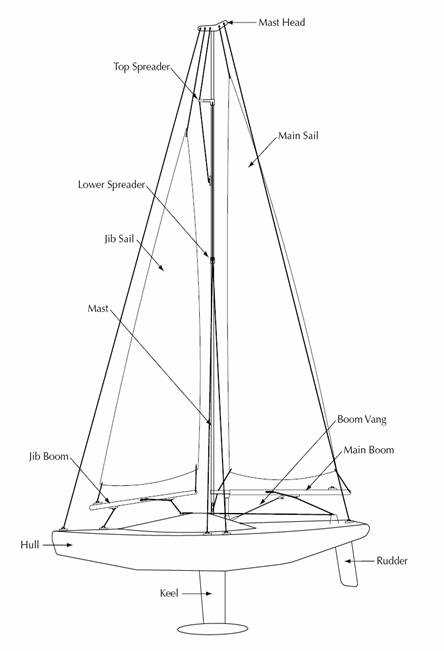
Understanding Sailboat Parts with a Comprehensive Diagram

Every seafaring craft consists of a multitude of essential elements that contribute to its functionality and performance. These individual segments, each designed with specific purposes in mind, work in harmony to ensure smooth navigation and safety on the water. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of these components is crucial for anyone looking to appreciate the intricacies of maritime travel.
From the structure that provides stability to the mechanisms that facilitate movement, each element plays a pivotal role. Recognizing how these various pieces interact can enhance one’s sailing experience, whether you are a seasoned navigator or a novice enthusiast. Moreover, understanding these features allows for better maintenance and optimal usage of the craft.
In this exploration, we will delve into the various components that make up these waterborne vessels, highlighting their functions and importance. By familiarizing yourself with the terminology and layout, you will be better equipped to engage with both the practical and theoretical aspects of sailing.
Understanding Sailboat Components
Grasping the fundamental elements of a sailing vessel is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the waters effectively. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and safety on the open sea. By familiarizing oneself with these key elements, sailors can enhance their skills and confidence while managing their craft.
Key Elements of the Vessel
At the heart of every watercraft are the essential structures that facilitate movement and stability. The hull serves as the primary body, providing buoyancy and shape. The rigging, consisting of ropes and cables, supports the sails and controls their position relative to the wind. Understanding the interplay between these components allows for better handling and maneuverability.
Functional Components
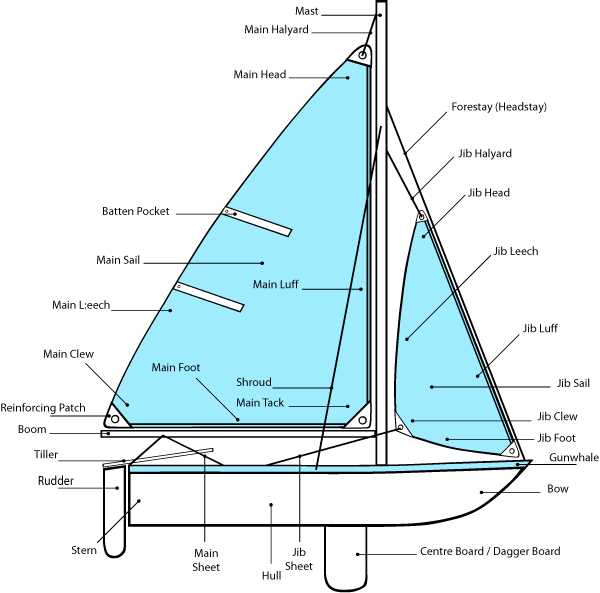
Among the various systems, the steering mechanism and sail setup are particularly important. The rudder enables direction control, while the sails capture wind energy to propel the vessel forward. Mastery of these functionalities can significantly impact a sailor’s experience and effectiveness on the water. Familiarization with each aspect leads to a deeper appreciation of maritime navigation.
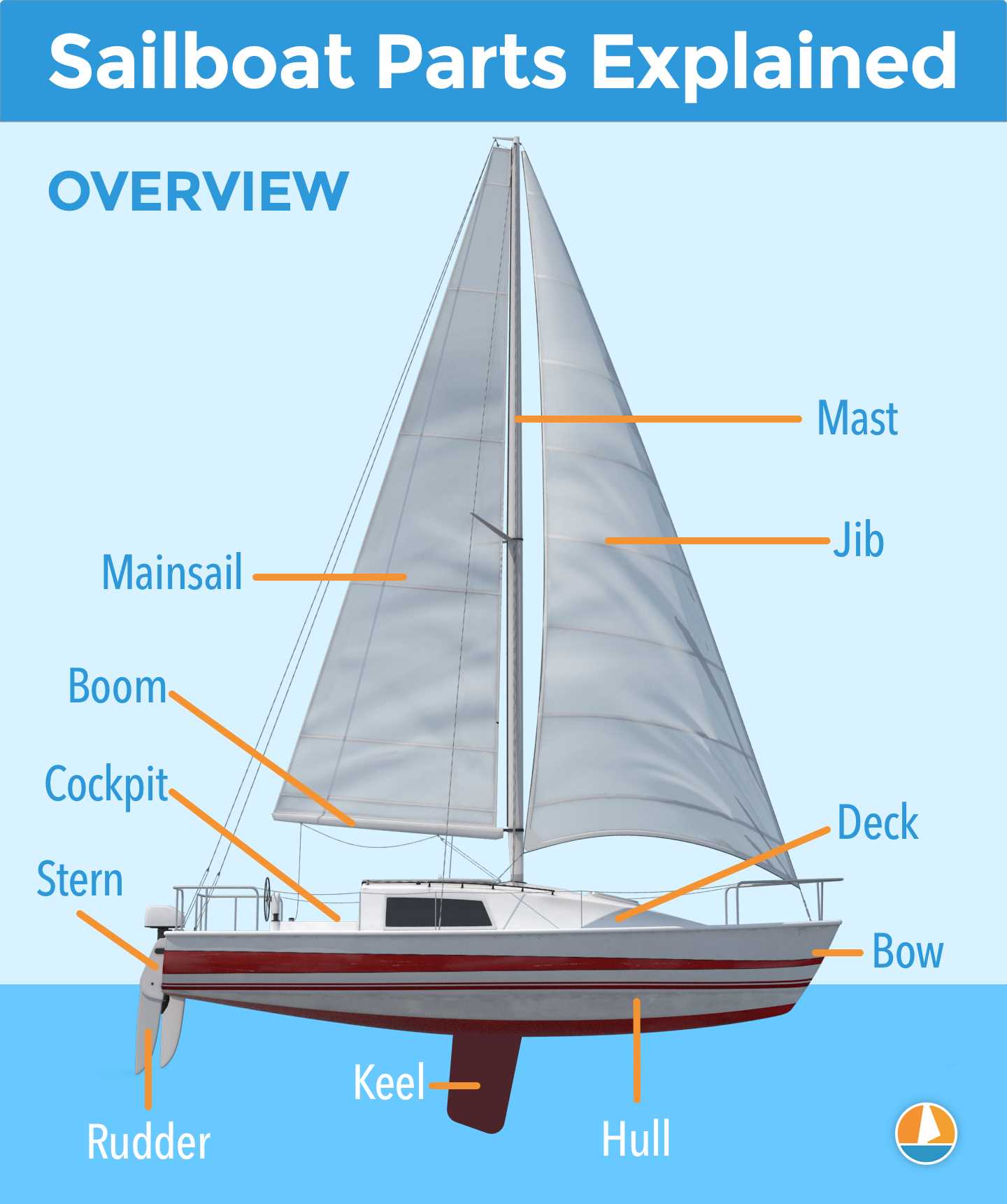
Key Parts of a Sailboat
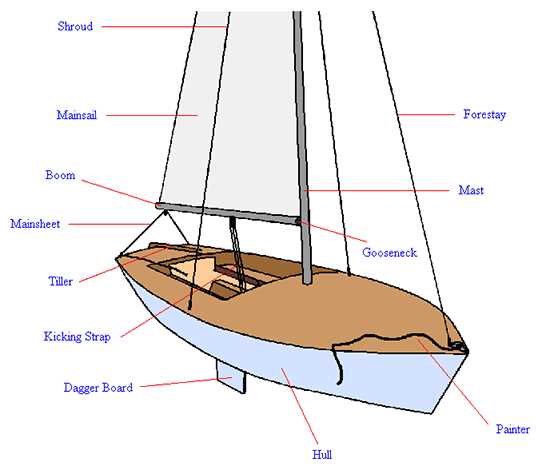
Understanding the essential components of a vessel designed for wind propulsion is crucial for anyone interested in navigating the open waters. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring stability, maneuverability, and overall performance while at sea.
Hull serves as the main body of the vessel, providing buoyancy and strength. Its shape affects how the craft moves through water and influences speed and agility.
Mast is a tall structure that supports the sail, allowing it to catch the wind efficiently. The height and positioning of this feature are vital for maximizing wind power.
Sails are large fabric surfaces that harness wind energy, propelling the craft forward. Different shapes and sizes cater to various sailing conditions, contributing to effective navigation.
Rudder is a crucial element for steering, allowing the operator to control the direction of the vessel. Its placement at the stern provides stability and responsiveness.
Keel is an underwater fin that enhances stability and prevents capsizing. This feature also plays a role in counteracting the sideways force of the wind on the sails.
Deck is the flat surface on top of the hull, serving as the working area for crew members. It houses various equipment and provides access to other vital elements.
Lines are ropes used to control the sails and rigging. Proper management of these lines is essential for adjusting the sails to changing wind conditions.
Familiarity with these fundamental components enables enthusiasts to appreciate the intricacies of sailing and enhances their experience on the water.
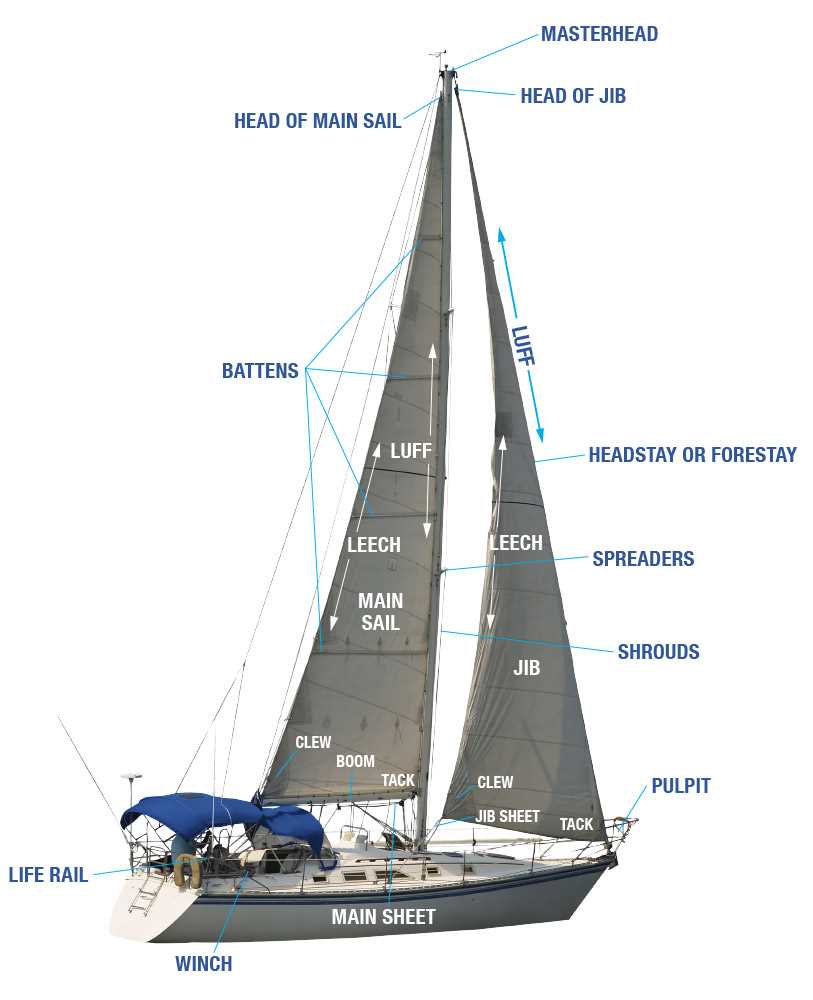
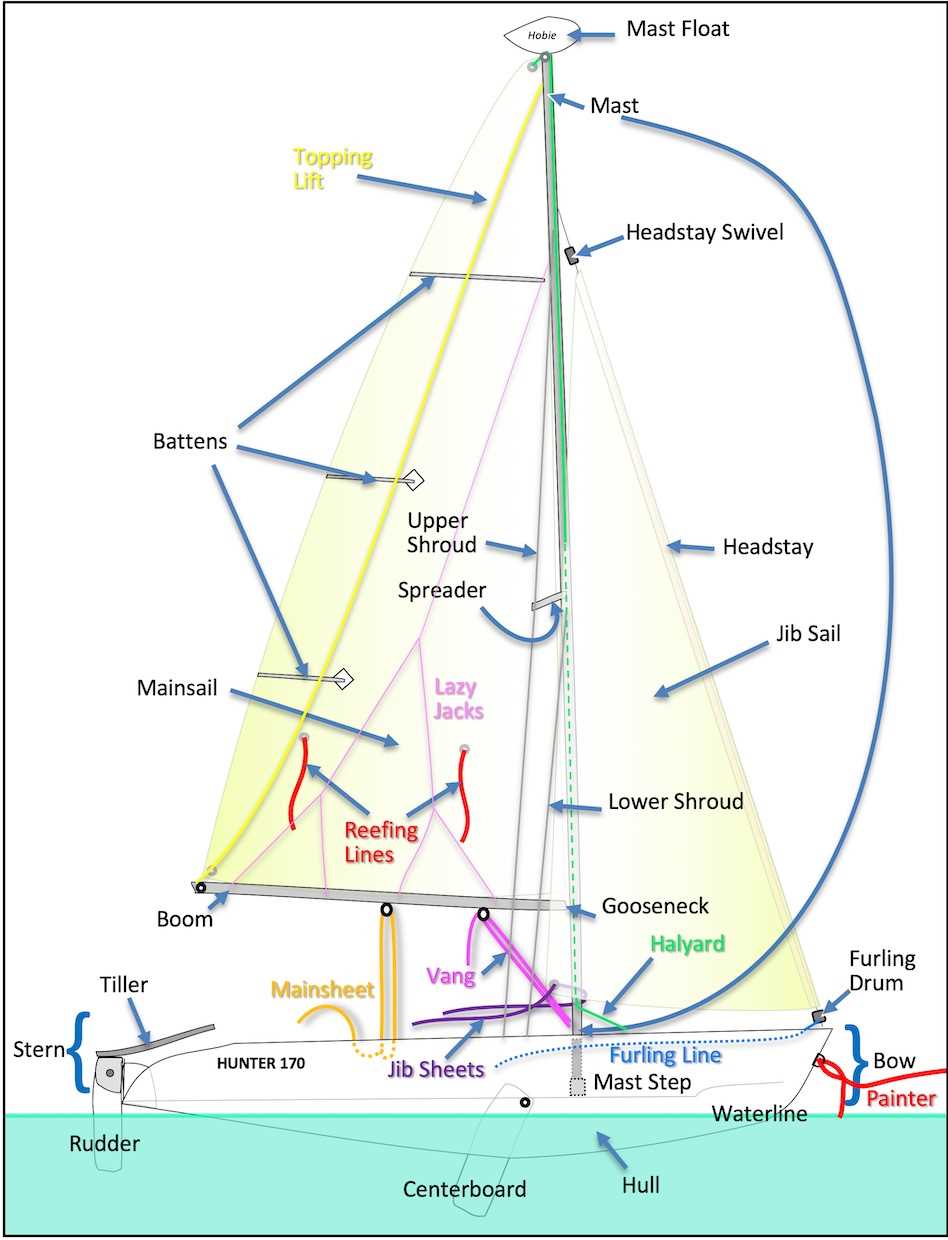
Function of the Sail Rigging
The rigging serves as the essential framework that supports the sails, enabling vessels to harness the power of the wind effectively. Its components work in harmony to adjust the shape and position of the fabric, optimizing performance under varying conditions. By maintaining tension and providing stability, the rigging ensures that the sails operate efficiently and safely.
This intricate system comprises various lines and fittings, each designed to fulfill specific roles. For instance, some lines allow for the adjustment of sail angle, while others contribute to the overall balance and control of the vessel. Proper rigging is crucial for achieving the desired speed and maneuverability, making it a vital aspect of seamanship.
Importance of the Hull Structure
The integrity and design of a vessel’s framework play a critical role in its overall performance and safety. This component serves as the primary line of defense against water intrusion and external forces, impacting stability, buoyancy, and navigation efficiency.
Key Functions of the Hull
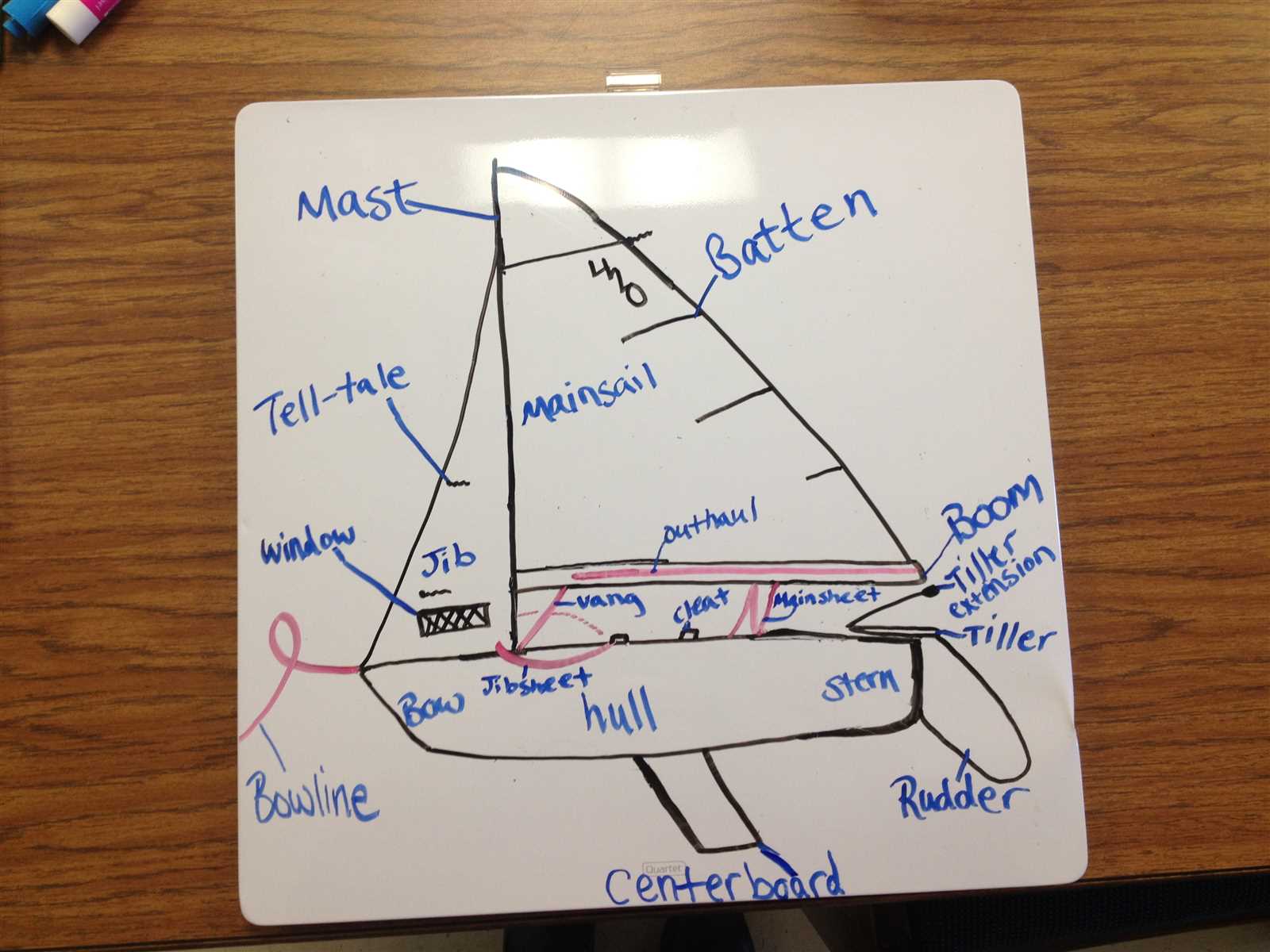
- Buoyancy: A well-constructed structure ensures that the craft remains afloat, distributing weight evenly.
- Stability: The shape and materials used affect how the vessel responds to waves and wind, ensuring a balanced ride.
- Durability: High-quality materials enhance resistance to wear and tear from environmental factors.
- Hydrodynamics: A streamlined design minimizes resistance, promoting speed and fuel efficiency.
Considerations for Design
- Material Selection: Different materials offer varying benefits in weight, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
- Shape Optimization: The hull’s form affects performance; optimizing for specific activities can enhance effectiveness.
- Maintenance: Regular inspections and repairs are essential to preserve structural integrity over time.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of this vital component is essential for anyone involved in marine activities. Its influence on performance and safety cannot be overstated, making careful consideration in design and maintenance imperative.
Types of Sail Configurations
The arrangement of fabric used for harnessing wind power is crucial for optimal performance and handling of vessels. Various setups offer unique advantages, allowing for versatility in different wind conditions and sailing styles. Understanding these configurations helps sailors choose the most effective design for their specific needs.
Main Configurations

- Gaff Rig: Characterized by a triangular sail supported by a spar angled upward, providing excellent control and shape.
- Sloop: A single-masted setup featuring a fore-and-aft sail configuration, known for its simplicity and efficiency.
- Catamaran: This design utilizes two hulls with sails that maximize stability and speed, often seen in recreational crafts.
- Yawl: Similar to a sloop but with an additional smaller mast located behind the main one, enhancing balance and maneuverability.
Advanced Configurations
- Knockabout: A straightforward design without a headsail, ideal for ease of handling and training.
- Barquentine: Features square sails on the foremast and fore-and-aft sails on the main and mizzen masts, providing versatility in various wind angles.
- Square Rig: Employs large sails mounted on horizontal spars, typically used on larger vessels for windward performance.
Each configuration presents distinct characteristics that cater to different sailing requirements and preferences. By selecting the appropriate setup, sailors can enhance their experience and efficiency on the water.
Role of the Keel in Stability

The keel serves as a critical component in maintaining the equilibrium of a vessel, significantly affecting its performance and safety. Its design and placement are crucial for providing the necessary resistance against the forces acting on the hull, particularly when navigating through challenging waters.
Functions of the Keel
- Weight Distribution: The keel adds weight to the lower part of the craft, lowering the center of gravity.
- Hydrodynamic Efficiency: Its shape allows for better movement through water, reducing drag.
- Resistance to Heeling: The keel counteracts the tilt caused by wind pressure on the sails.
Types of Keels
- Full Keel: Provides excellent stability and tracking but may be less maneuverable.
- Fin Keel: Offers better performance in speed and agility, commonly used in racing vessels.
- Bulb Keel: Enhances stability by shifting weight downwards, making it ideal for cruising.
Understanding the role of the keel is essential for anyone involved in maritime activities, as it directly influences both safety and navigational efficiency.
Navigation Instruments on Sailboats
Effective navigation is crucial for safe and successful voyages across water. Various tools and devices are utilized to determine position, direction, and distance, enabling mariners to chart their course with precision. These instruments are essential for both novice and experienced navigators, ensuring that they can respond to changing conditions and make informed decisions while at sea.
Essential Navigational Tools
A range of instruments is available to assist in navigation. Traditional tools like compasses and sextants provide fundamental directional guidance and celestial positioning. Modern advancements have introduced electronic devices such as GPS and chartplotters, which enhance accuracy and ease of use. Understanding how to interpret data from these various instruments is vital for effective navigation.
Weather and Environmental Monitoring
In addition to basic navigation, environmental instruments play a key role in ensuring a safe journey. Wind speed indicators, barometers, and temperature gauges provide critical information about weather conditions. By monitoring these factors, sailors can anticipate changes and adjust their course or sails accordingly, enhancing both safety and performance on the water.
Essential Safety Equipment Aboard

Ensuring safety during nautical adventures is paramount. Various tools and devices can significantly enhance security and provide peace of mind. Familiarizing oneself with these essentials is crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience on the water.
Critical Safety Gear
- Personal Flotation Devices (PFDs): These are vital for all individuals on board, providing buoyancy in case of emergencies.
- First Aid Kits: A comprehensive kit should include basic medical supplies to address minor injuries.
- Fire Extinguishers: Ensure you have easily accessible extinguishers to combat potential fires.
- Distress Signals: Flares or other signaling devices are essential for alerting nearby vessels in case of distress.
Navigation and Communication Tools
- VHF Radio: This device is crucial for communication with other vessels and emergency services.
- GPS Units: Accurate positioning tools help in navigating safely and avoiding hazards.
- Charts and Maps: Up-to-date navigational aids are necessary for planning routes and understanding local waters.
Common Materials Used in Construction
When embarking on the journey of crafting floating vessels, the selection of suitable materials plays a pivotal role in ensuring durability, performance, and aesthetics. Various substances are employed, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages that cater to specific needs.
Types of Materials
- Wood: A traditional choice known for its beauty and natural properties. It offers flexibility and is relatively easy to work with.
- Fiberglass: A popular synthetic option, it provides strength and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for various environments.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and strong, this metal is valued for its durability and resistance to rust.
- Steel: Known for its robustness, it is often used in larger constructions due to its structural integrity.
Considerations for Material Selection
- Weight: Lighter materials improve buoyancy and ease of handling.
- Durability: Resistance to environmental factors is crucial for longevity.
- Cost: Budget considerations can influence material choices significantly.
- Maintenance: Some materials require more upkeep than others, impacting long-term ownership.
Understanding these common materials and their properties is essential for making informed decisions in the construction process, ultimately influencing the performance and life of the vessel.
Maintenance Tips for Sailboat Parts
Proper upkeep of marine equipment is crucial for ensuring safety and performance on the water. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of components but also enhances overall functionality. Adopting a systematic approach to care can prevent issues and save costs in the long run.
Regular Inspections

Conducting routine checks is essential. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Pay close attention to critical elements such as rigging, hull, and deck fixtures. Identifying small problems early can prevent them from escalating into major repairs.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Keeping your equipment clean is vital. Rinse off saltwater and debris after each outing. Use appropriate cleaners for different surfaces to avoid damage. Additionally, ensure that moving parts are well-lubricated to maintain smooth operation. Regularly apply a quality lubricant to hinges and other mechanical components to minimize friction and wear.
Differences Between Monohulls and Multihulls
The choice between a single-hulled vessel and a multi-hulled craft involves various considerations that can significantly influence performance, comfort, and overall sailing experience. Understanding the distinctions between these two types is essential for enthusiasts looking to find the right fit for their adventures on the water.
Stability and Speed
One of the most notable differences lies in stability. Multi-hulled vessels typically offer greater stability due to their wider beam and lower center of gravity. This characteristic can lead to a more comfortable ride in choppy waters. Conversely, single-hulled designs may lean more during sailing, which can enhance speed but may also require more skill to manage effectively in challenging conditions.
Space and Accommodation
When it comes to living space, multi-hulls often provide more room for crew and storage, making them appealing for long-term cruising. Their design allows for larger cabins and additional amenities. In contrast, single-hulled vessels might have more compact interiors, which can limit accommodation but often result in lighter weight and improved maneuverability.
Understanding the Centerboard Functionality
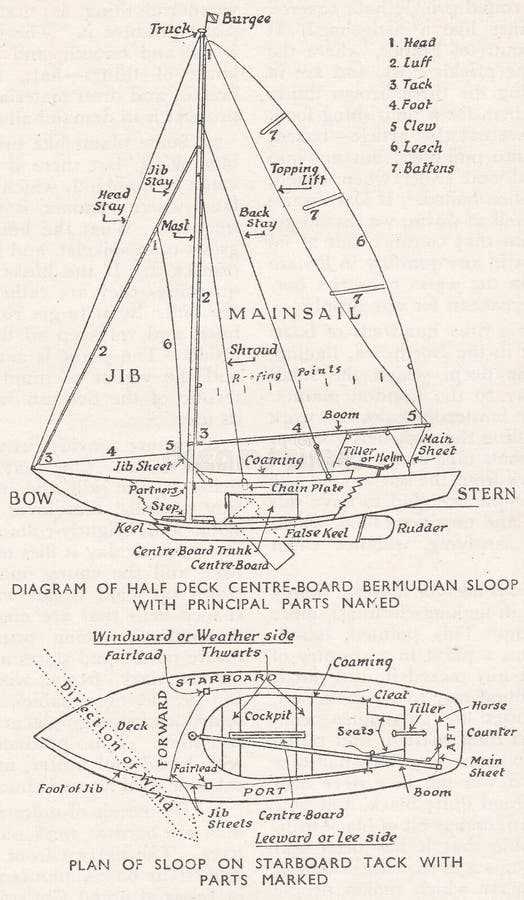
The centerboard plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and stability of a watercraft. By providing lateral resistance, it allows the vessel to maintain an upright position while navigating through various wind conditions. This mechanism is essential for achieving optimal speed and maneuverability, especially when sailing upwind.
When deployed, the centerboard extends into the water, creating a hydrodynamic effect that counters the force of the wind on the sails. This interaction not only prevents lateral drift but also allows for sharper turns and better control. Conversely, when retracted, it reduces drag, facilitating easier navigation in shallow waters.
Understanding how the centerboard functions helps sailors appreciate its importance in overall sailing strategy. Whether maneuvering through tight spaces or facing strong gusts, this component significantly influences the craft’s handling and efficiency on the water.
Exploring Sailboat Engine Types
When it comes to navigating the open waters, the choice of propulsion can significantly influence performance and experience. Various mechanisms are available, each offering unique benefits and operational characteristics. Understanding these options can help in making an informed decision suited to individual needs and preferences.
Below are some common engine types utilized in maritime vessels:
- Inboard Engines:
- Installed within the hull.
- Provides efficient power for longer voyages.
- Typically fueled by diesel, enhancing fuel economy.
- Outboard Motors:
- Mounted externally at the stern.
- Portable and versatile for various sizes of crafts.
- Can be easily replaced or serviced.
- Sailing Engines:
- Specifically designed for sailing vessels.
- Offers a balance between power and efficiency.
- Commonly features hybrid options for eco-friendliness.
- Electric Propulsion:
- Utilizes battery power for a quieter and cleaner operation.
- Ideal for short trips and environmentally-conscious sailors.
- Can require additional infrastructure for charging.
Each engine type presents its own set of advantages and challenges, making it essential for operators to assess their specific needs, such as cruising range, maintenance preferences, and environmental impact.