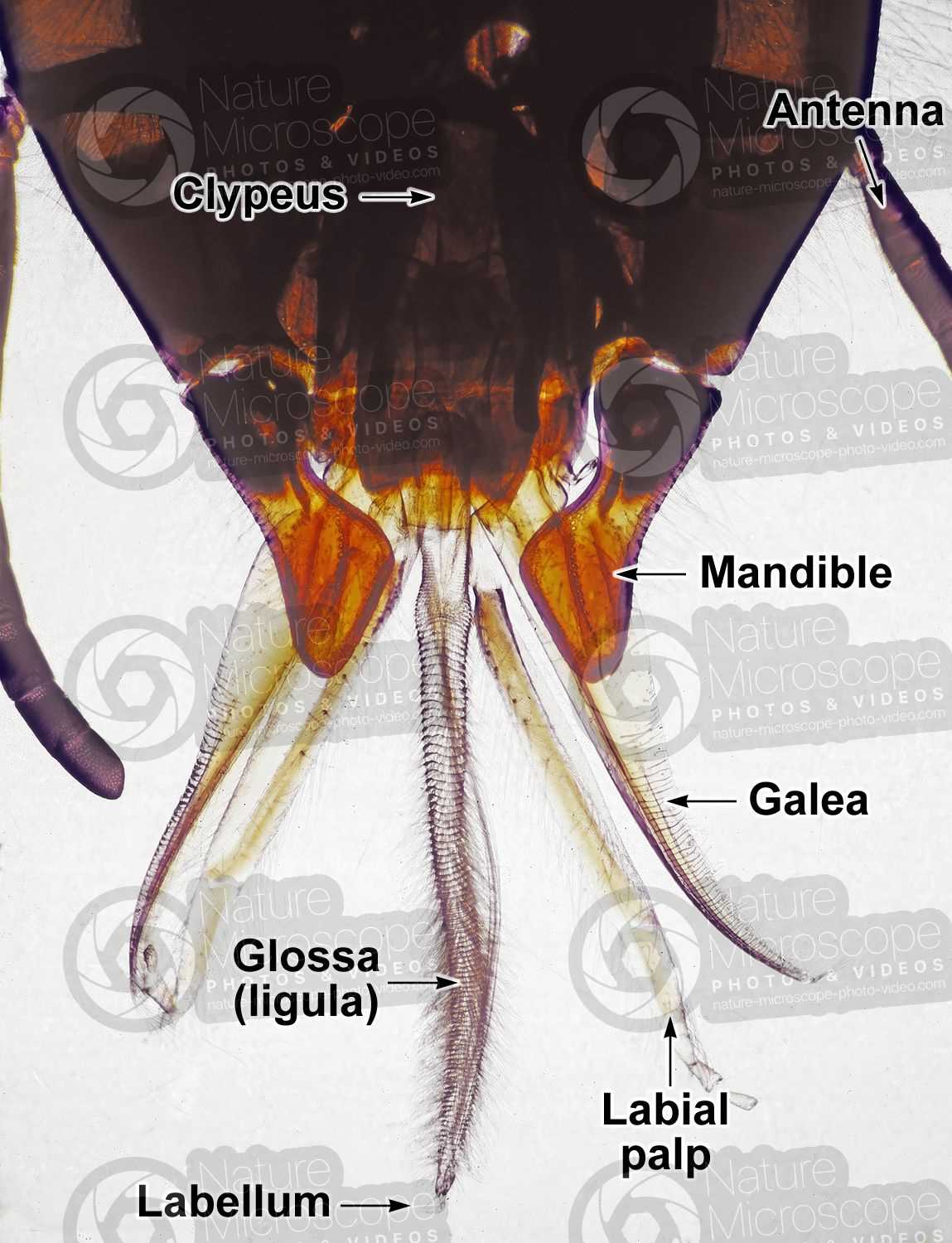
The process of gathering liquid sustenance is a remarkable feat of nature, showcasing intricate adaptations that enhance efficiency and productivity. In this section, we will explore the various techniques employed by these industrious insects to maximize their foraging efforts.
To effectively gather this vital resource, the insects utilize several specialized tools and methods:
- Proboscis Structure: Their elongated feeding structure allows them to reach deep into flowers, extracting liquid with precision.
- Pollination: While foraging, they inadvertently transfer pollen, aiding in plant reproduction and ensuring a consistent food supply.
- Social Cooperation: Working in groups, they communicate the location of rich nectar sources, increasing overall efficiency.
Several factors influence their ability to collect this nourishment:
- Flower Variety: Different species offer varying levels of accessibility and volume, influencing foraging patterns.
- Weather Conditions: Optimal temperatures and humidity levels affect the availability of nectar and foraging behavior.
- Foraging Duration: The time spent at each location is carefully calculated to maximize collection while minimizing energy expenditure.
Through these advanced techniques and considerations, these insects exemplify efficiency in their quest for sustenance, showcasing the complexity of their foraging behavior.
Adaptations for Pollen Collection
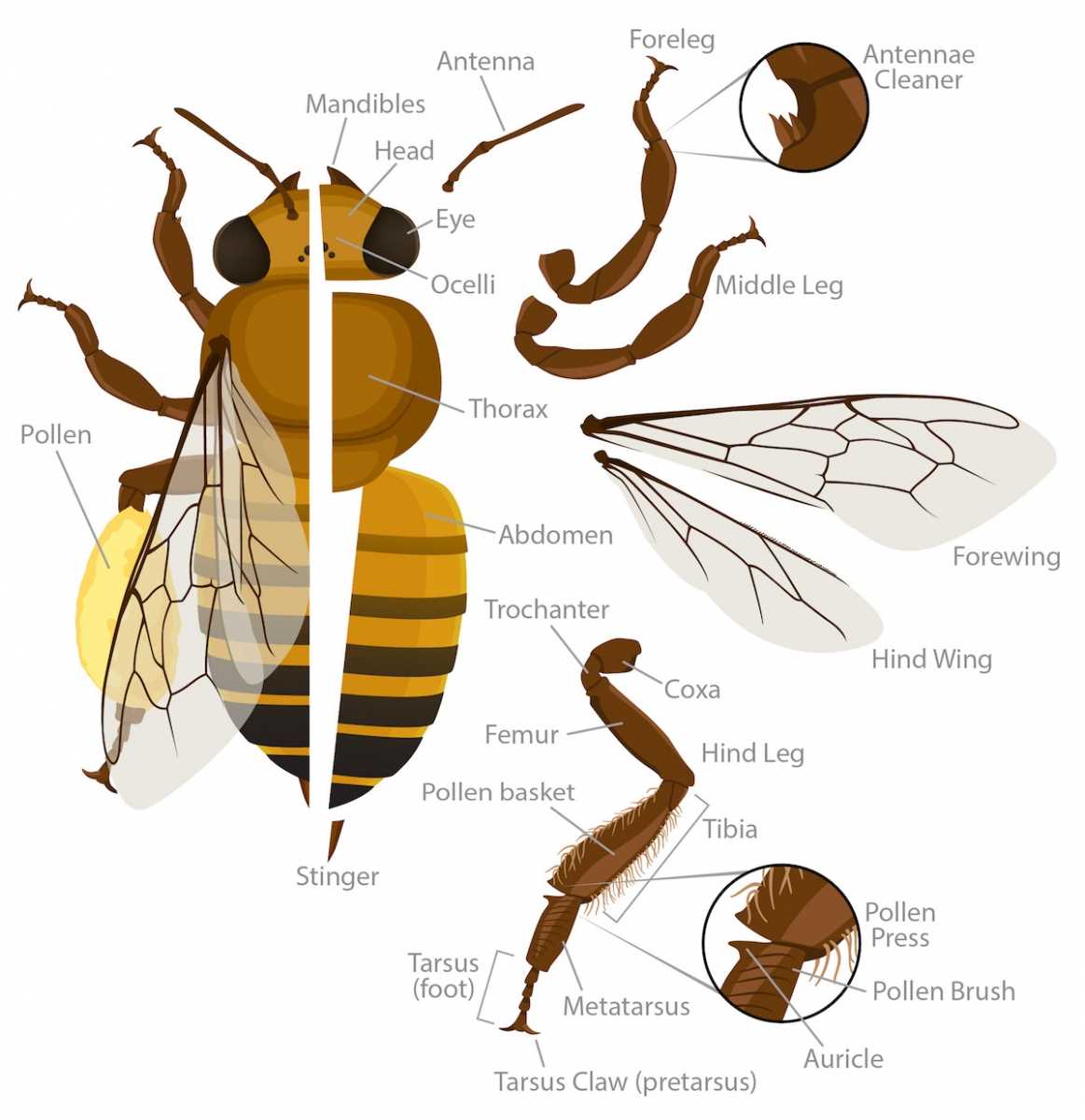
The remarkable adaptations seen in certain insects facilitate efficient pollen gathering, ensuring effective pollination and contributing to the ecosystem’s health. These modifications enhance their ability to collect and transport pollen grains, vital for the reproductive success of many flowering plants.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Specialized Hairs | Fine, branched hairs on the body trap pollen grains, making collection more efficient. |
| Proboscis Structure | A long, flexible tongue allows access to nectar deep within flowers while collecting pollen simultaneously. |
| Pollen Basket | Indented areas on the legs store gathered pollen securely during flight. |
| Body Size and Shape | Compact body design aids maneuverability, enabling easy navigation among flowers. |
These characteristics not only promote efficient foraging but also strengthen the symbiotic relationship between flora and fauna, highlighting the importance of these adaptations in the natural world.
The Role of the Proboscis
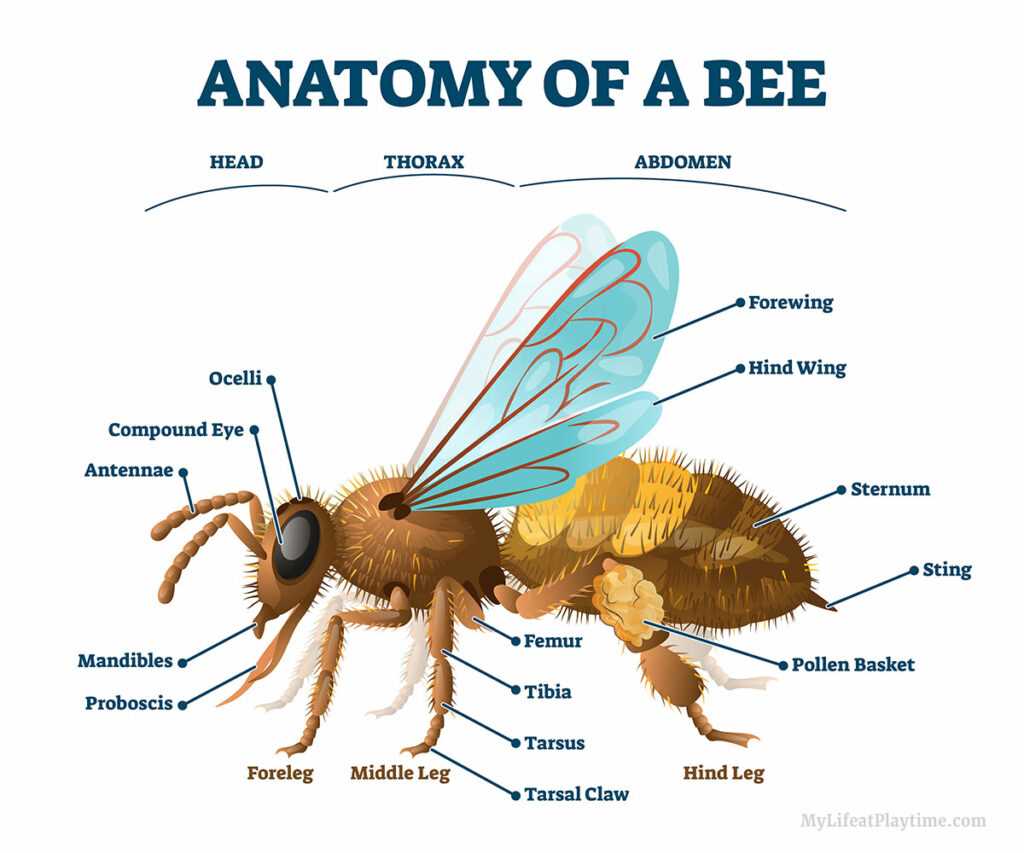
The elongated feeding organ serves as a vital tool for the insect, enabling it to access essential nutrients from various floral sources. This specialized structure plays a crucial role in the survival and efficiency of the creature, allowing it to thrive in diverse environments.
Structure and Function
With its unique anatomy, the feeding organ is capable of extending and retracting, facilitating the extraction of liquid sustenance. The flexibility and precision of this mechanism are key to optimizing foraging strategies.
Importance in Ecosystem
The effectiveness of this organ contributes significantly to pollination processes, supporting plant reproduction and biodiversity. By aiding in the transfer of pollen, it plays an ultimate role in maintaining ecological balance.
Comparing Bee Mouth Parts to Other Insects
This section explores the differences and similarities in the feeding mechanisms of various insects, focusing on how these adaptations suit their lifestyles and dietary needs.
Insects exhibit a remarkable diversity in their feeding structures, reflecting their ecological niches. While some are equipped for piercing, others are designed for sucking or chewing. Here’s a closer look:
- Chewing Insects:
- Grasshoppers have strong mandibles for grinding plant material.
- Beetles possess robust jaws that can crush hard substances.
- Sucking Insects:
- Butterflies and moths utilize long proboscises to extract nectar.
- Flies possess sponging mouthparts that allow them to lap up liquids.
- Piercing Insects:
- mosquitoes have elongated stylets for drawing blood.
- True bugs use specialized beaks to penetrate plant tissues and consume sap.
The unique structure of each insect’s feeding apparatus reflects its dietary habits and survival strategies. For example, the structures used by certain pollinators enable them to access nectar efficiently, while others have adapted to exploit different food sources.
Understanding these variations helps illustrate the evolutionary paths taken by insects in response to their environments and food availability.
Impact of Mouth Structure on Feeding

The anatomy of an insect’s feeding apparatus significantly influences its dietary habits and efficiency in resource extraction. Variations in structure allow for specialized functions, catering to diverse food sources and environmental niches.
Adaptations in feeding mechanisms enable insects to exploit various nutrients effectively. For instance, elongated structures can facilitate nectar extraction, while robust forms may be suited for processing solid materials. Such differences highlight the evolutionary significance of feeding morphology.
Moreover, the efficiency of feeding not only impacts individual survival but also plays a crucial role in ecological interactions, such as pollination and decomposition. Understanding these anatomical adaptations provides insight into the broader implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
Research on Bee Feeding Behavior
This section explores the fascinating interactions and mechanisms involved in the foraging habits of these essential pollinators. Understanding their feeding strategies is crucial for appreciating their role in ecosystems and agriculture.
Recent studies highlight several key aspects of their feeding behavior:
- Foraging Techniques: Various methods are employed to locate and extract nutrients from floral resources.
- Preference Factors: Color, scent, and reward availability influence the selection of flowers.
- Social Learning: Observational learning plays a significant role in optimizing foraging efficiency.
- Environmental Impact: Factors such as climate and habitat affect feeding patterns and resource availability.
Future research aims to delve deeper into these dynamics, providing insights that could inform conservation efforts and agricultural practices.
Conservation and Bee Anatomy Knowledge
Understanding the structure and function of certain insects is essential for fostering conservation efforts. By recognizing the intricacies of their anatomy, we can better appreciate their roles in ecosystems and the threats they face. This knowledge not only enhances our awareness but also informs strategies to protect these vital organisms.
Conservation initiatives benefit significantly from insights into insect anatomy, which can be summarized in the following points:
- Ecological Importance: These insects play crucial roles in pollination, contributing to biodiversity and food production.
- Behavioral Insights: Understanding how they interact with their environment aids in developing effective conservation strategies.
- Habitat Requirements: Knowledge of their structural features can inform habitat restoration projects.
In addition to the ecological benefits, awareness of anatomical structures helps in identifying specific challenges:
- Pesticide Impact: Certain chemicals can disrupt their functions, leading to population declines.
- Climate Change: Altered habitats affect their survival and reproductive rates.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Decreasing plant variety limits food sources and nesting sites.
In conclusion, merging anatomical knowledge with conservation efforts can enhance our strategies to protect these essential organisms, ensuring the stability of ecosystems and agricultural systems alike.