Iphone 8 Plus Parts Diagram Overview
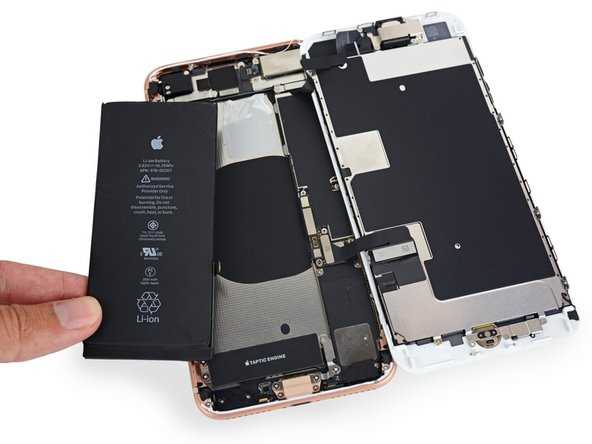

The intricate assembly of modern mobile devices showcases a blend of engineering excellence and cutting-edge technology. Understanding the arrangement of the various elements within these gadgets provides insights into their functionality and design. This section delves into the layout of key internal components, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Each element plays a vital role in the overall performance and user experience of the device. From the core processing unit to the various sensors, each piece contributes to the seamless operation that users have come to expect. This exploration will illuminate how these components work together harmoniously, ensuring optimal efficiency and reliability.
Additionally, examining the configuration of these essential elements can aid in troubleshooting common issues, enhancing the longevity of the device. Whether for repair purposes or a deeper understanding of mobile technology, this comprehensive overview will serve as a valuable resource for enthusiasts and technicians alike.
iPhone 8 Plus Overview
The model in discussion represents a significant advancement in mobile technology, showcasing a blend of innovative design and enhanced functionality. This device offers users a seamless experience, combining powerful hardware with sophisticated software capabilities.
Key features of this device include:
- Stunning display with vibrant colors and high resolution.
- Robust processing power for efficient multitasking.
- Advanced camera system for capturing high-quality images and videos.
- Durable construction with premium materials for enhanced longevity.
This device has garnered attention not only for its technical specifications but also for its user-friendly interface and sleek aesthetic. The integration of cutting-edge technology ensures that it meets the demands of modern users, providing an exceptional overall experience.
Key Components of the Device
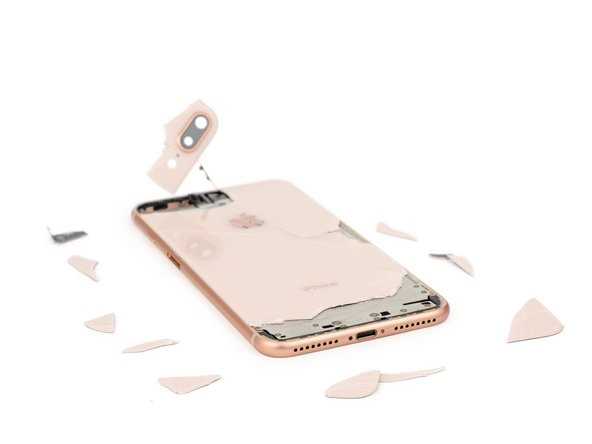

This section highlights the essential elements that make up a smartphone, providing insights into their functions and significance within the overall design. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the device operates smoothly and efficiently, contributing to the user experience.
Main Components
- Display: The screen serves as the primary interface, allowing users to interact with applications and content.
- Battery: This component powers the device, providing the necessary energy for prolonged usage.
- Processor: Often referred to as the brain of the device, it handles all computational tasks and operations.
- Camera System: This allows users to capture images and videos, enhancing communication and creativity.
- Memory: Storage space for apps, photos, and data, essential for a seamless user experience.
Support Elements
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components, facilitating communication and functionality.
- Speakers: These components deliver audio output, allowing users to enjoy multimedia content.
- Microphone: Captures sound for calls and recordings, enabling effective communication.
- Charging Port: This connection allows for power input, essential for recharging the device.
- SIM Card Slot: Enables cellular connectivity, allowing the device to access network services.
Understanding the Parts Diagram
The visual representation of the components within a device serves as a crucial reference for both enthusiasts and technicians. This overview aids in identifying each element’s location and function, facilitating better comprehension of the overall structure. By examining this schematic, one can gain insights into how various elements interact and contribute to the device’s performance.
Each segment of the visual guide is typically labeled, providing clarity on the roles of different elements. This organization helps users locate specific features quickly, whether for repair, enhancement, or general knowledge. Familiarity with these representations empowers users to troubleshoot issues effectively and perform maintenance with confidence.
Additionally, this illustration highlights the significance of each component’s layout, revealing how design choices impact the functionality and durability of the device. Understanding these relationships not only enhances repair efforts but also enriches the user’s appreciation of the engineering behind modern technology.
Mainboard and Its Functions
The main circuit board serves as the central hub for various components within a mobile device. It facilitates communication between hardware elements, manages power distribution, and coordinates operations to ensure smooth functionality. Understanding its structure and role is essential for comprehending how the device operates effectively.
Key Components of the Mainboard
- Processor: The primary processing unit responsible for executing instructions and managing tasks.
- Memory: Temporary storage used for running applications and processing data.
- Power Management IC: Regulates power distribution to different components, ensuring optimal performance.
- Connectivity Modules: Enable communication with networks and peripherals, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular capabilities.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Handles rendering of images and graphics, enhancing the visual experience.
Functions of the Mainboard
- Integration: Combines various electronic circuits into a single unit, streamlining device design.
- Communication: Facilitates data transfer between the processor, memory, and other components, enabling seamless operation.
- Power Distribution: Ensures that each component receives the necessary voltage and current for optimal performance.
- Data Storage: Provides interfaces for connecting external storage devices, allowing for data expansion and backup.
- Signal Processing: Manages input and output signals, crucial for touch responsiveness and audio/video performance.
Battery Specifications and Details
The power source plays a crucial role in the overall performance and functionality of modern mobile devices. Understanding its specifications and characteristics is essential for optimal use and maintenance.
Type: The energy storage unit is typically a lithium-ion, known for its high energy density and efficiency. This technology ensures a longer lifespan and improved performance compared to older battery types.
Capacity: The capacity of the battery is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), indicating the amount of energy the unit can store. A higher capacity translates to extended usage time, allowing users to enjoy their devices for longer periods without the need for frequent recharging.
Voltage: The nominal voltage is essential for compatibility with the device’s components. Most energy storage units operate at a standard voltage, ensuring efficient energy transfer and minimal loss.
Charging Specifications: Fast charging capabilities enable quicker replenishment of the battery, enhancing user convenience. Understanding the charging requirements, including voltage and current, is vital for using the appropriate chargers to avoid damage.
Temperature Range: Optimal performance is influenced by the operating temperature. It’s important to keep the energy source within specified temperature limits to prevent degradation and ensure longevity.
Display Assembly Features Explained
The display assembly is a critical component of modern smartphones, serving as the primary interface for user interaction. It encompasses various features that enhance functionality and user experience. Understanding these elements can provide insight into the overall performance and usability of the device.
One of the key features is the touch sensitivity, which allows users to navigate the interface effortlessly. This feature is enabled by capacitive sensors embedded within the display, making it responsive to even the lightest touch. Additionally, the assembly typically includes high-resolution capabilities, ensuring that visuals are sharp and vibrant, contributing to an immersive viewing experience.
The construction of the display assembly often involves multiple layers, including a protective glass layer to prevent scratches and damage. This layer is usually treated with an oleophobic coating to resist fingerprints, maintaining clarity and cleanliness. Moreover, many assemblies feature advanced technology like OLED or LCD, each offering distinct advantages in terms of color reproduction and energy efficiency.
Another significant aspect is the integration of the front-facing camera and sensors, which are crucial for functionalities such as facial recognition and video calls. These components are strategically placed to maximize usability while minimizing interference with the display’s aesthetics.
Lastly, the assembly is designed for easy replacement and repair, allowing technicians to replace damaged components without requiring a complete overhaul of the device. This modular design not only extends the lifespan of the smartphone but also makes maintenance more convenient for users.
Camera System and Placement
The imaging system of modern smartphones plays a crucial role in enhancing the user experience by delivering high-quality photographs and videos. The configuration and location of these components significantly influence their performance, making it essential to understand how they are integrated into the device.
Key Components
The main elements of the imaging assembly include the camera lenses, sensors, and stabilization mechanisms. These components work together to capture images with clarity and precision. The sensor’s size and type, as well as the quality of the lenses, are pivotal in determining the overall imaging capabilities.
Strategic Positioning
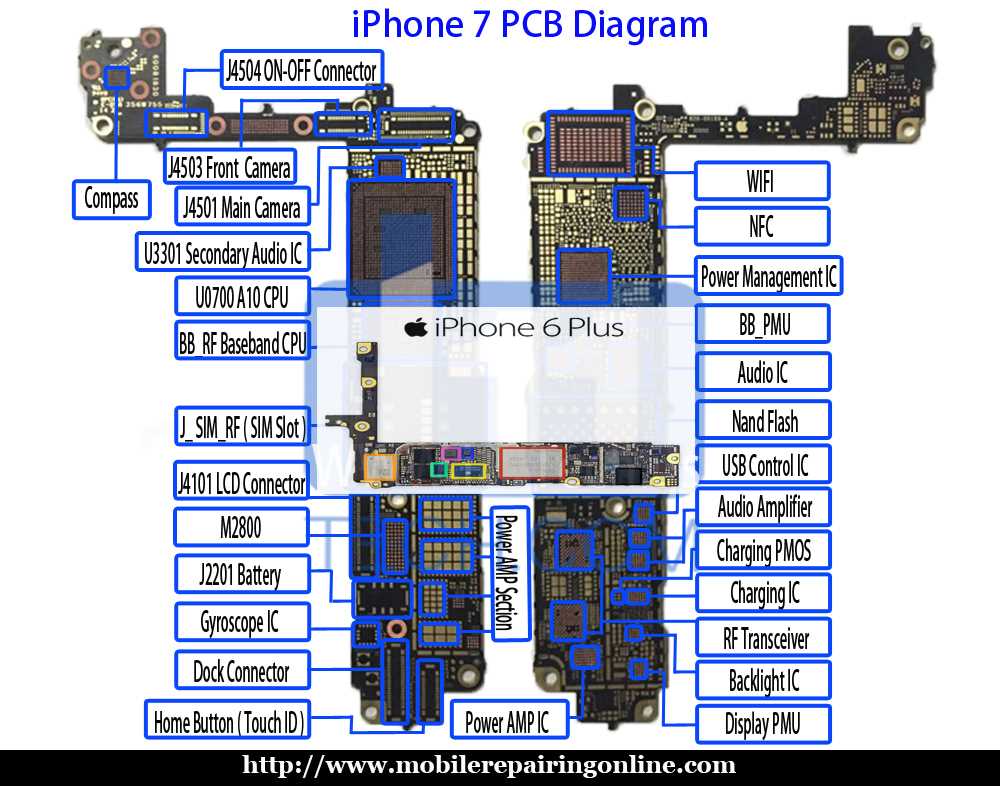
Placement within the device is meticulously designed to maximize functionality while minimizing interference. The rear camera is typically positioned to allow for optimal light entry, while the front-facing unit is often located for convenient selfies and video calls. This thoughtful arrangement ensures that users can capture moments effortlessly from various angles.
Internal Sensors and Their Roles
The intricate design of modern smartphones incorporates a variety of sensors that enhance user experience and device functionality. These components are essential for gathering data about the environment and user interactions, enabling a seamless integration of hardware and software.
Types of Internal Sensors
Among the primary sensors found in these devices are the accelerometer, gyroscope, and proximity sensor. The accelerometer measures the device’s orientation and movement, allowing for automatic screen rotation and gesture recognition. The gyroscope complements this by providing additional data about rotational motion, enhancing applications that require precise positioning.
Impact on User Experience
The proximity sensor plays a crucial role in improving battery efficiency by detecting when the device is close to the user’s face, thereby disabling the screen during calls. These sensors collectively contribute to a more intuitive and responsive interface, allowing users to interact with their devices in natural and meaningful ways.
Connecting Cables and Interfaces
Establishing reliable connections within electronic devices is crucial for ensuring seamless communication between various components. Properly interfacing these elements enhances functionality and performance, allowing for efficient data transfer and power management.
Types of Connections
- Flex Cables
- Connector Pins
- Audio Interfaces
- Charging Ports
Each connection type serves a specific purpose and is designed to accommodate the unique requirements of the device’s architecture. Understanding the various interfaces can aid in troubleshooting and repairing connectivity issues.
Best Practices for Connection
- Ensure proper alignment when connecting cables to avoid damage.
- Use appropriate tools for disassembly and assembly to prevent wear on connectors.
- Inspect cables for signs of wear or damage before installation.
- Keep connectors clean and free of debris to maintain optimal conductivity.
Adhering to these practices will not only extend the lifespan of connections but also enhance the overall reliability of the device.
Audio Components and Design
The audio system in modern smartphones plays a crucial role in delivering an immersive user experience. By combining various elements, designers create a harmonious blend of sound quality and functionality. This section explores the key features and innovative approaches taken to optimize sound performance within these devices.
At the heart of the audio experience are the speakers, which are engineered to produce clear and balanced sound across a wide frequency range. Advanced acoustic technologies ensure that audio output remains distortion-free, even at higher volumes. Additionally, the incorporation of dual speakers enhances stereo sound, providing a richer listening experience for music, videos, and calls.
Microphones are equally important, as they facilitate clear communication and capture high-quality audio. Advanced noise-canceling technologies are employed to filter out background noise, ensuring that voice recordings and calls maintain clarity and precision. The strategic placement of microphones allows for improved sound capture from different angles, enhancing overall audio quality.
Moreover, the integration of software plays a significant role in audio performance. Equalization settings allow users to customize sound profiles according to personal preferences, while algorithms optimize playback for various audio formats. This synergy between hardware and software results in a dynamic audio experience that meets the demands of users in diverse scenarios.
Enclosure and Structural Parts
The outer shell and supporting components of a mobile device play a crucial role in ensuring its durability and functionality. These elements not only protect the internal mechanisms but also contribute to the overall aesthetic and ergonomics of the gadget. Understanding the various structural components can help in appreciating how they work together to enhance performance and user experience.
Materials and Construction
The external casing is typically made from a combination of aluminum and glass, offering a balance of lightweight design and strength. The construction methods employed, such as unibody designs, increase structural integrity and reduce the risk of damage from everyday use. These materials are selected not only for their physical properties but also for their ability to support advanced technological features.
Integration of Components
The arrangement of structural elements is carefully engineered to accommodate other essential features, such as antennas and sensors. Strategic placement ensures optimal functionality while maintaining a sleek profile. Each component’s design is harmonized with others, allowing for seamless interaction and efficient performance in a compact form.
Assembly and Disassembly Process
The process of assembling and disassembling a mobile device involves several critical steps that require precision and care. Understanding this workflow is essential for effective repairs or upgrades. By carefully following each stage, users can ensure the integrity and functionality of the device while minimizing the risk of damage to internal components.
Preparation and Tools
Before beginning the assembly or disassembly, gather all necessary tools, such as precision screwdrivers, suction cups, and plastic prying tools. Ensuring a clean workspace will help prevent the loss of small parts. Additionally, it’s beneficial to familiarize oneself with the internal layout to streamline the process.
Step-by-Step Procedure
Start by powering down the device and removing any external accessories. Carefully use a suction cup to lift the screen, followed by a plastic prying tool to detach the display from the housing. Once opened, take note of the internal connections and components for reference. Reverse the steps for reassembly, ensuring that all screws are tightened properly and components are securely connected.
Common Repair Considerations
When tackling repairs on modern mobile devices, several important factors come into play. Understanding these aspects can help ensure a successful restoration, prolong the device’s lifespan, and improve overall performance. From component compatibility to proper tools, each consideration plays a vital role in the repair process.
Component Quality
Using high-quality components is crucial for effective repairs. Here are some points to consider:
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) components typically offer better reliability and compatibility than aftermarket alternatives.
- Warranty: Check if the components come with a warranty, as this can safeguard your investment.
- Supplier Reputation: Research suppliers to ensure they provide quality products and good customer service.
Repair Tools
Having the right tools is essential for efficient and effective repairs. Consider the following:
- Tool Kits: Invest in a comprehensive toolkit designed specifically for mobile device repairs.
- Precision Tools: Use precision screwdrivers and tweezers to handle small screws and delicate components.
- Safety Equipment: Wear safety glasses and use antistatic wristbands to protect yourself and the device.