Understanding Hoyer Lift Parts Diagram for Efficient Maintenance
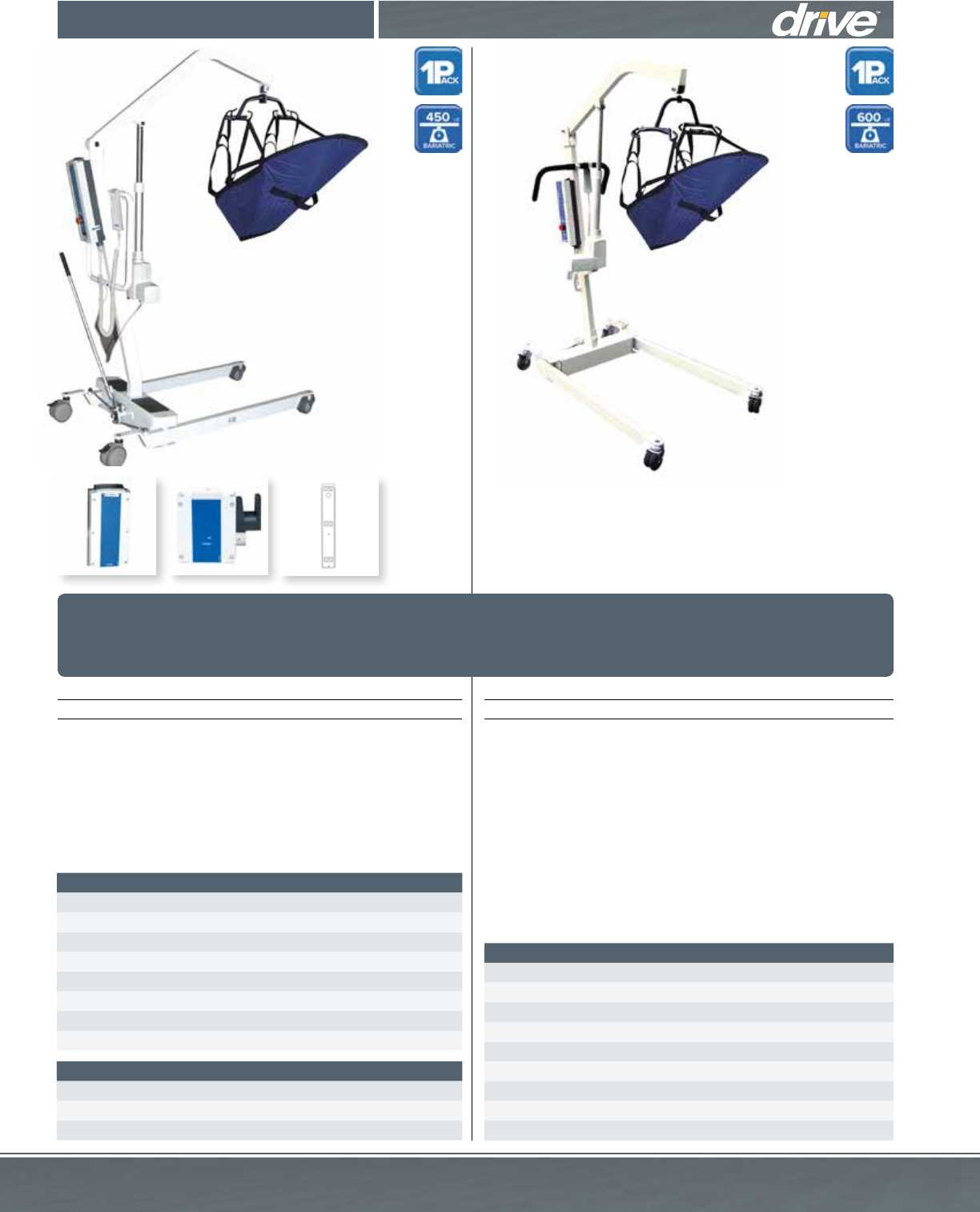
In various situations where assistance is needed for comfortable and safe movement, specialized equipment plays a vital role. Knowing how the elements of this equipment are organized can significantly improve its usability and maintenance. By familiarizing oneself with the specific structure, users can ensure proper operation and even handle basic troubleshooting.
This guide will delve into the essential features of mobility-support devices, offering a clear overview of their layout. We’ll cover the key sections, explain the importance of each connection, and highlight what to look out for in terms of wear or replacement. With the right knowledge, maintaining this equipment can be straightforward and efficient.
Through a detailed breakdown, we’ll walk through each core section, ensuring a better understanding of the framework and connections that enable smooth and secure movement. Whether for regular upkeep or deeper repairs, understanding the assembly is critical for ensuring long-term functionality and reliability.
Understanding the Components of a Hoyer Lift
When exploring the mechanical structure of mobility devices, it’s essential to recognize the key elements that work together to provide safe and effective movement. Each part has a specific function that contributes to the overall stability and ease of use, ensuring that the device operates smoothly and securely.
Base and Frame Structure
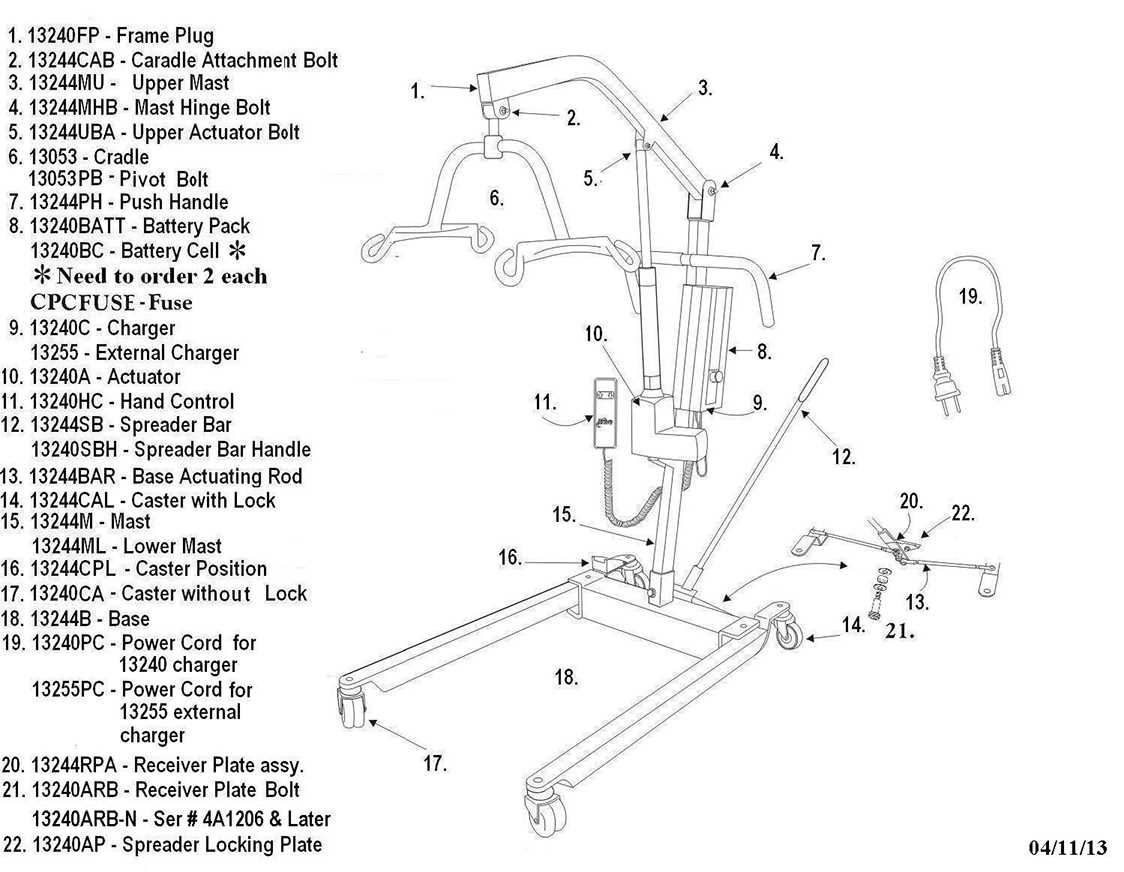
The foundation of the device is its sturdy frame, designed to support the user’s weight and allow for easy maneuverability. The base is typically equipped with wheels, providing the necessary mobility and allowing the equipment to be moved effortlessly across different surfaces.
Support Mechanisms
Another critical element involves the support arms and lifting mechanisms. These components are responsible for securely holding and raising the individual, ensuring a smooth transition from one position to another. They are engineered to provide both strength and flexibility, adapting to various needs and situations.
Slings are an integral part of the setup, crafted to cradle the individual comfortably during use. They offer both safety and comfort, making sure the user is properly supported throughout the entire process.
Key Mechanical Elements in Patient Lifts
When it comes to systems designed to assist with patient transfers, understanding the core components is essential. These systems rely on several critical mechanisms that ensure safety, ease of use, and efficiency in movement. Whether operated manually or powered, each component plays a vital role in the smooth operation of the equipment, enhancing both comfort and support.
Frame and Support Structure
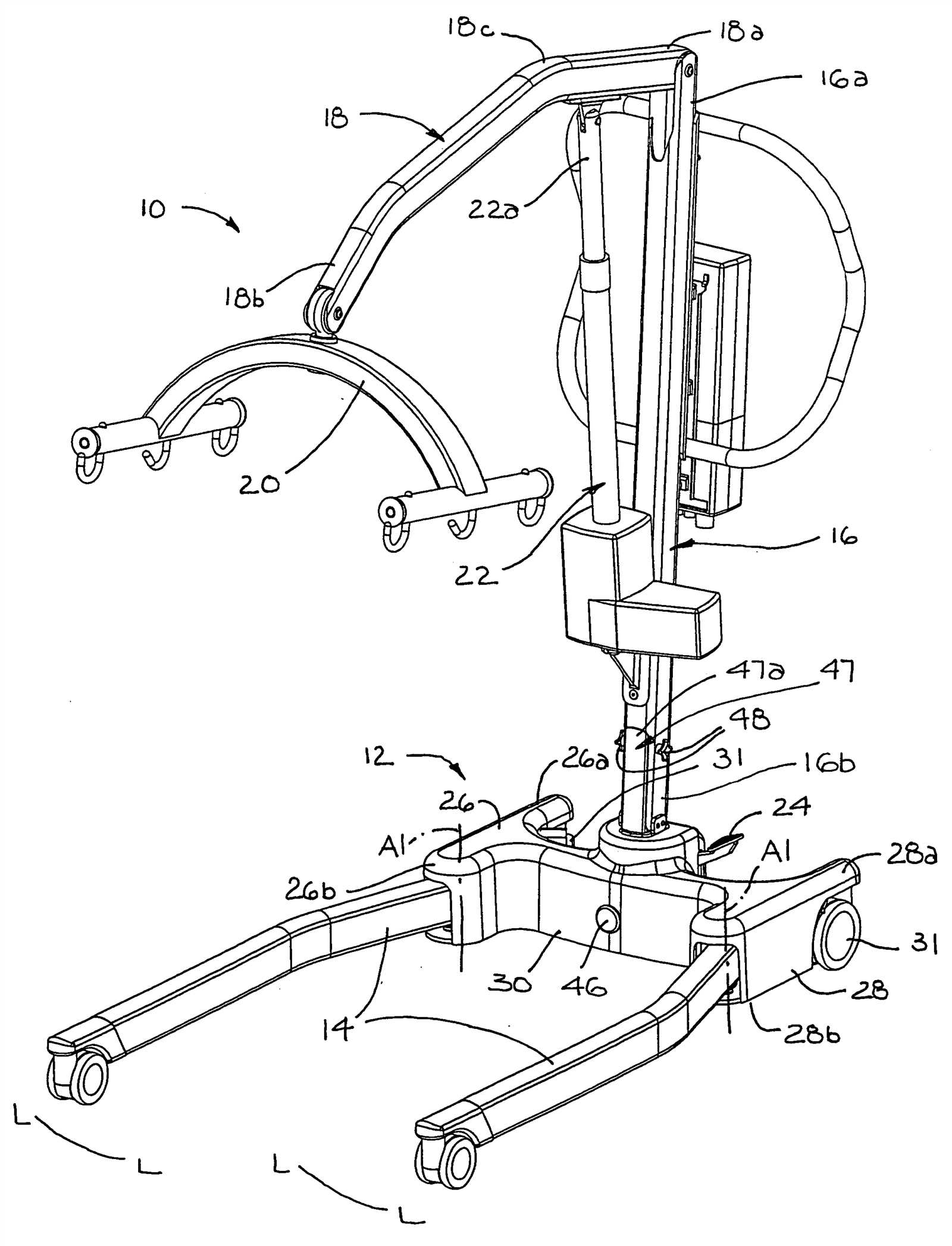
The backbone of any patient transfer system is its frame. This structure must be robust yet lightweight to allow easy maneuvering while providing stability. Strong materials are typically chosen to ensure long-term durability and to withstand repeated use under different conditions.
Hydraulic and Electric Systems
The movement mechanisms are powered either by hydraulic systems or electric motors, depending on the model. Hydraulic systems offer smooth and controlled movement through fluid pressure, while electric versions provide the convenience of remote or button-controlled adjustments. Both options are designed to handle the gradual lifting and lowering of weight, ensuring secure positioning during patient transfers.
Safety features such as emergency stop functions and adjustable speed controls further enhance the operation of these systems, making them versatile in various care environments.
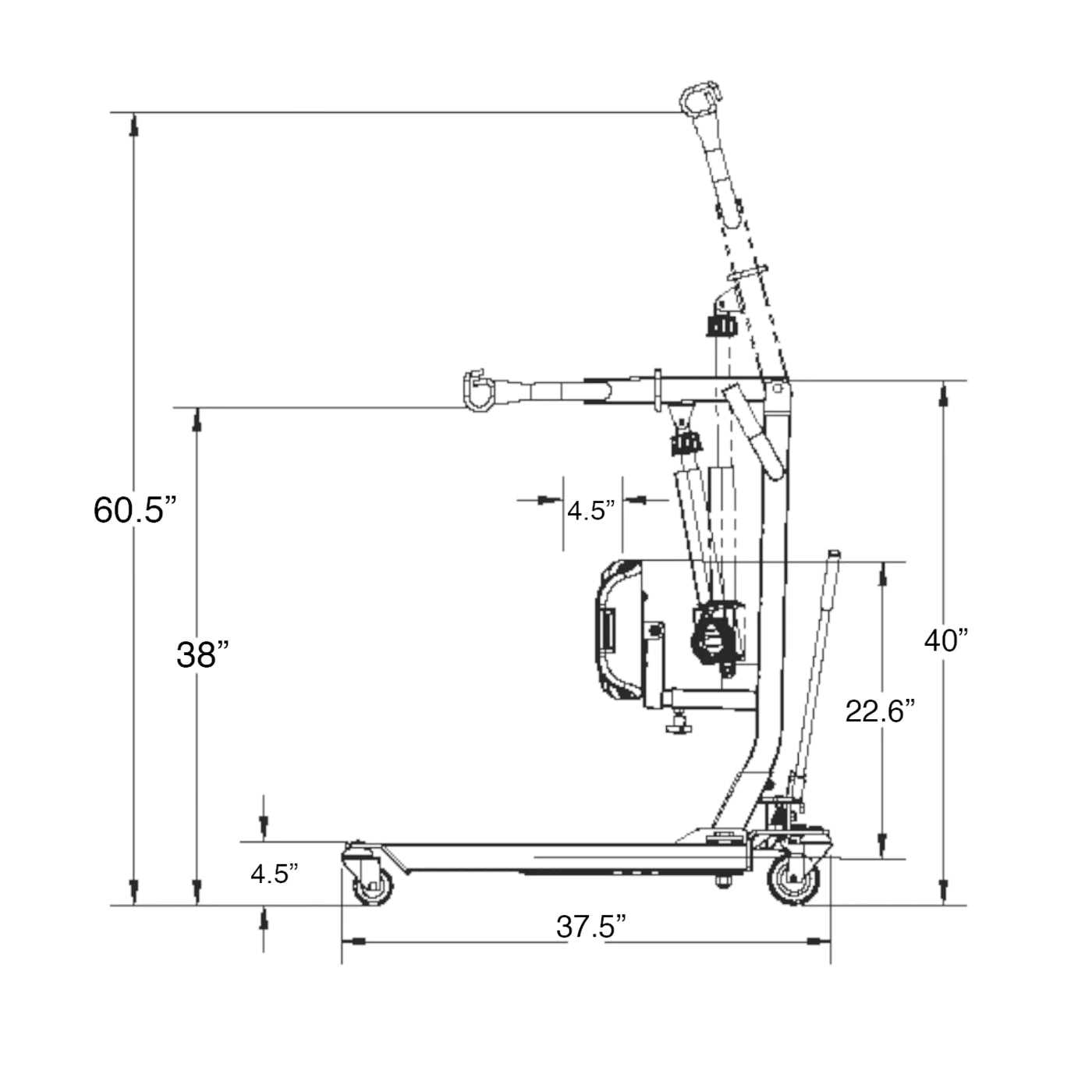
Exploring the Structure of a Lift’s Base
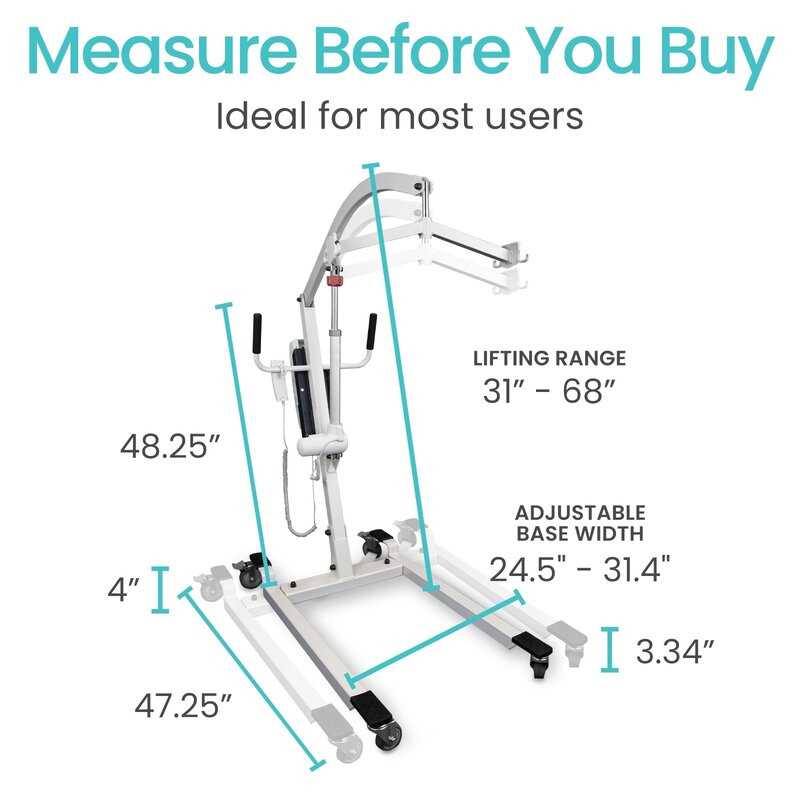
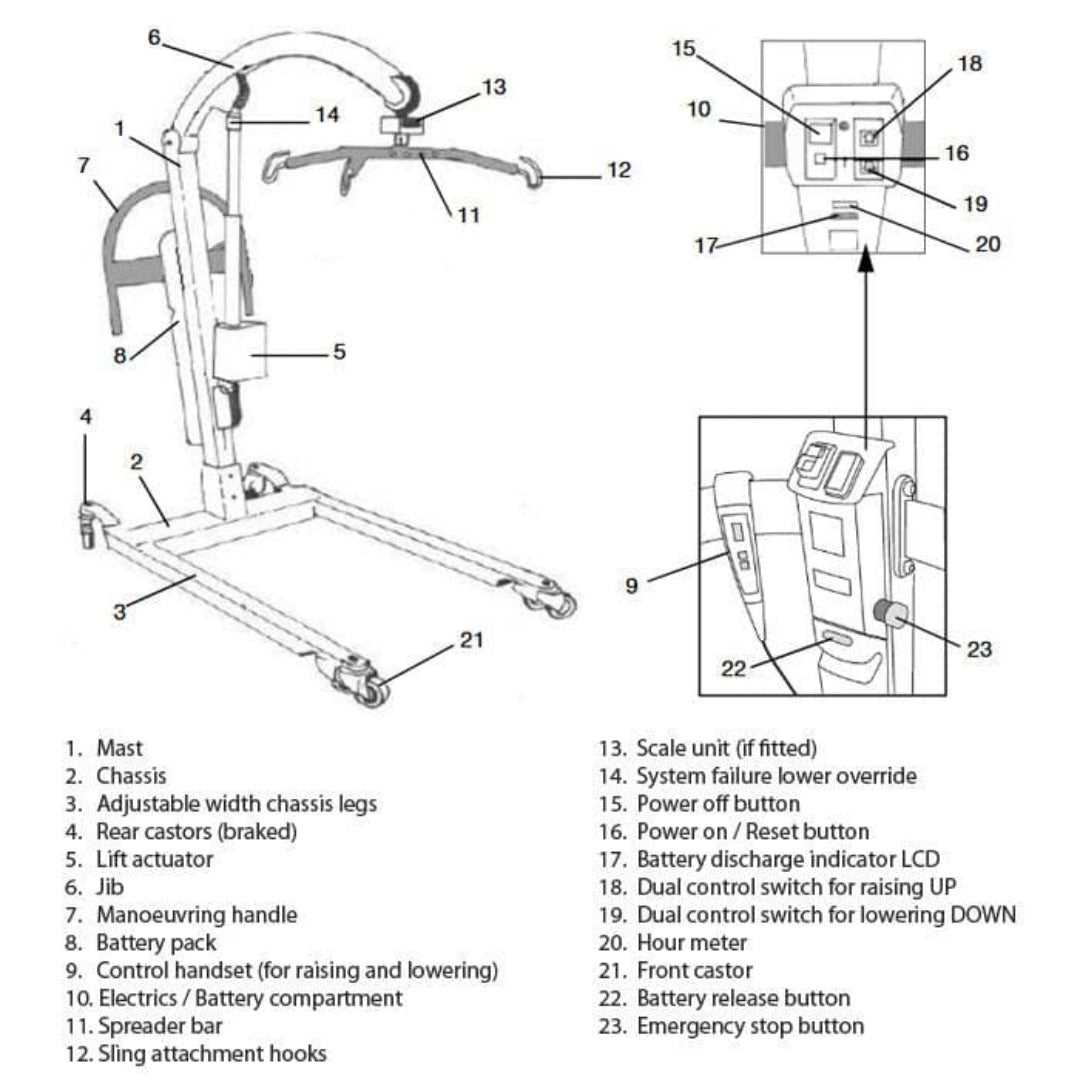
The foundation of any mobility device plays a crucial role in its overall functionality and stability. The base is designed to support the weight, ensure balance, and allow easy maneuvering across various surfaces. Understanding the specific elements that compose this foundation can provide insight into how the device operates smoothly and securely.
At the core of the base, reinforced beams are typically employed to handle significant loads without compromising durability. These beams are often constructed from high-strength materials to ensure long-term reliability. In addition to the beams, adjustable components may be included to provide flexibility for different settings and users.
Another key feature is the castor wheels, which are essential for mobility. These wheels are strategically placed to ensure smooth gliding and precise control, especially in tight spaces. The base may also include stabilizing elements, such as brakes or locking mechanisms, to enhance safety during stationary use. Each of these components works in harmony to form a reliable and secure foundation.
How the Lifting Arm Mechanism Works
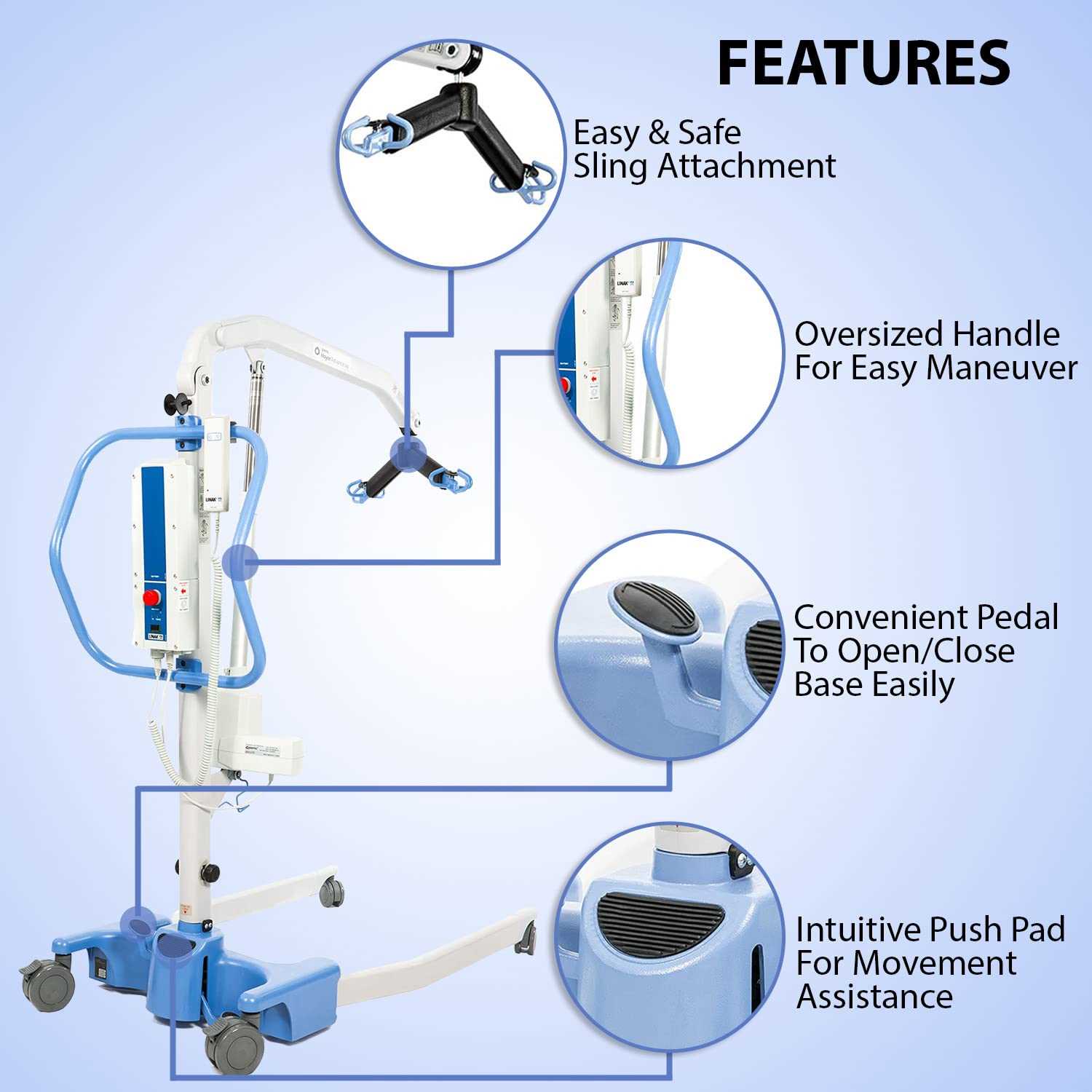
The lifting arm is designed to provide smooth and efficient motion, ensuring safe and controlled elevation of objects. The mechanism relies on several interconnected components that work together to support and transfer weight. Understanding how these elements function allows for better handling and operation of the device.
- Rotation Axis: The central axis enables the arm to pivot smoothly, allowing the extension and retraction of the arm.
- Hydraulic System: A pressure-driven system provides the necessary force to raise and lower the arm with minimal effort.
- Support Frame: The sturdy frame stabilizes the arm, ensuring balance and preventing unwanted movement during use.
- Safety Locks: Secure locking mechanisms hold the arm in place at various angles, enhancing user control and safety during operation.
Each part of the lifting arm is engineered to function seamlessly with the others, creating a reliable mechanism that supports a wide range of applications. Proper maintenance and understanding of these elements ensure long-term performance and safety.
Detailed Overview of Control Systems
Control systems play a vital role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of various types of equipment. These systems are designed to manage the interaction between different components, ensuring they work together seamlessly to achieve the desired functionality. Whether electronic or mechanical, control systems serve as the brain behind the device’s operational logic, helping to execute commands and regulate movements or actions.
The core of any control system lies in its ability to interpret input from the user or environment and respond accordingly. These responses are often governed by preset parameters that ensure safety and precision during use. Understanding how control systems function can provide valuable insights into maintaining, troubleshooting, and optimizing equipment for long-term reliability.
From basic wired setups to more complex programmable designs, control systems continue to evolve, offering enhanced features and more intuitive interfaces. Recognizing the key components and the principles behind their integration is essential for anyone looking to work with or modify such systems.
Wheels and Casters: Mobility Explained
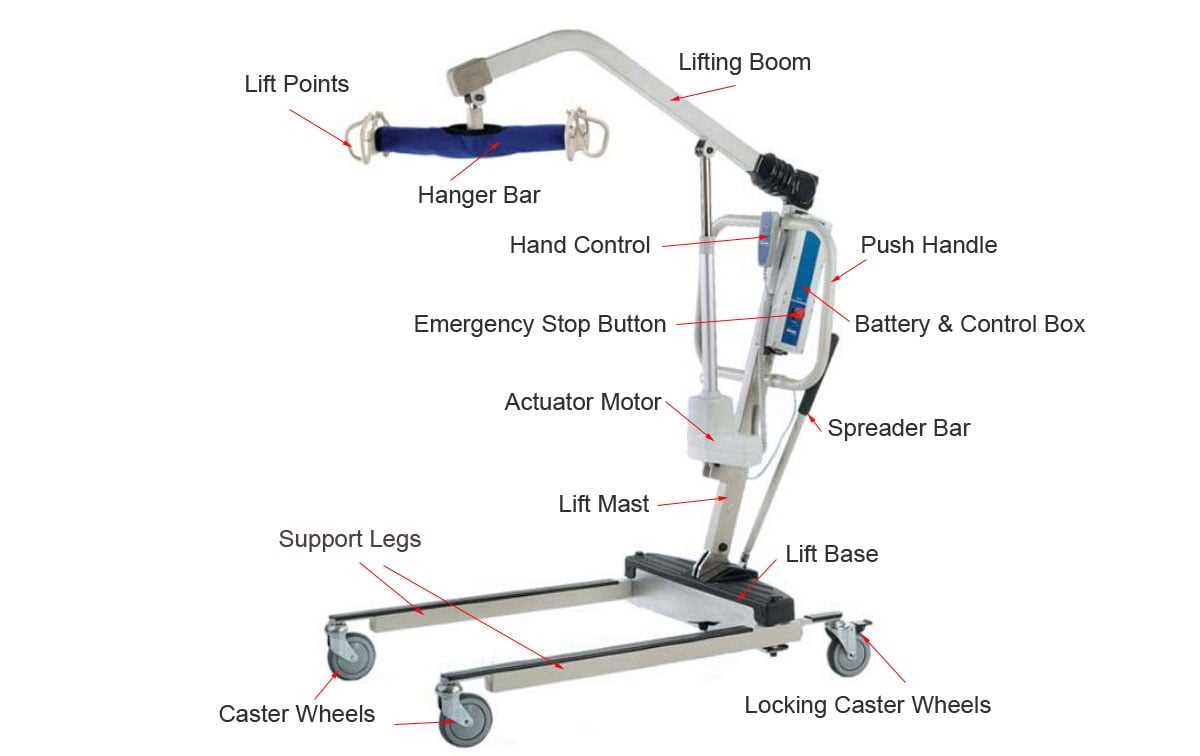
When it comes to enhancing the ease of movement in various devices, the role of wheels and casters cannot be overstated. These essential components enable smooth transitions across different surfaces, offering the flexibility needed for efficient maneuvering. Understanding their construction and functionality is key to ensuring the stability and mobility of any system requiring transportability.
Wheels and casters come in various designs, each tailored to specific needs. Below are some key factors that influence their performance:
- Material: The composition of the wheel impacts its durability and the type of surfaces it can handle, from soft rubber for smooth flooring to harder compounds for rougher terrain.
- Size: Larger wheels distribute weight more evenly, allowing for smoother movement over uneven surfaces. Smaller ones are more suitable for tight spaces.
- Swivel Mechanism: Swiveling casters offer greater maneuverability, allowing easy direction changes, while fixed wheels are ideal for stable, straight-line movement.
By selecting the right combination of materials, size, and design, mobility can be optimized, making the overall system more functional and adaptable to various environments.
Battery and Power Source Configuration
Ensuring a reliable and efficient power setup is essential for devices that rely on energy storage and distribution for operation. The power supply system includes various components designed to provide the necessary voltage and current to keep the unit functioning smoothly. Understanding how these components work together is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity.
The main power source configuration involves a rechargeable battery that stores energy for later use, as well as connectors and cables that facilitate the flow of electricity to the internal circuits. The correct voltage, capacity, and type of battery are vital to avoid power issues that can affect the overall efficiency.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores energy for powering the device. Types include lithium-ion or lead-acid. |
| Charger | Regulates the power input to recharge the battery safely. |
| Power Cable | Transfers electrical energy between the power source and the internal systems. |
| Power Switch | Controls the on/off state of the device by regulating the power flow. |
Proper maintenance of the power system includes checking battery health, ensuring correct charging procedures, and monitoring connectors for wear or corrosion. Regular checks help ensure that the unit operates at its optimal capacity.
Connecting the Sling to the Lift Safely
Ensuring secure attachment of the support fabric to the apparatus is crucial for the safety and comfort of the individual being assisted. Properly connecting the sling to the device guarantees effective handling while minimizing risks of slippage or mishandling. It’s important to follow the guidelines to achieve both security and stability throughout the transfer process.
Before beginning the connection, inspect the components for any wear or damage. Ensure that all hooks, straps, and fasteners are intact. The fabric should be placed evenly, ensuring there is no twisting or entanglement, which could affect stability.
Correct placement of the sling is key. Attach the loops or clips to the designated points on the device, making sure they are securely fastened. Avoid over-tightening, as this could lead to discomfort or undue strain on the user. The goal is to achieve a balance between firm attachment and flexibility to allow safe movement.
Always double-check that the fabric is securely in place before proceeding with the movement. If unsure, ask for assistance or review the device’s user manual to verify the correct procedure. Proper attachment is essential to ensure both the safety of the individual and the longevity of the equipment.
Maintenance Tips for Lift Components
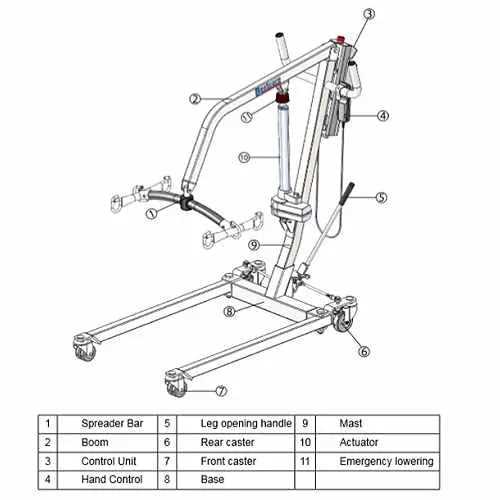
Proper upkeep of essential machinery elements is crucial to ensure reliable and safe operation. Regular inspection and attention to key components can extend their lifespan and reduce the risk of malfunction. By focusing on preventive measures, you can avoid costly repairs and maintain smooth functionality.
1. Regular Inspection: It is important to routinely check all moving parts for wear and tear. This includes verifying that all joints, cables, and mechanical connections are secure and free of damage. Pay close attention to any unusual noises or resistance during operation, as they can indicate potential issues.
2. Lubrication: Many components require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and ensure smooth movement. Apply the appropriate lubricant to joints, bearings, and any other surfaces that experience regular contact. Ensure that the lubricant is suitable for the material and environmental conditions to avoid damage.
3. Cleaning: Keeping all surfaces free of dust, debris, and any accumulated grime is essential. These particles can cause unnecessary wear on components, especially in sensitive areas. Regular cleaning will not only help maintain optimal performance but also prevent contamination from affecting functionality.
4. Load Monitoring: Avoid overloading machinery beyond its recommended capacity. Excessive weight can strain components, leading to premature failure. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding weight limits to ensure safe and efficient operation.
5. Professional Servicing: While regular maintenance can prevent many issues, it is still beneficial to have a professional service technician perform in-depth inspections and repairs. Their expertise can identify hidden problems that may not be immediately apparent and provide solutions to keep the system running optimally.
Common Replacement Parts for Lifts
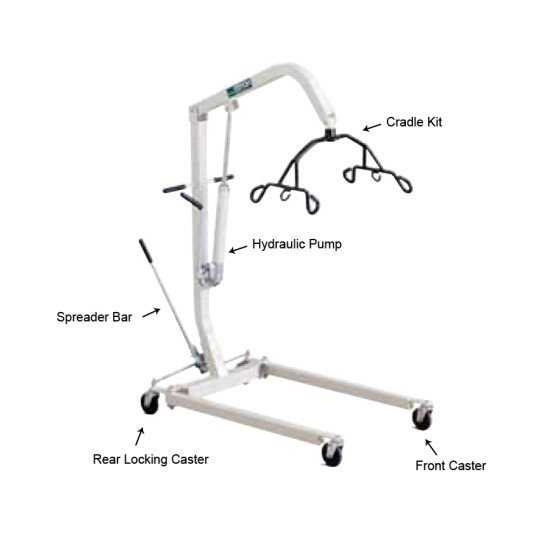

In the world of mobility equipment, ensuring optimal performance often requires replacing certain components over time. Regular maintenance and timely replacements are crucial for maintaining the functionality and safety of these machines. Some elements may wear out due to frequent use or external factors, leading to the need for replacements.
Hoist ropes are one of the most frequently replaced components. These strong cables or chains are essential for the smooth operation of the system, and they can become damaged over time. Control switches are another common item that requires attention, as their functionality is vital for safe operation. Battery packs, which power the equipment, often need replacement as they degrade with age or heavy use.
Additionally, motors may require servicing or replacement, especially if there are issues with movement or responsiveness. Hydraulic systems, which are responsible for lifting and lowering, can experience wear in seals or valves, leading to fluid leaks. Regular checks and proper maintenance ensure that these systems remain efficient.
Troubleshooting Issues in Lift Mechanisms
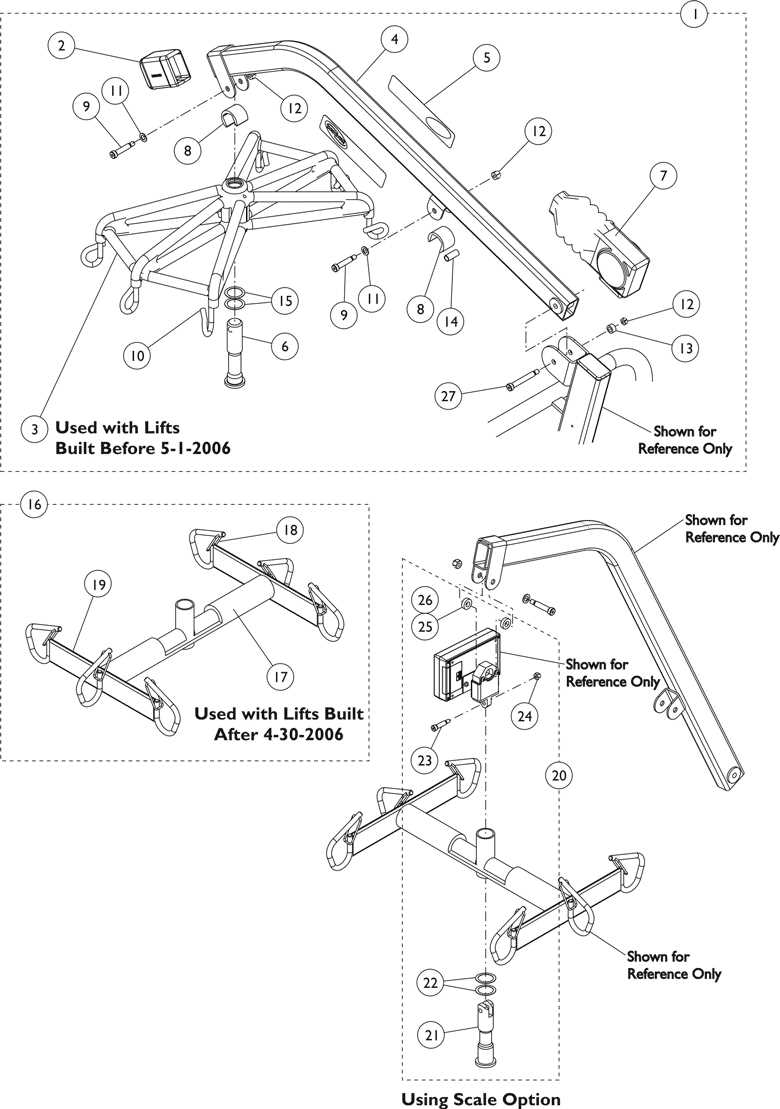
When operating mechanical systems that assist in vertical mobility, issues can arise that hinder proper functionality. Identifying and resolving these problems quickly is crucial to ensure safe and efficient operation. Below are some common challenges faced when dealing with these systems and suggested methods for troubleshooting.
- Inconsistent Movement: If the device fails to move smoothly or hesitates during operation, check for obstructions along the track or within the motor housing. Lubrication of moving components may also be necessary.
- Failure to Power On: Verify that the power source is connected and fully functional. Inspect the battery or power cable for wear and tear, ensuring there are no loose connections.
- Unexpected Noises: Unusual sounds may indicate mechanical wear. Listen for grinding or clicking noises, which could point to damaged gears or motors. Immediate inspection and possible replacement of these components may be required.
By following these steps, most operational issues can be addressed, helping to maintain the equipment’s reliability and performance.
Ensuring Long-Term Durability of Your Lift
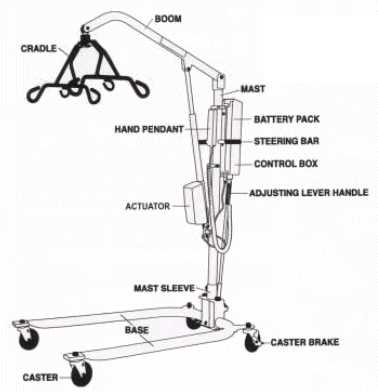
Maintaining the reliability and longevity of your equipment is essential to prevent premature wear and ensure optimal performance. Regular checks, proper usage, and timely maintenance contribute significantly to the durability of your device. By following certain precautions and care routines, you can extend its lifespan and reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
The key to long-term reliability lies in monitoring the condition of various components and performing periodic maintenance. Whether it’s mechanical adjustments, lubrication, or cleaning, each action plays a vital role in preserving the functionality of your equipment.
| Maintenance Task | Recommended Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Check for wear and tear | Monthly | Prevents unexpected failures |
| Lubricate moving parts | Every 3 months | Reduces friction and prolongs function |
| Inspect electrical connections | Every 6 months | Ensures safety and functionality |
| Clean and clear debris | Every month | Improves efficiency and prevents blockages |
Regularly following these guidelines not only helps avoid costly repairs but also enhances the safety and reliability of your equipment, providing peace of mind for years to come.