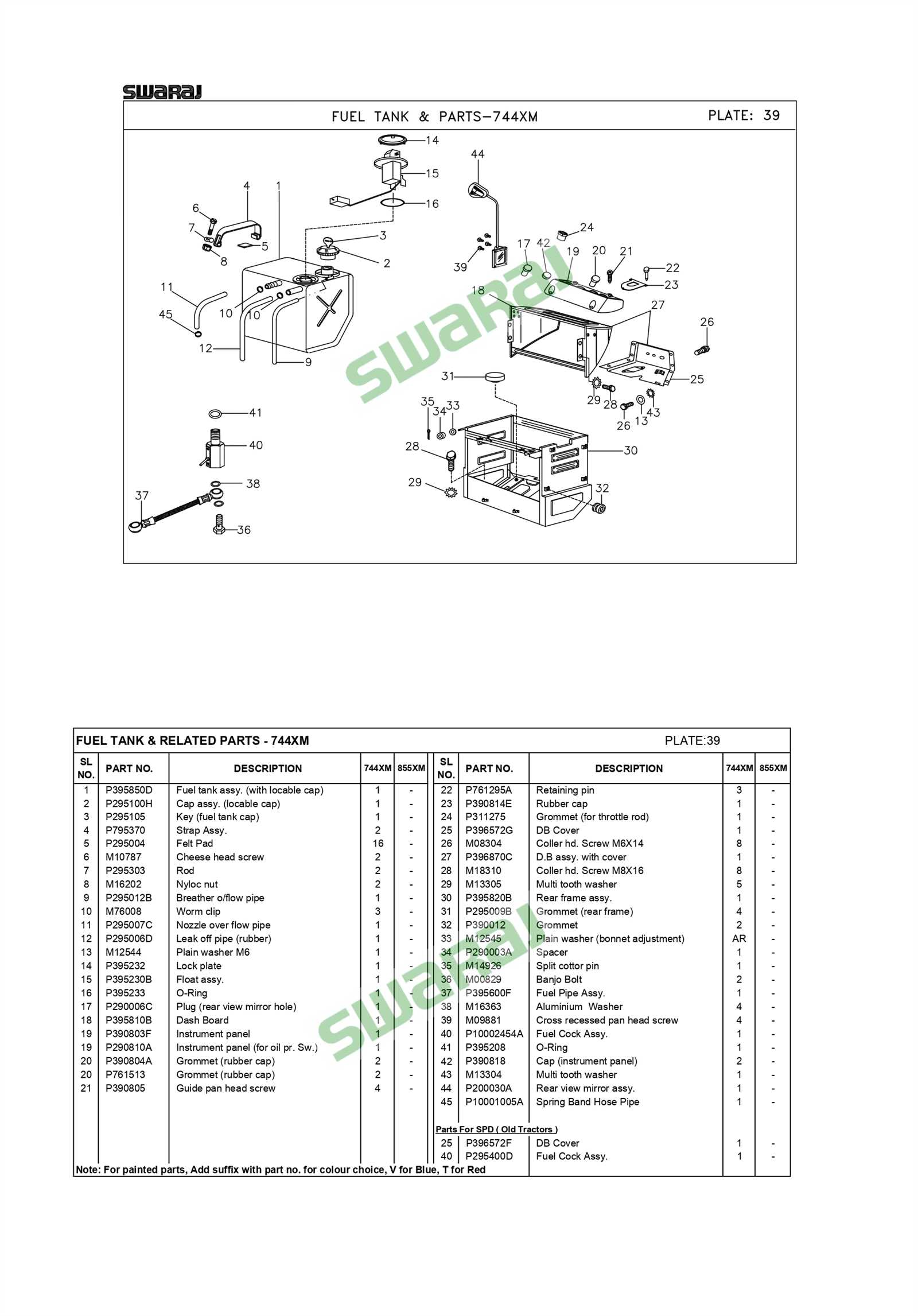
Components Overview of Fuel Tanks

The functionality and efficiency of any storage container system rely heavily on the careful integration of its various elements. Each component works in unison to ensure proper containment, transfer, and management of essential resources, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the system. By understanding these interconnected parts, users can better maintain and optimize their systems for long-term use.
Key sections of this system are responsible for regulating the flow, securing contents, and preventing leakage. Properly functioning mechanisms play a critical role in ensuring that the stored materials remain intact and usable. Identifying the key elements and their roles can simplify troubleshooting and improve maintenance practices.
In this guide, we will break down the core components, explaining their purpose and significance within the system. This overview aims to provide a clearer understanding of how each part contributes to the overall operation and how to keep everything running smoothly.
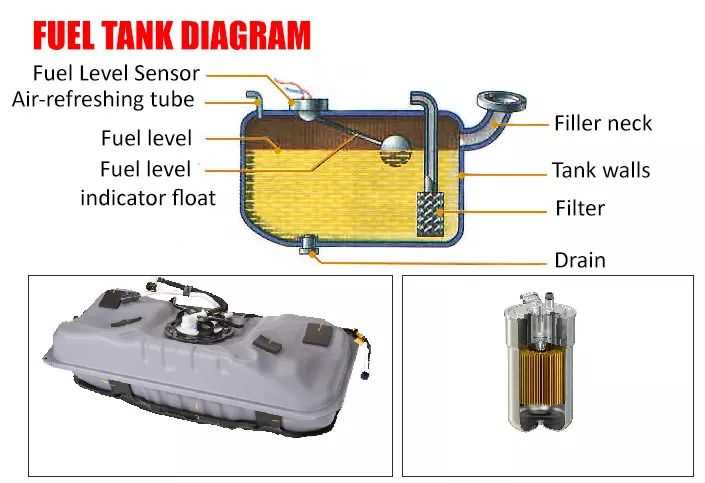
Understanding the Function of a Fuel Tank
One of the essential components in the operation of any vehicle is the container that stores the energy source required for movement. Its purpose is to ensure that this source is safely kept and available for the system that powers the engine. Without this mechanism, the smooth flow of energy would be impossible, leading to inefficient performance or complete stalling.
- Maintains a secure reserve of the energy source
- Allows controlled flow to the engine system
- Ensures safety from external hazards
This system must be designed to handle various conditions, from temperature changes to pressure fluctuations, ensuring that the vehicle operates reliably in different environments.
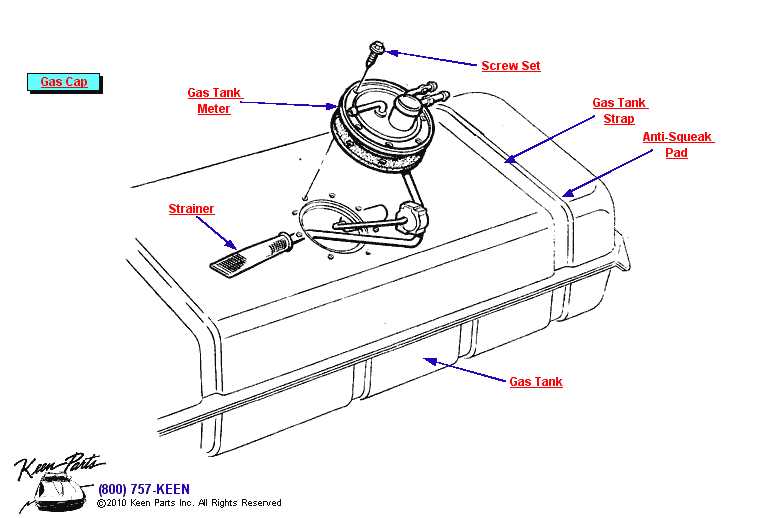
Main Components of a Fuel Storage System
Effective energy containment systems are designed with several key elements that ensure safety, functionality, and efficient operation. These components work together to store and manage liquids used for energy generation in a secure manner. Understanding these primary elements is crucial for maintaining operational integrity and preventing potential issues.
Containment Structure
The central element of the system is the containment structure. It is responsible for securely holding the liquid and preventing leaks. Built from durable materials, this component must withstand various environmental factors while maintaining the integrity of the stored substance.
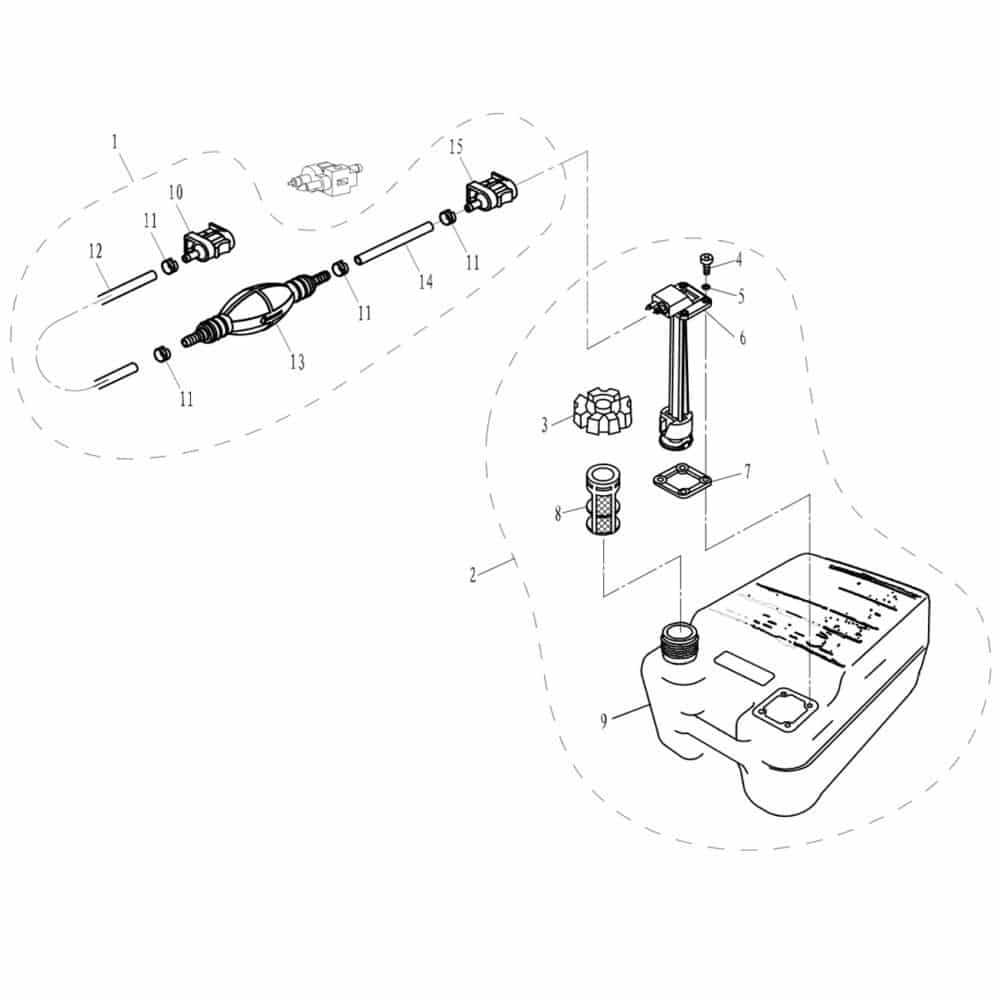
Control Mechanisms
Various control mechanisms are integrated into the system to regulate the flow and pressure of the stored liquid. These mechanisms ensure proper distribution and safeguard against overflow or excessive pressure build-up, which could lead to system failures.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Storage Structure | Holds the liquid in a secure, leak-proof environment |
| Control Valves | Regulate liquid flow and pressure |
| Ventilation System | Prevents pressure build-up and ensures proper airflow |
Fuel Pump and Its Role in Operation
The pump responsible for transferring liquid is a vital component in ensuring the proper movement of fluids throughout the system. Its primary function is to maintain a steady flow, which is critical for the overall efficiency and performance of the entire mechanism. Without a reliable source to propel the liquid, the system would struggle to operate smoothly, leading to potential issues or even failure.
The pump operates by drawing the necessary liquid from its source and pushing it through the system with adequate pressure. This ensures that all parts of the machinery receive the required amount of fluid for optimal function. The pump’s performance is crucial in maintaining consistent operations, especially under varying conditions and demands.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pump Motor | Drives the movement of liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pressure Regulator | Ensures stable flow through the system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Valves |
How the Fuel Filler Neck Works
The entry tube plays a crucial role in transferring liquid from the external environment into the vehicle’s storage container. This passageway is specifically designed to ensure a safe and efficient transfer process while minimizing any risk of spills or leaks. Main Components of the Entry Tube
Working Mechanism
Exploring the Fuel Sending UnitThe device responsible for monitoring liquid levels within a system plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate measurements. This component communicates valuable information to other parts of the mechanism, allowing for consistent operation. Understanding how it functions and interacts with other sections helps maintain the entire system’s reliability. Design and Structure Typically composed of a float, sensor, and electrical circuit, this unit measures the position of the liquid surface. The float adjusts based on the level, sending signals to the sensor, which translates them into readable data. These readings are then displayed, providing real-time updates. Common Issues Wear and tear over time can affect the accuracy of this unit. Corrosion or mechanical faults might cause incorrect readings, leading to operational inefficiencies. Regular checks and maintenance can help avoid potential problems, ensuring smooth system performance. Fuel Lines and Their Importance
In any vehicle, the system responsible for transferring essential liquids plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. These conduits must be designed to withstand various pressures and environmental conditions while maintaining efficiency. Understanding their significance can help vehicle owners appreciate the engineering that goes into these components. Functionality and DesignThe primary function of these conduits is to facilitate the movement of liquid from one point to another within the vehicle. They are designed with materials that can resist wear and corrosion, ensuring longevity. Proper installation and maintenance are vital to prevent leaks or blockages, which could lead to severe operational issues. Common Materials Used
By selecting appropriate materials and designs, manufacturers ensure that these conduits effectively fulfill their role in the overall functioning of the vehicle. Regular checks can help in identifying wear and tear, thus maintaining the system’s reliability. Vapor Recovery System Overview
The vapor recovery system plays a crucial role in minimizing emissions and enhancing environmental safety during the transfer and storage of volatile substances. This innovative technology is designed to capture and recycle vapors that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere, thereby reducing harmful pollutants and promoting sustainability. By effectively managing vapors, the system contributes to cleaner air quality and compliance with environmental regulations.
Common Issues with Fuel Tank Valves
Valves play a crucial role in the operation of various storage systems, and their proper functioning is essential for efficiency and safety. However, these components can encounter several problems that may lead to performance issues, resulting in leaks or malfunctions. Leakage ProblemsOne of the most prevalent issues is leakage, which can occur due to wear and tear, improper installation, or damage from external factors. Even a small leak can lead to significant losses and environmental concerns, making regular inspection and maintenance critical. Blockages and RestrictionsBlockages within the valve can also create serious complications. Debris, rust, or other contaminants can hinder flow, causing pressure build-up and potential damage. Regular cleaning and servicing can help mitigate this risk, ensuring smooth operation. How to Maintain Fuel Tank Efficiency
Ensuring optimal performance of your vehicle’s storage system is essential for longevity and cost-effectiveness. Regular maintenance practices can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of this crucial component. Here are some effective strategies to improve and sustain efficiency:
By implementing these practices, you can enhance the functionality of your vehicle’s storage system, ensuring it operates efficiently and effectively for years to come. Diagnosing Fuel Tank ProblemsIdentifying issues related to the storage container for combustible substances is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance. Various symptoms can indicate underlying complications, and understanding these signs is essential for timely intervention. Common Indicators: Unusual sounds, such as hissing or gurgling, may suggest air or liquid movement problems within the system. Additionally, visible leaks or corrosion around connection points can signal deterioration, requiring immediate attention. Testing Methods: Conducting visual inspections can help locate any external damage. Utilizing pressure tests is another effective method to evaluate the integrity of the container. These evaluations can reveal whether the structure is holding substances appropriately or if repairs are necessary. Preventive Measures: Regular maintenance checks can mitigate potential complications. Ensuring that seals are intact and monitoring for wear can prolong the lifespan of the storage unit and enhance overall functionality. |